-
中文名称:小鼠脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E04505m
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3800/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
The mouse BDNF ELISA Kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of BDNF concentrations in serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, or tissue homogenates. This kit exclusively recognizes mouse BDNF. BDNF is an important neurotrophic factor synthesized in the brain and ubiquitously distributed in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system. BDNF plays a prominent role in the neural structure and functional plasticity by promoting the survival, growth, differentiation, development of neurons, long-term potentiation, as well as regulation of synaptic transmission and activity. It is tightly associated with the pathogenesis of various diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and mood disorders. BDNF-TrkB signaling exerts roles in the CNS, especially in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus where it is involved in memory formation and long-term potentiation through the activation of several signaling pathways including MAPK/ERK, PLCg, and PI3K pathways.
The detection mechanism of this kit is based on the Sandwich-ELISA technique. BDNF in the sample is bound to the capture antibody immobilized on the microtiter plate and then sandwiched with a Biotin-labeled BDNF antibody. The solution color develops into blue after the ordinal addition of HRP-avidin and TMB. The color development is terminated after adding the stop solution, and the color turns from blue to yellow. The color intensity is positively correlated with BDNF content in the sample. The kit has been quality-controlled with high sensitivity, strong specificity, good linearity, high precision, high recovery, and high lot-to-lot consistency.
-
别名:BdnfBrain-derived neurotrophic factor ELISA kit; BDNF) [Cleaved into: BDNF precursor form ELISA kit; ProBDNF)] ELISA kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Cardiovascular
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse BDNF in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 91 Range % 88-96 1:2 Average % 101 Range % 97-105 1:4 Average % 96 Range % 92-100 1:8 Average % 104 Range % 99-109 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse BDNF spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 94 87-101 EDTA plasma (n=4) 88 81-96 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 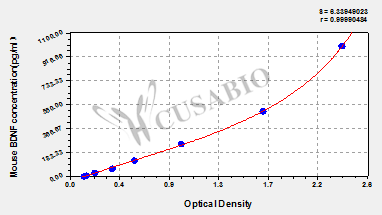
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 1000 2.420 2.355 2.388 2.251 500 1.712 1.685 1.699 1.562 250 0.984 0.994 0.989 0.852 125 0.587 0.568 0.578 0.441 62.5 0.393 0.377 0.385 0.248 31.2 0.223 0.236 0.230 0.093 7.8 0.150 0.160 0.155 0.018 0 0.134 0.139 0.137 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Radix Bupleuri aqueous extract attenuates MK801-induced schizophrenia-like symptoms in mice: Participation of intestinal flora S Zhang,Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy,2024
- Oxygen-loaded microbubble-mediated sonoperfusion and oxygenation for neuroprotection after ischemic stroke reperfusion YJ Ho,researchsquare,2023
- A novel rhein-huprine hybrid ameliorates disease-modifying properties in preclinical mice model of Alzheimer's disease exacerbated with high fat diet T Espinosa-Jiménez,Cell & bioscience,2023
- SIRT1/FOXO1 Axis-Mediated Hippocampal Angiogenesis is Involved in the Antidepressant Effect of Chaihu Shugan San S Zhang,Drug design, development and therapy,2022
- Intranasal Oxytocin Administration Ameliorates DSS-induced Abnormal Stress-related Behavior and Intestinal Inflammation in an IBD Mouse Model C Liu,ea Preprints,2020
- The Secretion from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Pretreated with Berberine Rescues Neurons with Oxidative Damage Through Activation of the Keap1-Nrf2 … C Wen,Neurotoxicity Research,2020
- Studies of pathology and pharmacology of diabetic encephalopathy with KK-Ay mouse model Shi S, et al,Cns Neuroscience & Therapeutics,2019
- Ascorbic acid attenuates cognitive impairment and brain oxidative stress in ovariectomized mice FatemehDelrobaei.et al,Pharmacological Reports,2018
- The Secretion from Neural Stem Cells Pretreated with Lycopene Protects against tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Induced Neurons Oxidative Damage Cuiqin Huang.et al,/,2018
- Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated via MyD88/NF-κB signaling in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis Xu D.et al,Sci Rep,2017
- Adenosine A1 Receptors Play an Important Protective Role Against Cognitive Impairment and Long-Term Potentiation Inhibition in a Pentylenetetrazol Mouse Model of Epilepsy Zhou Q.et al,Mol Neurobiol,2017
- Peony reverses tau phosphorylation level in mouse depression model via BDNF-Akt-GSK3 beta pathway Zhipeng Sun.et al,Int J Clin Exp Med ,2017
- Physiological and behavioral responses in offspring mice following maternal exposure to sulfamonomethoxine during pregnancy. Zhang Q.et al,Neurosci Lett.,2016
- Silibinin inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity and amyloid β peptide aggregation: a dual-target drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Duan S.et al,Neurobiol Aging.,2015
- The MRI marker gene MagA attenuates the oxidative damage induced by iron overload in transgenic mice Guan X. et al,Nanotoxicology,2015
- Silibinin Inhibits Acetylcholinesterase Activity and amyloid 脽 Peptide Aggregation: A Dual-Target Drug for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment Songwei Duan et al,Neurobiology of Aging,2015
相关产品
问答及客户评论
靶点详情
-
功能:Important signaling molecule that activates signaling cascades downstream of NTRK2. During development, promotes the survival and differentiation of selected neuronal populations of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Participates in axonal growth, pathfinding and in the modulation of dendritic growth and morphology. Major regulator of synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the CNS. The versatility of BDNF is emphasized by its contribution to a range of adaptive neuronal responses including long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), certain forms of short-term synaptic plasticity, as well as homeostatic regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability.; Important signaling molecule that activates signaling cascades downstream of NTRK2. Activates signaling cascades via the heterodimeric receptor formed by NGFR and SORCS2. Signaling via NGFR and SORCS2 plays a role in synaptic plasticity and long-term depression (LTD). Binding to NGFR and SORCS2 promotes neuronal apoptosis. Promotes neuronal growth cone collapse.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- We report here on the incorporation of a BDNF mimetic sequence into a supramolecular peptide amphiphile filamentous nanostructure capable of activating the BDNF receptor TrkB and downstream signaling in primary cortical neurons in vitro. PMID: 30211565
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest that Bdnf is involved in neuroprotection and regulation of synaptic protein loss in cerebral cortex due to oxidative stress caused by high-fat diet. PMID: 29277119
- Total abdominal irradiation exposure impairs cognitive function involving miR-34a-5p/BDNF axis. PMID: 28668331
- role in the maintenance of intestinal epithelial barrier function via anti-apoptotic properties PMID: 29527912
- upregulation of PAI-1 may be a critical mechanism underlying insufficient neurotrophic support and increased neurodegeneration associated with AD. Thus, targeting BDNF maturation through pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1 might become a potential treatment for AD. PMID: 28132883
- These observations suggest that GGA administration is a therapeutic candidate for depressive diseases by increasing hippocampal BDNF levels via HSP105 expression. PMID: 28580422
- In a model of traumatic brain injury, transcranial ultrasound stimulation increases brain BDNF levels. PMID: 28939348
- Results suggest that brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) activation in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) may overcome memory and plasticity deficits linked to Actl6a protein (BAF53b) mutations. PMID: 27226355
- Upregulating BDNF-AS inhibits osteogenesis, possibly through inverse regulation on BDNF and osteogenic signaling pathways PMID: 29247276
- miR-322 promotes Tau phosphorylation via negatively controlling BDNF-TrkB receptor activation PMID: 29464486
- BDNF preserves intestinal mucosal barrier function and alters gut microbiota in mice. PMID: 29475460
- Results demonstrate that heterotrimeric Galphai1 and Galphai3 proteins are essential for TrkB signaling and that disruption of Galphai1 or Galphai3 function could contribute to depressive behaviors. PMID: 29507199
