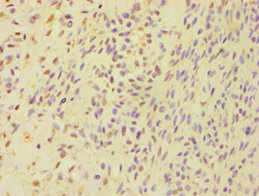
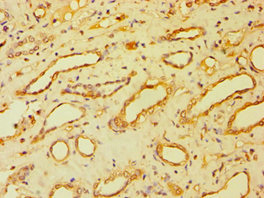
BSND Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA837883ESR1HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) BSND Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q8WZ55
-
基因名:BSND
-
别名:BART antibody; Bartter syndrome infantile with sensorineural deafness antibody; Bartter syndrome; infantile; with sensorineural deafness (Barttin) antibody; Barttin antibody; Bsnd antibody; BSND_HUMAN antibody; deafness; autosomal recessive 73 antibody; DFNB 73 antibody; DFNB73 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Barttin protein (54-320AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Functions as a beta-subunit for CLCNKA and CLCNKB chloride channels. In the kidney CLCNK/BSND heteromers mediate chloride reabsorption by facilitating its basolateral efflux. In the stria, CLCNK/BSND channels drive potassium secretion by recycling chloride for the basolateral SLC12A2 cotransporter.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results suggest that BSND is expressed only in normal salivary glands and oncocytic salivary gland tumors such as Warthin's tumor and oncocytoma PMID: 28470573
- results demonstrate that the carboxyl terminus of hClC-Kb is not part of the binding site for barttin, but functionally modifies the interplay with barttin. PMID: 26453302
- These results demonstrate that mutations in a cluster of hydrophobic residues within transmembrane domain 1 affect barttin-CLC-K interaction and impair gating modification by the accessory subunit PMID: 26063802
- R8W and G47R, two naturally occurring barttin mutations identified in patients with Bartter syndrome type IV, reduce barttin palmitoylation and CLC-K/barttin channel activity. PMID: 26013830
- BSND, was first modeled, and then, the identified mutation was further analyzed by using different bioinformatics tools. PMID: 21541222
- Case Report: G47R mutation decreases barttin expression, resulting CIC-K location being changed from the basement membrane to the cytoplasm in the tubule and might have varying effects on renal function associated with factors other than this gene. PMID: 21269598
- The mislocalization of CLC-K2 was identified as the molecular pathogenesis of Bartter syndrome by mutant barttins. PMID: 12761627
- ClC-Ka/barttin channels are regulated by SGK1 and SGK3, which may thus participate in the regulation of transport in kidney and inner ear. PMID: 15496163
- A missense, point mutation on gene BSND exon 1, affects the function of the CLC-K/barttin chloride channel and caused Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness in two families from Spain. PMID: 16572343
- Barttin mutations is associated with antenatal Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness PMID: 16773427
- Barttin modulates trafficking and function of ClC-K1 and ClC-Kb channels PMID: 16849430
- BSND-V43I, a common variant conferring partial loss of function, exhibits significant deviation from equilibrium in the Ghanaian normotensive control population PMID: 17954364
- Disruption of the gene encoding Barttin, BSND, results in a 'double knockout' of the functions of both ClCKA and ClCKB, manifesting as Bartter syndrome type IV with sensorineural deafness and an especially severe salt-losing phenotype. PMID: 18094726
- Bartter syndrome type IV can be caused by various derangements in the function of barttin, likely contributing to the diversity of observed phenotypes. PMID: 18776122
- Deletion of exons 2-4 in the BSND gene causes severe antenatal Bartter syndrome. PMID: 18843510
- In a large cohort of ante/neonatal Bartter syndrome, deafness, transient hyperkalaemia and severe hypokalaemic hypochloraemic alkalosis orientate molecular investigations to BSND, KCNJ1 and CLCNKB genes, respectively. PMID: 19096086
- Mutations of BSND can cause nonsyndromic deafness or Bartter syndrome. PMID: 19646679
- The molecular basis of DFNB73 autosomal recessive deafness is reported. PMID: 19646679
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Bartter syndrome 4A, neonatal, with sensorineural deafness (BARTS4A)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Expressed primarily in kidney. Expressed in specific nephron segments and in the stria vascularis of the inner ear.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 16512
OMIM: 602522
KEGG: hsa:7809
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000360312
UniGene: Hs.151291
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-