Recombinant Human Torsin-1A (TOR1A)
-
货号:CSB-YP024067HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP024067HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP024067HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP024067HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP024067HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:DQ2; Dystonia 1; Dystonia 1 protein; Dystonia 1 torsion; Dyt1; TOR1A; TOR1A_HUMAN; Torsin 1A; Torsin A; Torsin family 1 member A; Torsin family 1, member A (torsin A); Torsin-1A
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:21-332
-
氨基酸序列VEPISLGLAL AGVLTGYIYP RLYCLFAECC GQKRSLSREA LQKDLDDNLF GQHLAKKIIL NAVFGFINNP KPKKPLTLSL HGWTGTGKNF VSKIIAENIY EGGLNSDYVH LFVATLHFPH ASNITLYKDQ LQLWIRGNVS ACARSIFIFD EMDKMHAGLI DAIKPFLDYY DLVDGVSYQK AMFIFLSNAG AERITDVALD FWRSGKQRED IKLKDIEHAL SVSVFNNKNS GFWHSSLIDR NLIDYFVPFL PLEYKHLKMC IRVEMQSRGY EIDEDIVSRV AEEMTFFPKE ERVFSDKGCK TVFTKLDYYY DD
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Protein with chaperone functions important for the control of protein folding, processing, stability and localization as well as for the reduction of misfolded protein aggregates. Involved in the regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling, controls STON2 protein stability in collaboration with the COP9 signalosome complex (CSN). In the nucleus, may link the cytoskeleton with the nuclear envelope, this mechanism seems to be crucial for the control of nuclear polarity, cell movement and, specifically in neurons, nuclear envelope integrity. Participates in the cellular trafficking and may regulate the subcellular location of multipass membrane proteins such as the dopamine transporter SLC6A3, leading to the modulation of dopamine neurotransmission. In the endoplasmic reticulum, plays a role in the quality control of protein folding by increasing clearance of misfolded proteins such as SGCE variants or holding them in an intermediate state for proper refolding. May have a redundant function with TOR1B in non-neural tissues.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- TorsinA was post-transcriptionally upregulated upon acute ER stress, suggesting a role in this response. Increased basal phosphorylation of eIF2alpha in DYT1 transgenic rats was associated with abnormal response to acute ER stress. Unbiased RNA-Seq-based transcriptomic analysis of embryonic brain tissue in heterozygous and homozygous DYT1 knockin mice confirmed presence of eIF2alpha dysregulation in the DYT1 brain. PMID: 29289717
- Association between rs35153737 TOR1A variant and dystonia in a southwestern Chinese population. PMID: 28756192
- TOR1A exon 5 c.*302T>A is associated with isolated dystonia in southwestern Chinese. PMID: 28432771
- TOR1A variant found in sporadic focal dystonia impairs domains affected in DYT1 dystonia patients and animal models PMID: 27168150
- This study does not allow the establishment of genotype-specific clinical correlations for DYT1 in patient with isolated dystonia. PMID: 27477622
- This study show both MDYT1 and without clinical symptoms showed an abnormally enhanced Abnormal blink reflex recovery curve compared with the healthy controls. Moreover, the lack of a statistical difference between manifesting and nonmanifesting carriers suggests that their brainstem circuits are equivalently affected by the DYT1. gene PMID: 27508977
- A comparison of these structures shows, in atomic detail, the subtle differences in TorsinADeltaE-LULL1 activator interactions that separate the healthy from the diseased state. PMID: 27490483
- found that human Torsin1A and human FMRP were present in the same protein complexes, suggesting that this phenomenon is evolutionarily conserved PMID: 27313903
- The significant association of rs1182 and rs1801968 TOR1A variants was found in the development of focal dystonia and writer's cramp respectively. PMID: 28081261
