-
中文名称:小鼠Slit2酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E11039m
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3200/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse SLIT2 ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse SLIT2 protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL and the sensitivity is 0.078 ng/mL.
-
别名:Slit2 ELISA Kit; Slit homolog 2 protein ELISA Kit; Slit-2) [Cleaved into: Slit homolog 2 protein N-product; Slit homolog 2 protein C-product] ELISA Kit
-
缩写:SLIT2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL
-
灵敏度:0.078 ng/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Neuroscience
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse Slit2 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 98 Range % 94-102 1:2 Average % 101 Range % 97-104 1:4 Average % 95 Range % 88-99 1:8 Average % 97 Range % 92-103 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse Slit2 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 93 88-96 EDTA plasma (n=4) 96 89-99 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 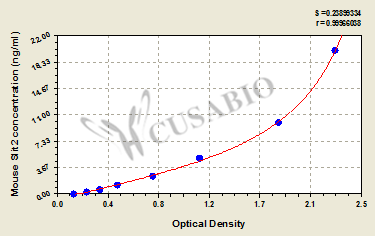
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 20 2.286 2.257 2.272 2.120 10 1.808 1.822 1.815 1.663 5 1.204 1.138 1.171 1.019 2.5 0.801 0.787 0.794 0.642 1.25 0.507 0.495 0.501 0.349 0.625 0.350 0.367 0.359 0.207 0.312 0.250 0.261 0.256 0.104 0 0.153 0.151 0.152 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Ductular reaction promotes intrahepatic angiogenesis through Slit2–Roundabout 1 signaling M Coll,Hepatology,2023
- SLIT2/ROBO1-signaling inhibits macropinocytosis by opposing cortical cytoskeletal remodeling VK Bhosle,Nature Communications,2020
- Slit2-Robo2 signaling modulates the fibrogenic activity and migration of hepatic stellate cells Zeng Z.et al,Life Sci,2018
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Thought to act as molecular guidance cue in cellular migration, and function appears to be mediated by interaction with roundabout homolog receptors. During neural development involved in axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions. SLIT1 and SLIT2 seem to be essential for midline guidance in the forebrain by acting as repulsive signal preventing inappropriate midline crossing by axons projecting from the olfactory bulb. In spinal chord development, may play a role in guiding commissural axons once they reached the floor plate by modulating the response to netrin. In vitro, silences the attractive effect of NTN1 but not its growth-stimulatory effect and silencing requires the formation of a ROBO1-DCC complex. May be implicated in spinal chord midline post-crossing axon repulsion. In vitro, only commissural axons that crossed the midline responded to SLIT2. In the developing visual system, appears to function as repellent for retinal ganglion axons by providing a repulsion that directs these axons along their appropriate paths prior to, and after passage through, the optic chiasm. In vitro, collapses and repels retinal ganglion cell growth cones. Seems to play a role in branching and arborization of CNS sensory axons, and in neuronal cell migration. In vitro, Slit homolog 2 protein N-product, but not Slit homolog 2 protein C-product, repels olfactory bulb (OB) but not dorsal root ganglia (DRG) axons, induces OB growth cones collapse and induces branching of DRG axons. Seems to be involved in regulating leukocyte migration.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- High Slit-2 expression is associated with hepatic fibrosis. PMID: 29660433
- Both ISL1-LHX3 and ISL1-LHX4 bound to the Slit2 enhancer. PMID: 27819291
- Study provides evidence that Slit2 is a novel quantitative trait gene and a positive regulator of the number and function of murine hematopoietic stem cells. PMID: 27503415
- Transgenic over-expression of slit2 enhances disruption of blood-brain barrier and increases cell death after traumatic brain injury in mice. This suggest that over expression of slit2 plays a detrimental role in the pathophysiology of mild TBI. PMID: 27521753
- Slit2 induces a robust activation of PKA signaling, which is required for its prothermogenic activity. PMID: 26876562
- Robo1-Slit2 interaction required for pathfinding mechanism essential to establish the functionally important habenulo-interpeduncular connection. PMID: 25366972
- overexpression promoted vascular remodeling by increasing the diameter of the maternal blood sinusoids and fetal capillaries PMID: 26282852
- Together, these observations suggest that Slit2 serves as a factor utilized by muscle Ctnnb1 to direct presynaptic differentiation. PMID: 26159615
- Slit2 acts as a repellant cue to mediate axon guidance in the formation of the anterior commissure. PMID: 25904499
- Slit2/Robo1 signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PMID: 25605242
- the two genes neuropeptide Y (Npy) and Slit homolog 2 (Drosophila) (Slit2) gradually increase during aging, and upon suppression of these two genes PMID: 26047956
- Cardiac defects in mutants for Robo or Slit range from membranous ventricular septum defects to bicuspid aortic valves. PMID: 25691540
- Data shows that modulation of angiostatic factor Slit2 by EphA2 receptor regulates endothelial responses to VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and tumor neovascularization. PMID: 25504371
- administration of Slit2 to atherosclerosis-prone LDL receptor-deficient mice inhibited monocyte recruitment to nascent atherosclerotic lesions. PMID: 26297762
- Results provide novel evidence that low expression of SLIT2 correlates with poor prognosis and promotes metastasis in ESCC, which may be regulated by the Cdc42-mediated pathways. PMID: 25490006
