CD48:初露锋芒的人体免疫共刺激分子,是“敌”或“友”?
日期:2021-08-26 17:25:25
2021年7月4日,发表在Frontiers in immunology(影响因子:7.561)杂志上的一篇文章表明,CD48在肾透明细胞癌(ccRCC)中高表达,并且其可能与肿瘤浸润性NK细胞免疫逃逸相关 [1]。目前,虽只有少量CD48与癌症相关的报道,但越来越多的疾病动物模型研究,确定了CD48的免疫调控作用。CD48已成为炎症性和过敏性疾病的一个重要生物标志物,以CD48为代表的免疫共刺激分子,或为肿瘤免疫治疗研究提供新的方向。那么,初露锋芒的CD48,其作为人类免疫疾病治疗的候选分子是如何发挥作用的呢?看完这篇文章,相信你会有所收获。
1. CD48的结构和表达
CD48(又称BLAST-1或SLAMF2)为糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)连接的免疫球蛋白超家族成员 [2]。CD48作为一个免疫共刺激分子和黏附分子,参与免疫性疾病的调控。人CD48基因定位于染色体1q21-23,其编码产物为一种糖蛋白,分子量约为45kD [3]。CD48在人血清和血浆中以可溶形式存在,其可溶性是如何产生的有待阐明 [4]。CD48蛋白结构包括信号肽,免疫球蛋白可变区(IgV)和恒定型2(IgC2)区和C-末端的GPI锚定蛋白 (图1)。其中,IgC2型结构域含有保守的半胱氨酸残基,可形成二硫键。CD48没有跨膜结构域,CD48通过GPI连接锚定于细胞膜,从而与相关信号分子结合,发挥生物学作用 [5, 6]。
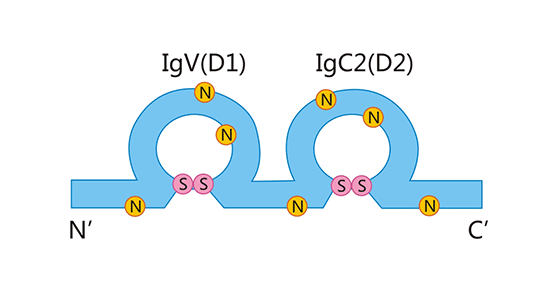
图1. CD48结构
*图片来源于Clinical Immunology出版物 [6]
CD48表达于NK细胞、T细胞、单核细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞表面,参与这些细胞的粘附和活化途径 [7]。CD48表达在炎性条件下会增加。研究发现当IFN-α、IFN-β、IFN-γ等细胞因子暴露时,可增加人外周血单核细胞CD48的表达 [8]。CD48通过结合不同的配体,在多种细胞中发挥作用,从而影响免疫过程。大量研究表明,CD48在许多疾病的病理生理机制中扮演多重角色。
2. CD48的配体
CD48的配体主要有CD2,CD244,FimH。CD48与多种配体结合,它的激活会引起脂质筏中信号因子的重新排列、Lck激酶的活性以及酪氨酸磷酸化,从而发挥不同的免疫功能 [9]。
配体CD2主要在T细胞和NK细胞上表达。配体CD244表达于NK细胞、部分记忆性CD8+T细胞、单核细胞和粒细胞等。CD48可以通过与其他造血细胞上的CD2和CD244结合来促进免疫细胞之间的相互作用,然而CD48对CD244的亲和力更高。CD48还可以结合大肠杆菌上的凝集素FimH,促进巨噬细胞和肥大细胞对细菌的识别和吞噬。此外,人体内,CD58是CD2的高亲和力配体 [9]。因此,CD48与其配体的相互作用受其配体和CD58表达以及每种受体-配体相互作用的亲和力的影响。如图2所示,CD48通过组成受体/配体对来参与许多免疫过程,包括T细胞活化,抗原呈递细胞的粘附,以及调节CD8+T细胞和NK细胞免疫 [10]。
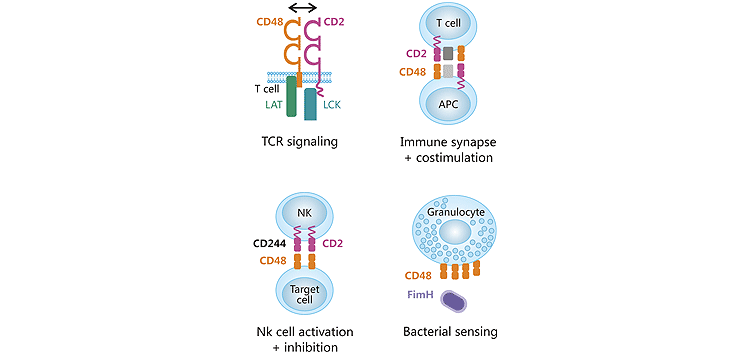
图2. CD48与其配体相互作用
*图片来源于Clinical Immunology出版物 [10]
3. CD48的反受体及其调节机制
