SLC39A6:锌离子转运蛋白,抗体偶联药物ADC新晋靶点!
日期:2022-12-02 15:34:12
近年来,抗体药物偶联物(ADC)新药交易迎来爆发,更多企业开始进军ADC领域。据Pharmsnap数据库显示,目前ADC新药交易合作或授权的项目近100项,达成的交易金额超过400亿美元。2022年迄今已达17项,SLC39A6成功上位,成为抗体药ADC新晋靶点之一。
SLC39A6作为新发的癌症相关因子,虽研究起步较晚,但近年来进展很快。早前,制药巨擘默沙东(Merck)与全球ADC领域的龙头公司Seagen达成协议,支付16亿美元收购其靶向SLC39A6/LIV-1的ADC药物(Ladiratuzumab Vedotin),用于转移性三阴性乳腺癌临床研究。默沙东还承诺将在研发的里程碑上投入高达26亿美元。目前,越来越多的研究表明,SLC39A6在多种肿瘤细胞中高表达,但在正常组织有限表达,成为ADC治疗有希望的候选者!今天我们一起来了解一下,抗体药ADC新晋靶点--锌转运蛋白SLC39A6!
1. 什么是锌转运蛋白家族?
SLC39A家族和SLC30A家族为已发现的哺乳动物中的两个锌转运蛋白家族,分别调节锌离子转进(influx)和转出(efflux)细胞的运输过程(图1) [1, 6]。SLC39A家族(又称ZIP家族),共有14个成员,即ZIP1-ZIP14 [2-3]。该家族多个成员已被证明可促进细胞外或细胞器内的锌离子转运到细胞质,具有锌离子吸收(influx)摄取功能。而SLC30A家族(又称ZIT家族),共有10个成员,与SLC39A/ZIP家族的功能相反,多个家族成员可协助锌离子从细胞质内流出到细胞外或流进到细胞器内,具有释放(efflux)锌离子功能 [2-3]。越来越多的证据表明,锌转运蛋白家族不仅直接参与细胞的锌离子稳态代谢,同时还通过复杂的机制影响着肿瘤和代谢疾病的发生和发展,其成员逐渐成为锌营养和代谢疾病的研究热点 [4-5]。
锌转运蛋白的两大家族成员在各种亚细胞器、细胞及器官中的分布不同,如ZIP4/SLC39A4、ZIP5/SLC39A5、ZIP6/SLC39A6、ZIP10、ZIP14以及ZnT1/SLC30A1主要分布在细胞膜上,而其它众多的锌转运蛋白主要分布在不同的细胞器膜上;在组织器官分布方面,ZIP4/SLC39A4和ZnT5分布小肠上皮细胞,ZIP10和ZnT1分布在肾脏上皮细胞,ZIP5、ZnT1及ZnT2分布在胰腺腺细胞,ZIP8及ZIP10分布在血细胞等等 [4-5]。

图1. 锌转运蛋白示意图 [6]
2. 什么是SLC39A6?