- The present study revealed that long-term exercise increased BDNF expression in the motor cortex and facilitated a transfer of motor learning from aerobic exercise to postural coordination. PMID: 29019708
- These results suggested that the effects of Valeriana fauriei (VF) extract on a model of fibromyalgia (FM)may be associated with its modulatory effects on the BDNF signaling pathway in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. In conclusion, the mechanism underlying the protective effects of VF as a therapeutic agent against FM may involve the BDNF signaling pathway PMID: 29115388
- findings demonstrate that not only is BDNF actively secreted by the transdifferentiated BDNF-mesenchymal stem cells, but also that it has the capacity to promote neurite sprouting and regeneration PMID: 28694020
- Results indicate a modulatory effect of valproic acid on the Bbrain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in the ventral striatum. Study brings initial insights into the involvement of neurotrophic mechanisms in the ventral striatum in ethanol-induced addictive-like behavior. PMID: 28889008
- significant increase of BDNF levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex was observed in ethanol-treated mice receiving ginseng extract G115. PMID: 28837087
- This findings consistently demonstrate that long-lasting nociceptive input activates VTA neurons and, via increased release of BDNF. PMID: 28390647
- increased BDNF-TrkB signaling and synaptogenesis in the nucleus accumbens by deletion of alpha7 nAChR plays a key role in depression PMID: 27821848
- Findings suggest that carriers of the BDNF-Met allele may exhibit greater vulnerability to anxiety disorders and anorexia nervosa, contributed by increased excitability of pyramidal neurons, due to the combination of decreased GABAergic innervation of distal dendrites and BDNF-mediated suppression of perisomatic inhibitory inputs. PMID: 27578497
- the ZnT3 null state removed synaptic zinc, it rather increased free zinc in the cytosol of brain cells, which appeared to increase MMP-9 activity and BDNF levels. The present results suggest that zinc dyshomeostasis during the critical period of brain development may be a possible contributing mechanism for ASD. PMID: 27352957
- the BDNFVal66Met polymorphism contribute to the individual propensity for arterial thrombosis related to acute myocardial infarction PMID: 26705390
- There was a significant decrease in the BDNF protein expression along with an increase in the mRNA expression of CRH, NR3C1, CART, and NPY in intact females PMID: 28527954
- Daily OMR testing during the critical period leads to general visual function improvements accompanied by increased DA and BDNF in the retina, with this process being requisitely mediated by TrkB activation PMID: 29408880
- The changes in the expression patterns of proBDNF, BDNF, and their receptors under the influence of chronic alcohol consumption in the depressive ASC strain and nondepressive CBA strain mice are different. PMID: 28900083
- These results suggest that BDNF is implicated in MDMA-induced dependence and psychosis by activating the midbrain serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons. PMID: 28472632
- newborn neurons improve social recognition persistence through a BDNF-independent mechanism. PMID: 27165290
- Study shows long-term physical exercise in mice led to a significant increase in the synthesis and release of brain derived neurotrophic factor along with an alteration in the morphology of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus. PMID: 27686571
- Mice exposed to aggressive confrontations exhibited a similar pattern of species-typical aggressive and non-aggressive behaviors on the first and the last session. Repeated aggressive confrontations promoted an increase in plasma corticosterone. Repeated sessions of social instigation or aggressive confrontation did not alter BDNF concentrations at the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. PMID: 28614436
- High-intensity acute exercise increased total Bdnf mRNA in hippocampus of sedentary mice. PMID: 28556463
- Thus, the expression of BDNF in the hippocampal CA1 region has the potential to improve fear and object location memory in wild type mouse strains when the region and expression levels of BDNF are well controlled. PMID: 27394686
- Study demonstrates the importance of 14,15-EET-mediated production of astrocyte-derived brain derived neurotrophic factor for enhancing viability of astrocytes and protecting neurons from the ischaemic injury and provides insights into the mechanism by which 14,15-EET is involved in neuroprotection. PMID: 26526810
