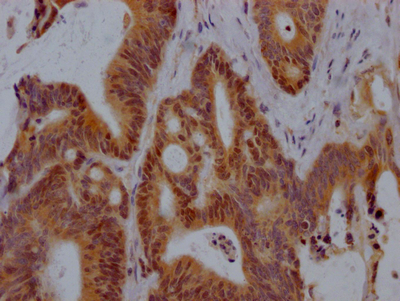
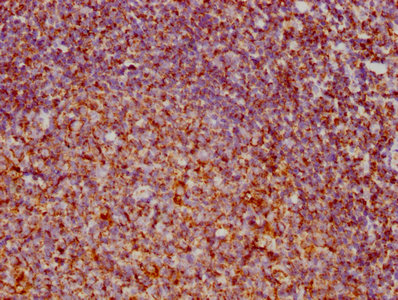
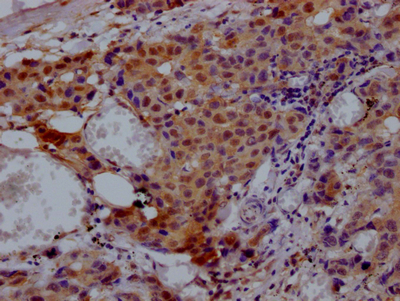
CAMK2G Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA004468GA01HU
-
规格:¥3,900
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q13555
-
基因名:
-
别名:CAMK2G antibody; CAMK antibody; CAMK-II antibody; CAMKGCalcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit gamma antibody; CaM kinase II subunit gamma antibody; CaMK-II subunit gamma antibody; EC 2.7.11.17 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Human CAMK2G
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that functions autonomously after Ca(2+)/calmodulin-binding and autophosphorylation, and is involved in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) transport in skeletal muscle and may function in dendritic spine and synapse formation and neuronal plasticity. In slow-twitch muscles, is involved in regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) transport and in fast-twitch muscle participates in the control of Ca(2+) release from the SR through phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor-coupling factor triadin. In the central nervous system, it is involved in the regulation of neurite formation and arborization. It may participate in the promotion of dendritic spine and synapse formation and maintenance of synaptic plasticity which enables long-term potentiation (LTP) and hippocampus-dependent learning.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- point mutation R292P sufficient to disrupt gene expression and spatial learning PMID: 29934532
- The data suggest T287 autophosphorylation regulates substrate gating, an intrinsic property of the catalytic domain, which is amplified within the multivalent architecture of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II holoenzyme. PMID: 29391954
- These findings indicate that the CaMKII-mediated GluA1 phosphorylation of S567 and S831 is critical for P2X2-mediated AMPAR internalization and ATP-driven synaptic depression. PMID: 27624155
- Laminin is instructive and CaMKII is non-permissive for the formation of complex aggregates of acetylcholine receptors on myotubes in culture. PMID: 27964993
- A new molecular mechanism mediated by CAMK2gamma in intestinal epithelial cells during colitis-associated cancer (CAC) development, thereby providing a potential new therapeutic target for CAC. PMID: 28319059
- oxidative stress activated the TRPM2-CaMKII cascade to further induce intracellular ROS production, which led to mitochondria fragmentation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential PMID: 28007458
- novel mechanism by which CAMK2gamma antagonizes mTORC1 activation during hepatocarcinogenesis PMID: 27819676
- Demonstrate that calcium/CaMKIIgamma/AKT signaling can regulate apoptosis and autophagy simultaneously in colorectal cancer cells. PMID: 26803057
- High CaMKIIgamma expression is associated with lung cancer. PMID: 25965829
- Dysfunction in CaMKII-based signaling has been linked with a host of cardiovascular phenotypes including heart failure and arrhythmia, and CaMKII levels are elevated in human and animal disease models of heart disease. PMID: 25577293
- Inhibition of CaMKII activity results in an upregulation of CaMKIV mRNA and protein in leukemia cell lines. PMID: 25446257
- CAMKIIgamma, HSP70 and HSP90 transcripts are differentially expressed in chronic myeloid leukemia cells from patients with resistant mutated disease. PMID: 24206096
- CaMKII-dependent microtube polymerization may be responsible for the enhanced uptake of PEI/ON complexes in A549 cells under oxidative stress conditions. PMID: 24634301
- Our data suggest that berbamine and its derivatives are promising agents to suppress liver cancer growth by targeting CAMKII PMID: 23960096
- CaMKII overexpression in mushroom body neurons increases activity dependent calcium responses. PMID: 23543616
- it can be concluded that CaMKII regulates the activity of ASIC1, which is associated with the ability of GBM cells to migrate. PMID: 24100685
- When inhibiting CaMKII, B-cell activating factor (BAFF) is attenuated and mediates protein phosphatase (PP)2A-Erk1/2 signaling and B-cell proliferation. PMID: 24269630
- the chronic gain-of-function defect in RyR2 due to CaMKII hyperphosphorylation is a novel mechanism that contributes to pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes PMID: 23516528
- results show that CAMKII and calmodulin contribute to IKK complex activation and thus to the induction of NF-kappaB in response to H. pylori infection PMID: 23463379
- Activated CaMK-II interacts with the C-terminal domain of diacylglycerol lipase-alpha (DGLalpha) and inhibits DGLalpha activity. PMID: 23502535
- Data indicate that CaMKII gamma as a specific and critical target of berbamine for its antileukemia activity. PMID: 23074277
- These findings revealed a fundamental role of CaMKII in the enteric nervous system. PMID: 22952977