SLC39A6(又名ZIP6或LIV-1)属于锌转运蛋白家族ZIP成员之一。根据蛋白结构特点,哺乳动物ZIP蛋白又被分成4个亚家族,即亚家族I,II,LIV-1和gufA。SLC39A6是LIV-1亚家族,存在755个氨基酸和433个氨基酸两种长度的异构体。SLC39A6蛋白包括6-8个跨膜域,其氨基和羧基末端均位于细胞外或囊泡内,第3和4跨膜域间存在富含组氨酸的结构域,该区域具有结合锌离子的功能,并具有金属蛋白酶活性(图2) [7]。SLC39A6的主要功能是将锌离子从细胞外转移至细胞内,并且是酶、转录因子和信号分子发挥作用机制中的关键蛋白 [8-9]。
SLC39A6的表达较为广泛,在胚盘、乳腺及前列腺中表达最为丰富。SLC39A6蛋白主要定位在细胞膜上,将锌离子由胞外运至胞浆,或将细胞器内的锌离子转运至胞浆。SLC39A6可通过调节锌离子稳衡代谢,在机体免疫反应中发挥重要作用。近年来,诸多关于SLC39A6的研究表明,SLC39A6在许多癌症中表达异常,如食管癌、宫颈癌、肺癌以及乳腺癌等等,提示SLC39A6蛋白在癌症发生过程具有重要作用 [10-15]。
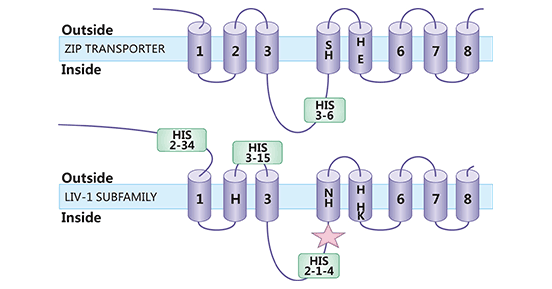
图2. SLC39A6结构示意图 [7]
3. SLC39A6相关的调节机制
锌转运体SLC39A6自发现以来一直受到广泛关注,其参与肿瘤相关的机制正在深入研究中,如JAK/STAT、PI3K/AKT、EGFR-Ras-ERK、MAPK/ERK等信号通路。SLC39A6作为肿瘤相关的潜力分子,SLC39A6在肿瘤发生过程的分子机制并不是单一的,其复杂的作用机制有待进一步阐明。
3.1 SLC39A6与STAT3信号
信号转导及转录激活因子3(STAT3)和锌指蛋白(Snail)是上皮间质转化(EMT)通路的主要标志物。SLC39A6被鉴定为STAT3的下游靶基因,促进锌指蛋白Snail的入核。而Snail基因可降低与细胞黏附有关的基因表达,在上皮细胞转化为间质细胞的过程中起重要作用 [16-17]。因此,SLC39A6可通过影响Snail表达,调节细胞分化过程。
另有研究指出,在乳腺癌中,SLC39A6运输锌离子进入细胞,会抑制GSK3β的活性,失活的GSK3β不能磷酸化Snail,使得Snail留在核内抑制细胞交联基因E-cadherin的转录,促进细胞迁移 [18]。研究发现,在食管鳞癌中,SLC39A6是STAT3的下游靶基因,SLC39A6通过调控SNAIL2基因,参与食管鳞癌的EMT过程 [19]。
3.2 SLC39A6与EGFR信号
EGFR属于膜受体酪氨酸激酶(receptor tyrosine kinase,RTK)家族,与表皮生长因子EGF、转化生长因子α(TGFα)、肝素结合EGF样生长因子(HBEGF)等配体结合后,可招募其他受体底物蛋白并激活一系列下游信号,如调控分裂增殖的Ras/MAPK、与癌症相关的PI3K/AKT通路等。研究发现,肿瘤微环境中SLC39A6的表达会被例如EGF、IGF-1(insulinlike growth factor)等生长因子所激活 [20]。
在前列腺肿瘤细胞系中,过表达SLC39A6后会引起EGFR磷酸化和ERK磷酸化,其下游信号可诱导细胞的迁移和入侵行为 [21]。在食管癌中,过表达SLC39A6的细胞,可激活AKT和ERK通路,调节MMP1、MMP3、MYC和SLUG表达(图3) [22]。目前,越来越多的研究揭示SLC39A6中可作为重要的癌相关基因,但SLC39A6在癌症中具体的作用机制仍需要进一步深入地研究。
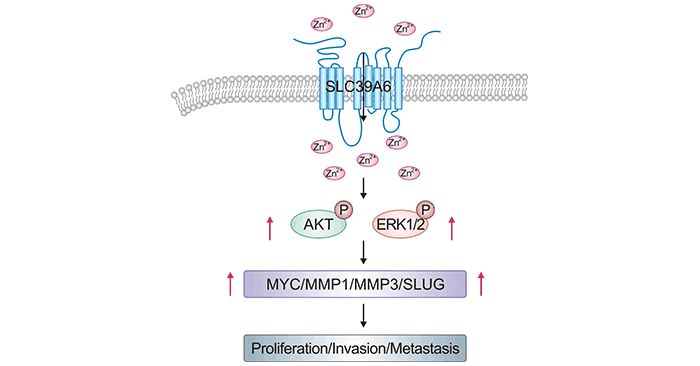
图3. SLC39A6通过激活AKT和ERK途径来促进ESCC [22]
4. SLC39A6在癌症治疗中的作用
在恶性肿瘤中,体内锌稳态的紊乱与恶性肿瘤的进展相关,癌细胞通常具有上调的锌转运蛋白和锌离子。因此,SLC39A6作为锌的重要转运蛋白在恶性肿瘤的进展具有重要作用。目前在消化系统肿瘤(如食管癌、肝癌及胰腺癌)、乳腺癌、胶质瘤、前列腺癌、肺癌、膀胱癌等中发现SLC39A6均有异常表达。
4.1 SLC39A6与食管癌
在食管癌中,SLC39A6表达下调可抑制食管癌细胞的增殖和侵袭。高表达的SLC39A6与肿瘤侵袭性、细胞内锌水平和患者生存时间有关。进一步的分析表明,在SLC39A6表达上调的细胞株中,基质金属蛋白酶 1、基质金属蛋白酶 3、髓细胞增生原癌基因和表面免疫球蛋白呈现高表达。陆续的研究认为SLC39A6在食管鳞癌(ESCC)中具有促肿瘤作用,提示SLC39A6可作为高危患者的早期探测器和预后的生物标志物,因而SLC39A6的靶向治疗可能是阻断ESCC的一种潜在治疗策略 [22, 23-24]。
4.2 SLC39A6与肝癌
通过miRNA微阵列分析发现,在发生转移的肝癌细胞系MHCC-97L,MHCC-97H和HCC-LM3中,miR-192在肝癌组织中表达下降,在肝癌患者血管细胞浸润组的表达水平较非浸润组下降。而SLC39A6是miR-192的直接和功能靶点,且SLC39A6与miR-192呈负相关,所以SLC39A6可能促进肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭 [25-27]。
4.3 SLC39A6与胰腺癌
有研究揭示,在72例胰腺癌组织中,SLC39A6表达水平与肿瘤大小及淋巴浸润有关。通过下调SLC39A6表达,构建裸鼠模型,体内和体外实验的结果表明,抑制SLC39A6可抑制胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移。由此说明,SLC39A6表达与胰腺癌肿瘤增殖相关,抑制SLC39A6可显著减少胰腺癌细胞转移或扩散 [28-29]。
4.4 SLC39A6与乳腺癌
SLC39A6最初在乳腺癌细胞系中被鉴定为雌激素诱导基因,故认为与乳腺癌的发生和发展密切相关。有关RNAseq分析的结果显示,在乳腺癌luminal分型组中,鉴定出SLC39A6、PGR、ESR1、BCL2、GATA3和NAT1在转移的肿瘤中出现下调,提示SLC39A6与乳腺肿瘤的分级、大小和分期可能有关 [30-32]。目前,靶向SLC39A6的ADC药物Ladiratuzumab vedotin(SGN-LIVI1),已在转移性三阴性乳腺癌的临床研究中与帕博利珠单抗(Keytruda)联合使用 [18, 33]。
4.5 SLC39A6与其它肿瘤
此外,其它多种肿瘤中也发现了SLC39A6异常表达,包括胶质瘤、卵巢癌、膀胱癌、前列腺癌、头颈癌、肺癌、和胃癌 [15, 21, 34-38]。SLC39A6被认为处于细胞质膜上,可导致细胞内锌水平增加,且SLC39A6在对类固醇激素敏感的组织如胎盘和前列腺中高表达 [1, 21, 39]。在胃癌中,SLC39A6的单核苷酸多态性rs1050631与手术切除胃腺瘤的患者预后相关 [38]。在胶质瘤中,SLC39A6高表达,并与级别呈显著相关 [34]。在非小细胞肺癌中,敲低SLC39A6可抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移,并使细胞停留在G1期 [15, 40]。