- Orthopedic surgery modulates the expression of neuropeptide Y and BDNF at the spinal and hippocampal levels. PMID: 27791037
- treating BACHD cortical neurons with ApiCCT1 prevented BACHD striatal neuronal atrophy by enhancing release of BDNF that subsequently acts through tyrosine receptor kinase B (TrkB) receptor on striatal neurons. Our findings are evidence that TRiC reagent-mediated reductions in mHTT enhanced BDNF delivery to restore the trophic status of BACHD striatal neurons. PMID: 27601642
- BDNF in the lower parts of the auditory system drives auditory fidelity along the entire ascending pathway up to the cortex by increasing inhibitory strength in behaviorally relevant frequency regions. PMID: 26476841
- Results highlight the biological significance of alternative brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts and provide evidence that individual isoforms serve distinct molecular and behavioral functions. PMID: 26585288
- A critical period of susceptibility to cigarette smoke exposure exists in the prenatal and early postnatal period, which results a downregulation in brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tyrosine kinase receptor B signaling in the hippocampus and enhances depression-like behaviors later in life. PMID: 26503133
- Deletion of Bdnf in DRG neurons leads to a temporary dysregulation of miR-1. PMID: 27346077
- Excitatory synaptic activation-dependent up-regulation of XBP1 directly facilitated transcriptional activation of BDNF. BDNF in turn drove its own expression via IRE1-XBP1 pathway in a protein kinase A-dependent manner. Exogenous treatment with BDNF promoteSynaptic activity- and BDNF-dependent distinct activation of dendritic IRE1-XBP1 cascade drives BDNF expression in cell soma and may be involved in dendritic extension. PMID: 28921568
- We hypothesize that BDNF in the developing brain regulates fear circuit plasticity during a sensitive period in early adolescence, and alterations in BDNF expression (genetic or environmental) have a persistent impact on fear behavior and fear-related disorders. PMID: 27699937
- High BDNF expression is associated with neuropathic pain. PMID: 29054488
- The s show that BDNF acts cell autonomous and autocrine, as wildtype neurons are not capable of rescuing growth deficits in neighboring MeCP2 deficient neurons in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 27782879
- BDNF acts retrogradely on TrkB in climbing fibers , and facilitates elimination of climbing fibers synapses from Purkinje cells somata during the third postnatal week. PMID: 28775326
- EGCG significantly ameliorated insulin resistance and cognitive disorder by up-regulating the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)/AKT and ERK/cAMP response element binding protein (CREB)/brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling pathways. PMID: 28739640
- Results suggest that activity-dependent BDNF signaling is critical for regulating oscillatory activity, which may contribute to altered behavior. PMID: 27552586
- the transcriptional induction of Bdnf by a mnemonic stimulus is impaired in aged hippocampal neurons. PMID: 27626660
- BDNF deficiency results in depression-like behavior, regardless of age and gender. PMID: 27648918
- Study reports that an endogenous molecule released after exercise is capable of inducing key promoters of the Mus musculus Bdnf gene. The metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate, which increases after prolonged exercise, induces the activities of Bdnf promoters, particularly promoter I, which is activity-dependent. PMID: 27253067
- Results show that (1) large-soma retinal ganglion cells are particularly susceptible to optic nerve injury; and (2) overexpression of BDNF prolongs the survival of retinal ganglion cells, including large-soma retinal ganglion cells. PMID: 28101532
- GR downregulates Bdnf expression through direct binding to Bdnf regulatory sequences. PMID: 28403881
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.; [BDNF precursor form]: Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:NGF-beta family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the dorsal root ganglion and the spinal cord (at protein level). Detected in brain, especially in brain cortex, hippocampus, midbrain and cerebellum.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