- CaMKII T286A showed a mildly but significantly reduced rate of Ca(2+)/CaM-stimulated phosphorylation for two different peptide substrates (to ~75-84% of wild type). PMID: 22615928
- The CaMKII phosphorylation motif in the Nav1.5 DI-DII cytoplasmic loop is a critical point for proarrhythmic changes. PMID: 23008441
- CaMKII was also necessary for the phosphorylation of Raf-1 at S338 by serum, fibronectin and Ras. PMID: 22592532
- increases in Ca(2+) lead to CaMKII activation and subsequent Lck-dependent p66Shc phosphorylation on Serine 36. This event causes both mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired Ca(2+) homeostasis, which synergize in promoting Jurkat T-cell apoptosis. PMID: 21983898
- we review the cellular colocalization of CaMKII isoforms with special regard to the cell-type specificity of isoform expression in brain--REVIEW PMID: 22612808
- CaMKII binding to and phosphorylation of the NHE3 C terminus are parts of the physiologic regulation of NHE3 that occurs in fibroblasts as well as in the brush border of an intestinal Na(+)-absorptive cell. PMID: 22371496
- study demonstrates that premitotic condensation involves the activation of ClC-3 by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in glioma cells PMID: 22049206
- study shows CaMKII is recruited to the immunological synapse where it interacts with and phosphorylates Bcl10; propose a mechanism whereby Ca(2+) signals can be integrated at the immunological synapse through CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl10 PMID: 21513986
- Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase II participate in control of cell cycle progression and survival of irradiated CML cells. PMID: 21063097
- These results indicated that PP6 and CaMKII regulated apoptosis by controlling the expression level of p27. PMID: 20851109
- The interaction between CaMKII and its binding proteins was altered by the phosphorylation state of both the CaMKII and the partner. PMID: 20060891
- CaMKII is a molecular link translating intracellular calcium changes, which are intrinsically associated with glioma migration, to changes in ClC-3 conductance required for cell movement PMID: 20139089
- Our results suggest a first observation that CaMKII regulates TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of fibroblast-like synovial cells through Akt, standing an upstream of caspase-8-dependent cascades. PMID: 20149311
- Study further supports self-aggregation of CaMKII holoenzymes as the underlying mechanism that involves inter-holoenzyme T286-region/T-site interaction. PMID: 19840793
- cloning, genomic structure and detection of variants in subjects with Type II diabetes PMID: 12032636
- CaMKIIgamma is necessary to suppress MCAK depolymerase activity in vivo. PMID: 15775983
- A transgenic, constitutively active, Ca2+-independent form of CaMKgamma reduces positive selection of T cells by maintaining association of SHP-2 with the T cell receptor (TCR) complex, and halting TCR signaling. PMID: 16002660
- Amphetamine in a cell line induces a robust increase in cytosolic Ca2+ and concomitant activation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). PMID: 17032905
- Significant cross-talk between calcium and retinoic acid signaling pathways regulates the differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. PMID: 17431504
- insulin in the presence of Angiotensin II inhibits protein phosphatase-2A (PP-2A) and stimulates autonomous CaM kinase II activities and thus vascular smooth muscle migration PMID: 17553505
- IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic peptide/BNP expression via Galphaq interaction and protein kinase C-alpha/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. PMID: 18434368
- CaMKIIgamma is a critical regulator of multiple signaling networks regulating the proliferation of myeloid leukemia cells PMID: 18483256
- In Turner yndrome, loss of voltage-dependent inactivation is an upstream initiating event for arrhythmia phenotypes that are ultimately dependent on CaMKII activation. PMID: 19001023
- increased RyR2-dependent Ca2+ leakage due to enhanced CaMKII activity is an important downstream effect of CaMKII in individuals susceptible to AF induction. PMID: 19603549
- P2X7 receptor-triggered signalling pathways that regulate neurite formation in neuroblastoma cells. PMID: 19682070
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CaMK subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in skeletal muscle.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1463
OMIM: 602123
KEGG: hsa:818
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000319060
UniGene: Hs.523045
Most popular with customers
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-
VDAC1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
VCP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP
Species Reactivity: Human, Rat