5. SLC39A6的临床应用前景
来自Pharmsnap的数据显示,已有1款基于SLC39A6的ADC抗体药(Ladiratuzumab vedotin)处于临床2期,用于腺癌、食管癌、乳腺癌等多种肿瘤治疗。涉及SLC39A6靶点,有11项临床试验进行中,用于非小细胞肺癌和三阴性乳腺癌等实体瘤的治疗。目前已上市的ADC产品共14款,已进入临床的在研产品主要聚焦在HER2和TROP2,此外FRα、VEGF、CD19、CD22、CD30、EGFR、KAAG1、NaPi2b、c-MET、CLDN18.2、HER3、LIV-1/SLC39A6、Nectin-4、MSLN等靶点也纷纷入局。近年来,ADC赛道竞争白热化,差异化布局,选择其他潜力靶点已是众多ADC研发的制胜法宝。SLC39A6作为新发肿瘤相关分子,新晋ADC靶点,有望在食管癌和乳腺癌等癌症治疗方面取得突破。
为鼎力协助各药企针对SLC39A6在食管癌和乳腺癌等其它肿瘤在临床中的研究,CUSABIO推出SLC39A6活性蛋白产品,(Code:CSB-BP621669HU1),助力您在SLC39A6机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
Recombinant Human SLC39A6, partial (Active) (CSB-BP621669HU1)

The purity was greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
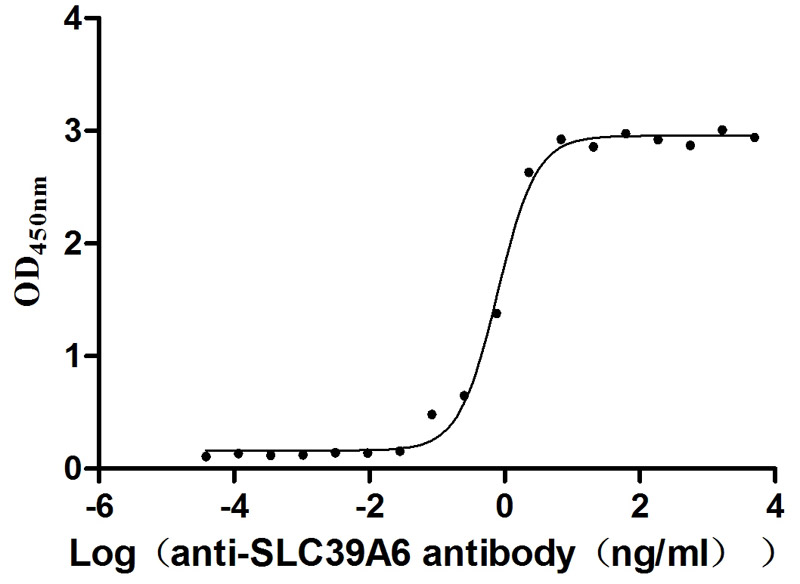
Immobilized Human SLC39A6 at 1 μg/ml can bind Anti-SLC39A6 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA621669MA1HU), the EC50 is 0.6873-0.9010 ng/mL.
参考文献:
[1] Prasad, Ram R., et al. "Stage-specific differential expression of zinc transporter SLC30A and SLC39A family proteins during prostate tumorigenesis." Molecular Carcinogenesis 61.5 (2022): 454-471.
[2] Singh, Chandra K., et al. "Role of zinc transporters in prostate cancer and a potential association with racial disparity." Cancer Research 77.13_ Supplement (2017): 4139-4139.
[3] Meng, Jie, et al. "Accumulation of different metals in oyster Crassostrea gigas: significance and specificity of SLC39A (ZIP) and SLC30A (ZnT) gene families and polymorphism variation." Environmental Pollution 276 (2021): 116706.
[4] Nagamatsu, Shino, et al. "Sophisticated expression responses of ZNT1 and MT in response to changes in the expression of ZIPs." Scientific reports 12.1 (2022): 1-13.
[5] Satarug, Soisungwan, et al. "Aberrant expression of ZIP and ZnT zinc transporters in UROtsa cells transformed to malignant cells by cadmium." Stresses 1.2 (2021): 78-89.
[6] Fukada, T., & Kambe, T. (2011). Molecular and genetic features of zinc transporters in physiology and pathogenesis. metallomics: integrated biometal science, 3(7), 662 -674.
[7] Taylor, Kathryn M., and Robert I. Nicholson. "The LZT proteins; the LIV-1 subfamily of zinc transporters. "Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)- Biomembranes 1611.1-2 (2003): 16-30.
[8] Ghaderi, Hajarossadat, et al. "Preparation of heavy chain polyclonal antibody against zinc transporter SLC39A6 and its diagnostic application." (2021): 274-280.
[9] Ghaderi, Hajarossadat, et al. "Development of camelid monoclonal nanobody against SLC39A6 zinc transporter protein." Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 24.12 (2021): 1726.
[10] Bagheri, Sajedeh, et al. "Recombinant expression of Zinc transporter SLC39A6 and its functional antibody production." Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy 38.2 (2019): 70-74.
[11] Zhao, Lei, et al. "SLC39A6/ZIP6 is essential for zinc homeostasis and T-cell development in zebrafish." biochemical and biophysical research communications 511.4 (2019): 896-902.
[12] Cui, Xiao-Bin, et al. "SLC39A6: a potential target for diagnosis and therapy of esophageal carcinoma." journal of translational medicine 13.1 (2015): 1 -16.
[13] Zhao, Le, Wei Chen, and Xu Li. "Expression of LIV-1 mRNA in human cervical carcinoma and endometrial carcinoma." Nan Fang yi ke da xue xue bao= Journal of Southern Medical University 27.10 (2007): 1590-1592.
[14] Takatani-Nakase, Tomoka, et al. "ZIP6-centered zinc regulatory and malignant characteristics of breast cancer cells." Metallomics Research 2.1 (2022): rev-29.
[15] Wan, Xuechao, et al. "Co-expression analysis revealed PTCH1-3'UTR promoted cell migration and invasion by activating miR-101-3p/SLC39A6 axis in non- small cell lung cancer: implicating the novel function of PTCH1." oncotarget 9.4 (2018): 4798.
[16] Hogstrand, Christer, et al. "A mechanism for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and anoikis resistance in breast cancer triggered by zinc channel ZIP6 and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3)." Biochemical Journal 455.2 (2013): 229-237.
[17] Brethour, Dylan, et al. "A ZIP6-ZIP10 heteromer controls NCAM1 phosphorylation and integration into focal adhesion complexes during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition." Scientific reports 7.1 (2017): 1-19.
[18] Saravanan, Roshni, et al. "Zinc transporter LIV1: A promising cell surface target for triple negative breast cancer." Journal of Cellular Physiology (2022).
[19] Cheng Xinxin, et al. "The expression of STAT3, SLC39A6 and SNAIL family genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma." Proceedings of the National Academic Conference on Tumor Epidemiology and Tumor Etiology. 2015.
[20] Grattan, Bruce J., Kavitha Sankavaram, and Hedley C. Freake. "Regulation of LIV-1 expression in breast cancer cells. "The FASEB Journal 23 (2009): 897-25.
[21] Sussman, Django, et al. "LIV-1 antibody-drug conjugate: A novel therapeutic agent for breast and prostate cancer." Cancer Research 71.8_Supplement (2011): 3620-3620.
[22] Cheng X, Wei L, Huang X, et al. Solute Carrier Family 39 Member 6 Gene Promotes Aggressiveness of Esophageal Carcinoma Cells by Increasing Intracellular Levels of Zinc, Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling, and Up-regulating Genes That Regulate Metastasis. 2021 May;160(6):2228-2229]. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(8):1985-1997.e12.
[23] Cheng, Xinxin, et al. "Solute carrier family 39 member 6 gene promotes aggressiveness of esophageal carcinoma cells by increasing intracellular levels of zinc, activating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling, and up-regulating genes that regulate metastasis." Gastroenterology 152.8 (2017): 1985-1997.
[24] Wang, An-Hui, et al. "Epidemiological studies of esophageal cancer in the era of genome-wide association studies. "World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology 5.3 (2014): 335.
[25] Lian, Junwei, et al. "miR-192, a prognostic indicator, targets the SLC39A6/SNAIL pathway to reduce tumor metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma." Oncotarget 7.3 (2016): 2672.
[26] Pascut, Devis, et al. "HCV Proteins Modulate the Host Cell miRNA Expression Contributing to Hepatitis C Pathogenesis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development." Cancers 13.10 (2021): 2485.
[27] Wan, Zhen, and Xuzhen Wang. "Role of SLC39A6 in the development and progression of liver cancer." Oncology letters 23.3 (2022): 1-13.
[28] Zhu, Bo, et al. "Increased expression of zinc transporter ZIP4, ZIP11, ZnT1, and ZnT6 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer." Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology 65 (2021): 126734.
[29] Liu, Mingyang, et al. "ZIP4 Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Repressing ZO-1 and Claudin-1 through a ZEB1-Dependent Transcriptional MechanismZIP4 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Invasion and Metastasis." Clinical Cancer Research 24.13 (2018): 3186-3196.
[30] Garcia-Recio, Susana, et al. "FGFR4 regulates tumor subtype differentiation in luminal breast cancer and metastatic disease." the Journal of clinical investigation 130.9 (2020): 4871-4887.
[31] Taylor, Kathryn M. "A distinct role in breast cancer for two LIV-1 family zinc transporters." (2008): 1247-1251.
[32] Lim, Wai Feng, et al. "Significantly decreased expressions of CaN, VEGF, SLC39A6 and SFRP1 in MDA-MB-231 xenograft breast tumor mice treated with Moringa oleifera leaves and seed residue (MOLSr) extracts." Nutrients 12.10 (2020): 2993.
[33] Pegram, Mark D., et al. "HER2-Overexpressing/Amplified Breast Cancer as a Testing Ground for Antibody-Drug Conjugate Drug Development in Solid TumorsDrug Development of HER2 Antibody-Drug Conjugates." Clinical Cancer Research 26.4 (2020): 775-786.
[34] Do, Minchenko, et al. "Hypoxic regulation of the expression of genes encoded estrogen related proteins in U87 glioma cells: eff ect of IRE1 inhibition." Endocrine Regulations 51.1 (2017): 8-19.
[35] Burgetová, Lenka. "Investigating the role of zinc transporter ZIP 6 and STAT3 in mitosis." (2013).
[36] SU, Juan. "Expression of SLC39A6 in Hnman Bladder Cancer. "Journal of Medical Research (2018): 35-38.
[37] Ressnerova, Alzbeta, et al. "Zinc and copper homeostasis in head and neck cancer: review and meta-analysis." current medicinal chemistry 23.13 (2016): 1304-1330.
[38] Gao, Jian, et al. "Involvement of SLC39A6 in gastric adenocarcinoma and correlation of the SLC39A6 polymorphism rs1050631 with clinical outcomes after resection." bmc cancer 19.1 (2019): 1-15.
[39] Piqué Borràs, Maria Riera. "Identification of molecular subtypes and gene expression patterns of breast cancer analysing RNA-seq data."(2014).
[40] Zhou, Heng, et al. "Evaluation of the prognostic values of solute carrier (SLC) family 39 genes for patients with lung adenocarcinoma." Aging (Albany NY) 13.4 (2021): 5312.
上一篇: 抗肿瘤治疗界后起之秀--CD93
下一篇: 单克隆抗体药物综述