- This study demonstrated that whole-exome sequencing show reveled TOR1A mutation with early-onset generalized dystonia. PMID: 27666935
- This study showed that the Phosphodiesterase-10A Inverse Changes in Striatopallidal and Striatoentopeduncular Pathways of a Transgenic Mouse Model of DYT1 Dystonia. PMID: 28115486
- Genetic screening targeted at currently known disease-causing mutations in TOR1A, THAP1, and TUBB4 appears to have low diagnostic yield in sporadic spasmodic dysphonia. In our cohort, only 2 patients tested positive for novel/rare variants in THAP1. PMID: 27188707
- there might not be an association between TOR1A or THAP1 and patients with adult-onset primary focal dystonia PMID: 26803725
- This processing occurs not only in stress-exposed cell lines but also in primary cells from distinct organisms including stimulated B cells, indicating that Torsin conversion in response to physiologically relevant stimuli is an evolutionarily conserved process. PMID: 26953341
- Our patient and three other reported carriers of non-c.907_909delGAG-mutations within the first three exons of TOR1A showed similar phenotypes of adult-onset focal or segmental cervical dystonia PMID: 26297380
- Plasma salusin-alpha and salusin-beta levels are increased in endometrioma patients and positively correlated with endometrioma size. PMID: 26008602
- the common rs2296793 and rs3842225 SNPs of TOR1A do not play a major role in cervical dystonia in a Chinese population. PMID: 26704435
- Certain TOR1A genotypes may be regarded as factors predisposing to focal and segmental dystonia. PMID: 25203860
- DYT1 mutations are associated with dystonia disorders PMID: 26596547
- TorA(DeltaE) in Drosophila brains may activate the UPR and increase the expression of HSP22 to compensate for the toxic effects PMID: 25903460
- The results of this study indicate that a loss of function of torsinA during cerebellar synaptogenesis induces important developmental alterations. PMID: 26183317
- Salusin-beta but not saluin-alpha is able to promote inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PMID: 25210730
- This review summarizes the current state of knowledge regarding the potential functions of torsin 1A in the context of hypothetical pathomechanisms responsible for torsion dystonia type 1. PMID: 26281352
- study reports 2 new, putative TOR1A mutations (p.A14_P15del and p.E121K)in dystonia patients that were examined functionally compared with wild-type and 2 known mutations (DeltaE and p.R288Q); findings demonstrate functional changes for all 4 mutations on different levels PMID: 24931141
- Data show that mutation of arginine 563 in lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1) reduces its ability to stimulate TorsinA PMID: 25149450
- DYT1 is caused by mutations of the TOR1A gene, located on 9q34, which causes dysfunction of the D1 direct pathway or the indirect pathway[review] PMID: 25192508
- These findings provide functional evidence for the potential pathogenic nature of these rare sequence variants in the TOR1A gene, thus implicating these pathologies in the development of dystonia. PMID: 24930953
- LAP1 and LULL1 regulate Torsin ATPase activity through an active site complementation mechanism. PMID: 25352667
- This study demonistrated that Combined occurrence of a novel TOR1A and a THAP1 mutation in primary dystonia. PMID: 24862462
- analysis for TOR1-A mutations should be performed only in patients with early onset, generalized, and familial dystonia. PMID: 25337725
- Primary dystonia in the Amish-Mennonites is genetically diverse and includes not only the THAP1 indel founder mutation but also different mutations in THAP1 and GNAL as well as the TOR1A GAG deletion. PMID: 24500857
