-
中文名称:小鼠神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E08603m
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse GFAP ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse GFAP protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 3.12 pg/mL-200 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 0.78 pg/mL.
-
别名:GfapGlial fibrillary acidic protein ELISA Kit; GFAP ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:3.12 pg/mL-200 pg/mL
-
灵敏度:0.78 pg/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Neuroscience
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse GFAP in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 90 Range % 85-94 1:2 Average % 98 Range % 95-101 1:4 Average % 102 Range % 97-108 1:8 Average % 94 Range % 91-97 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse GFAP spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 97 91-104 EDTA plasma (n=4) 93 90-96 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 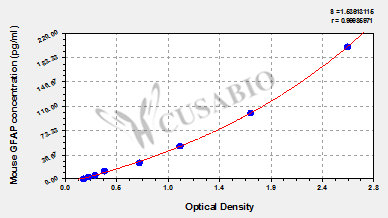
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 200 2.563 2.595 2.579 2.400 100 1.636 1.764 1.700 1.521 50 1.027 1.095 1.061 0.882 25 0.704 0.667 0.686 0.507 12.5 0.387 0.359 0.373 0.194 6.25 0.286 0.284 0.285 0.106 3.12 0.233 0.222 0.228 0.049 0 0.173 0.184 0.179 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Skin Wound following Irradiation Aggravates Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in a Mouse Model M Xiao,International journal of molecular sciences,2023
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-specific marker that, during the development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- This report the successful prediction and validation of Gfap as an miR-3099 target gene using a combination of bioinformatics resources with enrichment of annotations based on functional ontologies and a spatio-temporal expression dataset. PMID: 28597341
- These results indicate that autoantibodies against GFAP could serve as a predictive marker for the development of overt autoimmune diabetes. PMID: 28546444
- GFAP is specifically expressed in the auricular chondrocytes, and assumes a pivotal role in resistance against mechanical stress. PMID: 28063220
- compared open-skull and thinned-skull imaging methods for two-photon laser microscopy of live astrocytes in neocortex of GFAP-GFP transgenic mice PMID: 28107381
- work reveals that an Alexander disease-causing mutation alters GFAP turnover kinetics in vivo and provides an essential foundation for future studies aimed at preventing or reducing the accumulation of GFAP. PMID: 28223355
- Tat expression or GFAP expression led to formation of GFAP aggregates and induction of unfolded protein response (UPR) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in astrocytes. PMID: 27609520
- Study provides evidence that transcription of one of the astrocyte-specific genes, Gfap, is cooperatively regulated by co-expressed genes and their regulatory factors. PMID: 27041678
- This study demonstrated the GFAP-ApoE4 mice exhibited motor impairments when compared to GFAP-ApoE3 and wild-type mice. PMID: 26892275
- PINK1 deficiency causes defects in GFAP-positive astrogliogenesis during brain development. PMID: 26746235
- Gnasxl deficiency does not directly affect glial development in the hypothalamus, since it is expressed in neurons, and Gfap-positive astrocytes and tanycytes appear normal during early postnatal stages. PMID: 27080240
- Induction of glial cytokine expression was sequential, aligned with active sickness behavior, and preceded increased Iba-1 or GFAP immunoreactivity after lipopolysaccharide challenge PMID: 26470014
- Study provides a mechanistic link between the GFAP mutations/overexpression and the symptoms in those affected with Type II Alexander disease PMID: 26190408
- Study described GFAP-expressing non-myelinating Schwann cells in the lung, validated a transgenic mouse line that drives expression of cre under a GFAP promoter PMID: 26442852
- findings thus show that the inability to produce GFAP and Vim affects normal retinal physiology and that the effect of IF deficiency on retinal cell survival differs, depending on the underlying pathologic condition PMID: 26251181
- CUL4B as a negative regulator of GFAP expression during neural development. PMID: 26025376
- Astrocytes deficient of GFAP and vimentin showed decreased Notch signal sending competence and altered expression of Notch signaling pathway-related genes PMID: 26118771
- Absence of GFAP, or both GFAP and vimentin, alters Alzheimer's disease-induced changes in gene expression profile of astrocytes, showing a compensation of the decrease of neuronal support genes and a trend for a higher inflammatory expression profile PMID: 25731615
- Data indicate that glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was up-regulated in satellite glial cells (SGCs) in dorsal root ganglia 14 days after streptozotocin injection. PMID: 25312986
- Findings demonstrate that ENT1 regulates GFAP expression and possibly astrocyte function PMID: 25365803
- Data suggest that prenatal alterations in expression of various fetal brain proteins (including down-regulation of Gfap) are associated with aberrant behavioral characteristics of transgenic mice that model autism-like behavior. PMID: 25849768
- Study shows that increased levels of astrocytic GFAP can contribute to increases on inter-ictal spikes but do not represent a risk factor for appearance of post-traumatic seizures, even when there is increase in reactive gliosis PMID: 25069089
- The Phactr4 signals were not associated with F-actin fibers but were closely associated with intermediate filaments such as nestin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) fibers. PMID: 24748504
- Report increasing glial fibrillary acidic protein expression and electron microscopic features of brain edema in rodent cerebral malaria. PMID: 24966914
- absence of GFAP and vimentin in glial cells does not seem to affect the outcome after peripheral motoneuron injury but may have an important effect on the response dynamics PMID: 24223940
- the astrocyte became activated, exhibiting significantly increased levels of GFAP expression directly related to the level of HIV/VSV replication PMID: 24254728
- traumatic scratch injury to astrocytes triggered a calcium influx from the extracellular compartment and activated the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway to switch on GFAP PMID: 24123203
- Data show that CD8 T cells reactive to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a protein expressed in astrocytes, drive unique aspects of inflammatory central nervous system autoimmunity. PMID: 24591371
- Brain levels of GFAP and Tau proteins decreased significantly at 6 h and increased considerably at 24 h after repeated blast exposures. Plasma samples showed a similar initial decrease and later increase over this timeframe. PMID: 23933206
- Data indicate that Gfapdelta is expressed in the in developing mouse brain sub-ventricular zones in accordance with the described localization in the developing and adult human brain. PMID: 23991052
- GFAP was found to be downregulated in HSV-1 acute infection in cornea and upregulated in late stage, suggesting that GFAP might play some role during HSV-1 infection in cornea. PMID: 23758602
- Data show that neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-inactivation results in a cell-autonomous increase in glial fibrillary acidic protein+ (GFAP+), but not in NG2 proteoglycan NG2+, cell proliferation in vitro. PMID: 23318450
- this study demonistrated that mouse models of Alexander disease exhibit significant pathology in GFAP-positive radial glia-like cells in the dentate gyrus, and suffer from deficits in adult neurogenesis. PMID: 24259590
- These studies demonstrate that transactivation of the Gfap promoter is an early and sustained indicator of the disease process in the mouse. PMID: 23432455
- These data suggest that all astroglia cells in the developing and adolescent mouse brain express GFAPdelta, regardless of their neurogenic capabilities. PMID: 23285135
- The GFAP-stained intensity of the retinal area is increased in contralateral eyes and decreased in retinal ganglion cells of eyes with laser-induced ocular hypertension. PMID: 22583833
- Postulate that glial cells with increased Gfap expression support the elongation of new neurites from retinal ganglion cells possibly by providing a scaffold for outgrowth. PMID: 23259929
- GFAP expression is almost not affected by melatonin treatment in aged mice. PMID: 22200709
- differential regulation of GFAP isoforms is not involved in the reorganization of the intermediate filament network in reactive gliosis or in neurogenesis in the mouse brain. PMID: 22912745
- CD44-positive cells are APCs in the early postnatal cerebellum; surviving cells gradually express glial fibrillary acidic protein GFAP), a marker for mature astrocytes, indicating differentiation into mature astrocytes is the default for these cells. PMID: 21732075
- GFAP-negative astrocytes are fully inflammation-competent, displaying phenotypic heterogeneity as is commonly observed in brain astrocytes. PMID: 22072312
- In a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), GFAP is not necessary for the initiation of disease; instead, it plays some modulatory roles in the progression of ALS. PMID: 21453731
- Treadmill exercise training decreased the expression of GFAP in the striatum of chronic Parkinsonian mice, which can partially explain the beneficial neuroprotective role of exercise in patients with parkinson disease. PMID: 21725169
- The study shows opposing pattern of nestin and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in mouse hippocampus occuring in early postnatal development, suggesting that it is important for neural differentiation and positioning in the hippocampus. PMID: 21368556
- In the mouse there is a slight increase in the number of GFAP positive cells in the white matter after 3 days of severe cerebral contusion trauma. PMID: 20479526
- Increased expression of GFAP in Muller cells of mer knockout mice occur at P20d in the peripheral retina and P4w in the central retina. GFAP expression in Muller cells appears to be a secondary response to the loss of retinal neurons. PMID: 20497693
- One protein, GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), was found to be elevated in the LINCL mice compared with normal controls in both isolated storage bodies and a lysosome-enriched subcellular fraction that contains storage material. PMID: 20370715
- The results of this study suggested that GFAP is necessary for morphological retention and distribution of reactive astrocytes during prion disease, and that there is a GFAP-dependent function of glial filaments in reactive astrocytes. PMID: 19931516
- Report demonstrated for the first time that GFAPdelta is specifically expressed in radial glia and SVZ neural progenitors during human brain development. PMID: 20040497
- The exact expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in trigeminal ganglion and dental pulp. PMID: 11838710
- Human influenza viral infection in utero alters GFAP immunoreactivity in the developing brains of neonatal mice. PMID: 12140787
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Intermediate filament family
-
组织特异性:Brain; isoform 2 expressed at 20-fold lower level than isoform 1.
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