在人NK细胞中,CD48是NK细胞重要活化剂CD244的反受体,即CD48作为受体CD244的配体。CD48/CD244的结合在细胞-细胞的相互作用中起到重要作用。有研究提示,CD48/CD244可能在促进或抑制下游信号通路中发挥了各种不同的功能。在促进下游信号通路中,CD48/CD244可激活T细胞活化连接蛋白(LAT),还可诱导免疫受体酪氨酸转换基序(ITSM)的磷酸化并募集接头蛋白SAP。SAP与ITSM结合招募酪氨酸激酶Fyn,Fyn促使下游蛋白磷酸化,从而激活NK细胞(图3A)。然而,在抑制下游信号通路中,CD48/CD244的调控机制如何尚未明确阐明,有可能类似于抑制性受体Ly49的方式抑制下游信号途径(图3B) [11]。有研究报道,CD48和CD244相互作用,在人NK细胞中诱导活化信号,而在鼠NK细胞中则发出抑制信号 [12]。
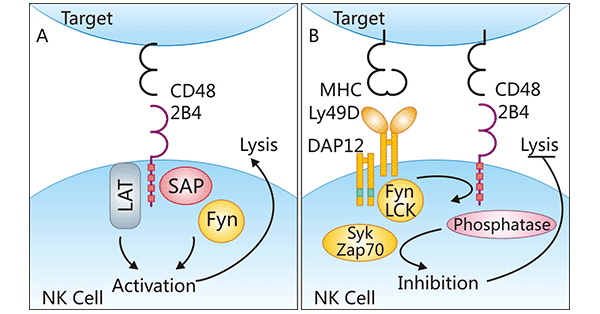
图3. CD48的反受体及其调节机制
*图片来源于Molecular immunology出版物 [11]
4. CD48在疾病中的作用
CD48作为一种粘附分子,在B和T淋巴细胞、NK细胞、肥大细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞中参与免疫调节机制。大量的研究揭示了CD48在自身免疫、炎症、过敏、造血以及肿瘤中的作用。
在炎症性肠道疾病小鼠模型中,CD48/CD244可抑制CTL细胞的分化或效应CTL功能 [13]。在小鼠肿瘤模型中,CD244在功能失调的CD8+T细胞上高度表达 [14]。另外,CD244与CD8+T细胞耗竭有关 [14]。然而,尚不清楚CD48是如何发挥作用的。有体外研究表明,CD48与CD244的结合,可抑制IFN-β的产生延长了DC细胞的存活;IFN-β介导了成熟DC细胞的凋亡,并促进了颗粒酶B抑制剂PI-9的产生,从而减少活化T细胞耗竭 [15]。这些研究表明,CD48与CD244作用不但影响NK细胞的功能,而且还调节T细胞的增殖与效应功能。
另有报道指出,CD48在CD8+T细胞上的表达降低,可能在类风湿关节炎发病过程中起作用。其研究分析,CD48分子在外周血CD8+T细胞上的表达降低,促使CD8+T细胞的激活和增殖降低。CD8+T细胞的数量减少,导致抑制性T细胞作用减弱,从而使类风湿关节炎患者发病 [16]。此外,越来越多的研究指出,CD48的高表达与过敏性疾病密切相关,包括间歇性过敏性鼻炎(IAR)[17]、过敏性鼻炎 [18]、哮喘 [19]。还有研究者指出,CD48的表达与小鼠的造血干细胞功能失调有关。同样值得关注的是,近年有研究指出CD48与少量癌症相关,比如乳腺癌 [20],胶质瘤 [21],肝细胞癌 [22],皮肤T细胞淋巴瘤 [23],但其具体机制,仍有待确定。总的来说,进一步阐明CD48的免疫保护或者是损害机制,对各种疾病的治疗将非常重要。
5. CD48的临床应用前景
近年来,通过对CD48分子功能的研究,人们发现,CD48分子参与调节体液及细胞免疫应答,与多种细胞活化的调节有关,影响有关疾病的发生发展。CD48作为免疫应答的关键效应分子,很可能是自身免疫性疾病或过敏反应性疾病的一个重要的生物标志物或治疗靶点。CD48蛋白或抗体在临床研究中的应用可能对治疗过敏、炎症和自身免疫综合征起到作用。目前仅有一款靶向CD48抗体偶联药物处于临床一期(SGN-CD48A),用于多发性骨髓瘤。越来越多针对CD48的研究,正在探索一种或更多种与CD48相关的病症,包括治疗过敏性病症、其他炎症性病症、肿瘤等。迄今为止,CD48研究只是冰山一角,未来有望发现CD48作为受体或反受体在免疫或其它方面所扮演的重要角色。
6. CD48科研产品服务
CD48蛋白
Recombinant Human CD48 antigen(CD48) (Active) (Code: CSB-MP004941HU)
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
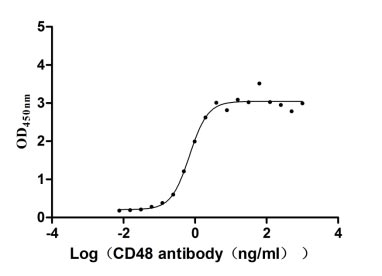
Immobilized CD48 at 2 μg/ml can bind Anti-CD48 rabbit monoclonal antibody, the EC50 of human CD48 protein is 0.5806-0.8463 ng/ml.