- Slit2 may promote angiogenesis by upregulating Robo1 and activating the VEGFR2-ERK1/2 pathway. PMID: 26244297
- Mutations of the SLIT2-ROBO2 pathway genes SLIT2 and SRGAP1 confer risk for congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract PMID: 26026792
- Slit2 signaling through Robo1 and Robo2 has a role in retinal neovascularization PMID: 25894826
- Results suggest that Slit2 might be involved in skin tumorigenesis. PMID: 24840330
- Slit production is required for beta-cell survival and optimal function via a mechanism involving endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis and actin remodeling. PMID: 24065825
- Prostaglandin F2alpha upregulates Slit2 and Robo1 expression in mouse corpus luteum during luteolysis. PMID: 23814012
- Slit/Robo signaling imposes a restriction force on spiral ganglia neurons to ensure their precise positioning for correct spiral ganglia-cochlear hair cells innervations. PMID: 23884932
- This study demonistrated that Slit2 can act alone to control aspects of retinal axon routing across the ventral diencephalic midline. PMID: 23320558
- Slit/Robo1 signaling is involved in regulating neural tube development by tightly coordinating cell proliferation and differentiation during neurulation. PMID: 23438940
- This study report that central nervous system progenitors express Robo1 and Robo2, receptors for Slit proteins that regulate axon guidance, and that absence of these receptors or their ligands leads to loss of ventricular mitoses. PMID: 23083737
- The cell motility modulator Slit2 is a potent inhibitor of platelet function. PMID: 22865890
- Data show that the gooseberry/gooseberry-neuro (gsb/gsb-n) transcription factor genes act to specify MP3 cell fate. PMID: 22912413
- The results of this study supported the idea that Slit2 promotes axon fasciculation via an autocrine and/or juxtaparacrine mechanism. PMID: 22306607
- Over-expression of human Slit2 in transgenic mouse significantly increased brain vessel density and the permeability of brain vessels to large molecules. PMID: 21986575
- the midline repellent Slit2 orients migration of corridor neurons and thereby switches thalamic axons from an external to a mammalian-specific internal path. PMID: 21435555
- Cooperation between Slit2 and ephrin-A1 regulates a balance between the pro- and antiangiogenic functions of Slit2. PMID: 21135133
- Slit2 expression (and that of Slit3) are linked to posttranscriptional regulation of Robo receptors during blood vessel development. PMID: 20947829
- the newly identified Slit2 gradient at the bronchus-alveoli axis induces attractive PI3K signaling in eosinophils and repulsive srGAP1 signaling in neutrophils through differential srGAP1 expression during lung inflammation. PMID: 20944010
- Activating with the soluble ligand Slit an endothelium-specific, Robo4-dependent signaling pathway that strengthens the vascular barrier, diminishing deleterious aspects of the host's response to the pathogen-induced cytokine storm. PMID: 20375003
- N-Slit2 promoted neuronal survival and neurite extension in chick dorsal root and autonomic ganglia. Slit2 also promoted neuronal survival in mouse dorsal root ganglia. PMID: 12488830
- Slit2 mRNA was intensely expressed in GFAP-positive astrocytes surrounding necrotic brain tissue, suggesting that slit2 might prevent regenerating axons from entering into the lesion. PMID: 12655597
- The principle function of Slit2 at the cortical midline may be to channel the axons along the correct path and possibly repel them away from the midline. We find no evidence that Slit2 prevents axons from recrossing the midline in the brain. PMID: 12954881
- Slit2 inhibits the migration of Langerhans cells out of the skin, suppressing the development of contact hypersensitivity responses after hapten sensitization. PMID: 14662852
- Experiments with triple mutant mice demonstrate a key role for Slit2 signaling in vertebrate midline commissural axon guidance. PMID: 15091338
- Mutants lacking SLIT2 develop supernumerary ureteric buds that remain inappropriately connected to the nephric duct; the SLIT2 signal is transduced in the nephrogenic mesenchyme. PMID: 15130495
- Slit-2 and Robo-1 expression is present throughout mesenchyme at midgestation and is not detectable by newborn day 1 PMID: 15162513
- SLIT2 acts in parallel with NTN1 to generate cell boundaries along ducts during bi-layered tube formation. PMID: 16439476
- Slit2 helps prevent retinal ganglion cell axons from crossing the diencephalic/telencephalic boundary in the developing optic tract. PMID: 16828733
- The role of Slit2-Robo signaling in gthe generation, migration and morphological differentiation of cortical interneurons is reported. PMID: 18054781
- Slit2 plays a role in regulating in vitro osteoblast differentiation. PMID: 19033678
- Slit2 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of fibrosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on cell cycle and apoptosis signal pathways is an important mechanism for Slit2-mediated tumor suppression PMID: 19048120
- These findings suggest that the combination of Netrin and Slit may be involved in proper axonal projection from the mammillary bodies and that their misexpression in the diencephalon may cause the misrouting of these axons in Pax6 mutant mice. PMID: 19115401
- Slit2 potently inhibits chemotaxis but not random motion of circulating neutrophils PMID: 19759280
- Slit2 mRNA level decreased during development of vascular decline in pulmonary fibrosis. PMID: 17496152
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in developing eye, in the optic stalk, and in the ventral diencephalon.
-
数据库链接:













