-
中文名称:大鼠精氨酸酶1(ARG1)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E17519r
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Rat ARG1 ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Rat ARG1 protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL and the sensitivity is 0.078 ng/mL.
-
别名:Arg1Arginase-1 ELISA kit; EC 3.5.3.1 ELISA kit; Liver-type arginase ELISA kit; Type I arginase ELISA kit
-
缩写:ARG1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
检测范围:0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL
-
灵敏度:0.078 ng/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Metabolism
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat ARG1 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 96 Range % 89-101 1:2 Average % 98 Range % 91-102 1:4 Average % 94 Range % 85-97 1:8 Average % 92 Range % 84-95 -
回收率:
The recovery of rat ARG1 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 104 95-109 EDTA plasma (n=4) 101 91-105 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 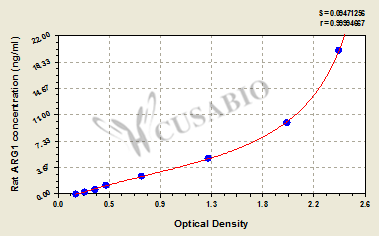
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 20 2.446 2.345 2.396 2.225 10 1.992 1.914 1.953 1.782 5 1.255 1.326 1.291 1.120 2.5 0.716 0.732 0.724 0.553 1.25 0.420 0.433 0.427 0.256 0.625 0.321 0.338 0.330 0.159 0.312 0.239 0.247 0.243 0.072 0 0.169 0.173 0.171 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Interplay in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Rat Model FAM Abo-Aziza,International immunopharmacology,2023
- Targeting α7-nAChR by galantamine mitigates reserpine-induced fibromyalgia-like symptoms in rats: involvement of cAMP/PKA, PI3K/AKT, and M1/M2 microglia … AA Atta,European journal of pharmacology,2023
- The impact of L-citrulline on murine intestinal cell integrity, immune response, and arginine metabolism in the face of Giardia lamblia infection HS Zoghroban,Acta tropica,2022
- EXPANSION, ACTIVATION AND FUNCTION PROMOTION OF MYELOID-DERIVED SUPPRESSOR CELLS IN ADJUVANT-INDUCED ARTHRITIS Abd-Elhalem S S, et al,European Journal of Biomedical,2019
- Lipopolysaccharide-induced chorioamnionitis and postnatal lung injury: The beneficial effects of L-citrulline in newborn rats Arben Dedja.et al,Experimental Lung Research,2018
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Key element of the urea cycle converting L-arginine to urea and L-ornithine, which is further metabolized into metabolites proline and polyamides that drive collagen synthesis and bioenergetic pathways critical for cell proliferation, respectively; the urea cycle takes place primarily in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys.; Functions in L-arginine homeostasis in nonhepatic tissues characterized by the competition between nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and arginase for the available intracellular substrate arginine. Arginine metabolism is a critical regulator of innate and adaptive immune responses. Involved in an antimicrobial effector pathway in polymorphonuclear granulocytes (PMN). Upon PMN cell death is liberated from the phagolysosome and depletes arginine in the microenvironment leading to suppressed T cell and natural killer (NK) cell proliferation and cytokine secretion. In group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) promotes acute type 2 inflammation in the lung and is involved in optimal ILC2 proliferation but not survival. Plays a role in the immune response of alternatively activated or M2 macrophages in processes such as wound healing and tissue regeneration, immune defense against multicellular pathogens and parasites, and immune suppression and allergic inflammation; the regulatory outcome seems to be organ specific. In tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells (DCs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) plays a role in suppression of T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Arg1 expression, which is abundant in polarized M2 cells, is associated with strain/genotype differences from different pathways. PMID: 25872571
- Arginase promotes endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in obesity by reducing arginine bioavailability. PMID: 25557182
- Lower activity and expression levels of iNOS and higher activity and expression levels of arginase-1 in rat alveolar macrophages were found to be linked to the susceptibility of T. gondii infection in these cells PMID: 23691079
- Diabetes-induced increases in arginase I were involved in the diabetes-induced impairment of retinal blood flow by a mechanism involving vascular endothelial cell dysfunction. PMID: 23232640
- Report utility of arginase-1 for monitoring drug-induced liver injury in rat model. PMID: 22872058
- Arginase and methylated arginine derivatives appear to be essential modulators of the inflammatory response in the acute phase of a multiple sclerosis model. PMID: 22507752
- This study suggested that the increased level of arginase-1 in SCI is associated with an increase in macrophages and reactive astrocytes, possibly contributing to the modulation of inflammation during the course of SCI. PMID: 22325098
- we postulate that the increased level of arginase-1, which is partly from M2 macrophages, contributes to the modulation of neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis lesions PMID: 22483960
- Arginase contributes significantly to L-proline supply for collagen synthesis in rat fibroblasts, in which arginase I is the predominant isoenzyme PMID: 20107769
- These findings reveal the basis for thrombin induction of endothelial arginase I and indicate that arginase inhibition may be an attractive therapeutic alternative in the setting of arterial thrombosis and its associated endothelial dysfunction. PMID: 20032511
- crystal structure: arginase-boronic acid complex highlights a physiological role in erectile function PMID: 10542097
- Regulates low-level NO production by neuronal NOS (nNOS), most likely by competing for L-arginine. PMID: 11829529
- Mechanisms involved in substrate binding and catalysis are elucidated via synthesis and evaluation of alternative substrate. PMID: 12020133
- The upregulation of the arginase expression in wound derived fibroblasts underlines the distinct regulation of l-arginine metabolism in WFBs. PMID: 12069499
- Total arginase activity and arginase I and II protein expression did not differ between the young and aged groups in the prefrontal cortex. PMID: 15013576
- The highest affinity inhibitorsof Arg1 displace the metal-bridging hydroxide ion (and sometimes occupy a Mn(2+)(A) site found vacant in the native enzyme) and maintain a conserved array of hydrogen bonds with their alpha-amino and -carboxylate groups. PMID: 15248756
- Arg I plays a critical role in the pathobiology of age-related endothelial dysfunction. PMID: 16380531
- Arginase I protein was undetectable in the non-pregnant myometrium and up-regulated at term gestation, contributing to enhanced overall arginase activity at term gestation. PMID: 16735458
- Arginase acts as central regulator of trophic factor-deprived motor neuron survival by suppressing nitric oxide production and consequent peroxynitrite toxicity. Resistance of motor neurons to trophic factor deprivation may result from increased arginase. PMID: 16914676
- Thus, in addition to enhancing the expression of Arg I and spermine in repaired spinal cords, our treatment may recruit activated macrophages and create a more favorable environment for axonal regrowth. PMID: 17418108
- diabetes-induced impairment of vasorelaxation to acetylcholine was correlated with increases in reactive oxygen species and arginase activity and arginase I expression in aorta and liver. PMID: 17967788
- Arginase promotes neointima formation in rat injured carotid arteries. PMID: 19164802
- upregulation of Arg I and increased synthesis of polyamines play an important role in the conditioning lesion effect, and spermidine is sufficient to promote optic nerve regeneration in vivo PMID: 19641117
- Data indicate that iNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation of arginase 1 and the increase in arginase activity lead to eNOS uncoupling, contributing to the nitroso-redox imbalance, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular stiffness observed in vascular aging. PMID: 19661445
- Limits iNOS-mediated NO synthese in macrophages, probably by limiting L-arginine availability for iNOS (substrate competition) PMID: 9179379
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic granule.
-
蛋白家族:Arginase family
-
组织特异性:Detected in liver (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-