CD48 Antibody (ELISA, WB) (CSB-RA178195A0HU)
参考文献:
[1] Ziblat, Andrea, et al . "Circulating and Tumor-Infiltrating NK Cells From Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Exhibit a Predominantly Inhibitory Phenotype Characterized by Overexpression of CD85j, CD45, CD48 and PD-1." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 2143.
[2] Moran, Miriana, and M. Carrie Miceli. "Engagement of GPI-linked CD48 contributes to TCR signals and cytoskeletal reorganization: a role for lipid rafts in T cell activation." Immunity 9.6 (1998): 787-796.
[3] Vassen, Lothar, et al. "Growth Factor Independence 1 (Gfi1) Regulates Cell-Fate Decision of the Bipotential Granulocytic-Monocytic Precursors Defined by Expression of CD48 As a New Marker." Blood 118.21 (2011): 3217.
[4] Gangwar, Roopesh S., et al. "CD 48 on blood leukocytes and in serum of asthma patients varies with severity." Allergy 72.6 (2017): 888-895.
[5] Velikovsky, C. Alejandro, et al. "Structure of natural killer receptor 2B4 bound to CD48 reveals basis for heterophilic recognition in signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family." Immunity 27.4 (2007): 572-584.
[6] Pahima, Hadas, Pier Giorgio Puzzovio, and Francesca Levi-Schaffer. "2B4 and CD48: A powerful couple of the immune system. "Clinical Immunology 204 ( 2019): 64-68.
[7] Morandi, Barbara, et al. "Distinctive lack of CD48 expression in subsets of human dendritic cells tunes NK cell activation." The Journal of Immunology 175.6 (2005): 3690-3697.
[8] Branicka, Olga, et al. "Elevated Serum Level of CD48 in Patients with Intermittent Allergic Rhinitis." International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 182.1 (2021): 39-48.
[9] McArdel, Shannon Leah. Immunoregulatory roles of CD48 in autoimmunity and tolerance. Harvard University, 2015.
[10] McArdel, Shannon L., Cox Terhorst, and Arlene H. Sharpe. "Roles of CD48 in regulating immunity and tolerance. "Clinical immunology 164 (2016): 10-20.
[11] McNerney, Megan E., Kyung-Mi Lee, and Vinay Kumar. "2B4 (CD244) is a non-MHC binding receptor with multiple functions on natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells." Molecular immunology 42.4 (2005): 489-494.
[12] Vaidya, Swapnil V., and Porunelloor A. Mathew. "Of mice and men: different functions of the murine and human 2B4 (CD244) receptor on NK cells. "Immunology letters 105.2 (2006): 180-184.
[13] O'Keeffe, Michael S., et al. "SLAMF4 is a negative regulator of expansion of cytotoxic intraepithelial CD8+ T cells that maintains homeostasis in the small intestine." Gastroenterology 148.5 (2015): 991-1001.
[14] Blackburn, Shawn D., et al. "Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection." Nature immunology 10.1 (2009): 29-37.
[15] Kis-Toth, Katalin, and George C. Tsokos. "Engagement of SLAMF2/CD48 prolongs the time frame of effective T cell activation by supporting mature dendritic cell survival." The Journal of Immunology 192.9 (2014): 4436-4442.
[16] Sun, Lin, et al. "Advances in Understanding the Roles of CD244 (SLAMF4) in Immune Regulation and Associated Diseases." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021) : 731. : 731.
[17] Branicka, Olga, et al. "Elevated Serum Level of CD48 in Patients with Intermittent Allergic Rhinitis." International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 182.1 (2021): 39-48.
[18] Zeddou, Mustapha, Philippe Delvenne, and Amr E. El-Shazly. "Dynamics and function of eosinophils' CD48 molecules in allergic rhinitis and in response to eotaxin stimulation." Advances in Cellular and Molecular Otolaryngology 1.1 (2013): 22389.
[19] Munitz, Ariel, Ido Bachelet, and Francesca Levi-Schaffer. "CD48 as a novel target in asthma therapy. "Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery 1.1 (2007): 9-12.
[20] Mamoor, Shahan. "CD48 (SLAMF2) is differentially expressed in the lymph nodes of patients with metastatic breast cancer."(2021).
[21] Zou, Cunyi, et al. "CD48 is a key molecule of immunomodulation affecting prognosis in glioma." OncoTargets and therapy 12 (2019): 4181.
[22] Wu, Yan, et al. "Monocyte/macrophage-elicited natural killer cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated by CD48/2B4 interactions." Hepatology 57.3 (2013): 1107-1116.
[23] Dulmage, B. O., et al. "Black cat in a dark room: the absence of a directly oncogenic virus does not eliminate the role of an infectious agent in cutaneous T -cell lymphoma pathogenesis." British Journal of Dermatology 172.5 (2015): 1449-1451.