- These results provide evidence for a regional specificity of the electrophysiological abnormalities observed and demonstrate the reproducibility of such alterations in distinct models of DYT1 dystonia. PMID: 24503369
- Data indicate that BiP (GRP78/Kar2) stabilizes torsinA and torsinADeltaE in mammalian cells. PMID: 24627482
- Current known dystonia genes include those related to dopamine metabolism, transcription factor, cytoskeleton, transport of glucose and sodium ion, etc. PMID: 23782819
- This study did not identify any significant association of 4 SNPs in the TOR1A gene in Dutch patients with torsion dystonia. PMID: 23460578
- The results of this study demonstrated a significantly higher frequency of H216 variant in PTD patients not carrying the DeltaGAG as compared with control subjects in Argentina. PMID: 23405979
- The results of this study suggested that genetic analysis for GAG deletion of DYT-1 gene may be performed even if dystonia starts at a very young age or it spreads to involve oromandibular muscles. PMID: 22770546
- In this study, we found that the rs1801968 variant of TOR1A was associated with early-onset primary dystonia . PMID: 23107556
- in dystonia DYT1 and DYT6 gene mutation carriers, diffusion tensor imaging detected fewer fibers in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical pathways PMID: 22987473
- No association of the rs1182 of TOR1A with Chinese primary dystonia was found. PMID: 23058565
- The DYT1 904-906 del GAG mutation is responsible for some of Iranian dystonia patients. PMID: 22487959
- variable clinical manifestation in different ethnic groups may suggest that ethnicity is a significant modifier of DYT1 dystonia PMID: 22622408
- In transgenic mice with DYT1 dystonia mutation stimulation of thalamostriatal axons triggered abnormal spiking activity in interneurons. PMID: 22933784
- The data of this study showed that the The GAG deletion in Tor1A (DYT1) is a rare cause of complex musician's dystonia. PMID: 22226333
- The results of this study did not support the hypothesis that common TOR1A variants affect susceptibility for sporadic primary dystonia. PMID: 22172551
- This study do not confirm that the allele contributes to the risk of D216H SNP primary dystonia. PMID: 22054283
- The DYT1 carrier state increases energy demand in the olivocerebellar network. PMID: 21241782
- The s provide evidence that torsinA, a ubiquitously expressed ATPase, has a role in herpes simplex virus 1 nuclear egress. PMID: 21775450
- ER retention & membrane association are perturbed by a subset of nonconservative mutations to the N-terminal domain, suggesting that a helical structure with defined orientation in the membrane is required. PMID: 21785409
- Several genetic mutations have been identified that cause different forms of dystonia. [DYT1 gene -review article] PMID: 21636841
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Dystonia 1, torsion, autosomal dominant (DYT1)
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Nucleus membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cell projection, growth cone. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
-
蛋白家族:ClpA/ClpB family, Torsin subfamily
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Highest levels in kidney and liver. In the brain, high levels found in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, as well as in the neocortex, hippocampus and cerebellum. Also highly expressed in the spinal cord.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3098
OMIM: 128100
KEGG: hsa:1861
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000345719
UniGene: Hs.534312
Most popular with customers
-
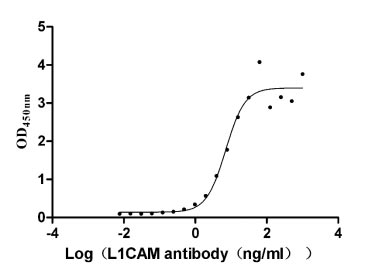
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
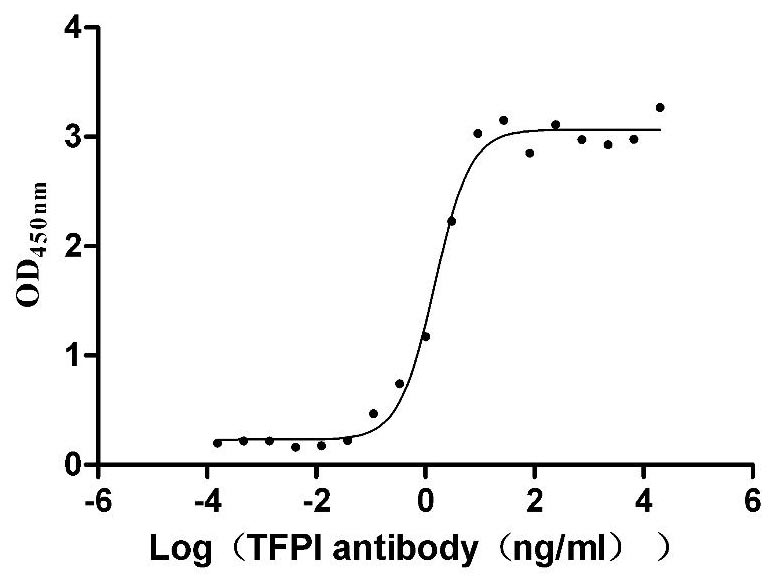
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
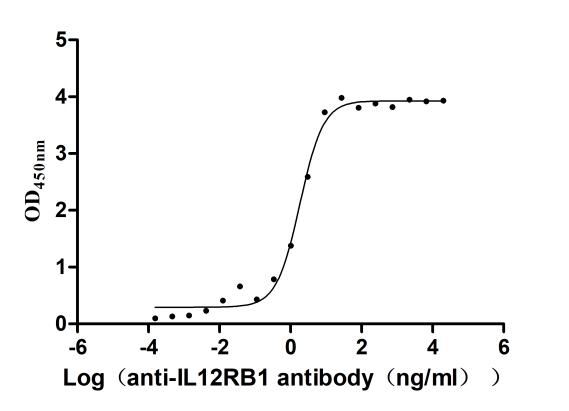
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)