CCNE1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA183203
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
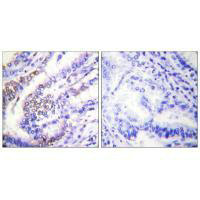
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma tissue using Cyclin E1 antibody.
-
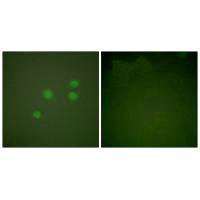
Immunofluorescence analysis of A549 cells, using Cyclin E1 antibody.
-
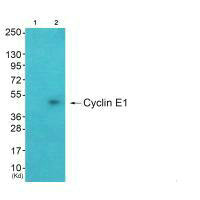
Western blot analysis of extracts from K562 cells, using Cyclin E1 antibody.
-
Western blot analysis of extracts from A549 cells (Lane 2), using Cyclin E1 antiobdy. The lane on the left is treated with systhesized peptide.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CCNE1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P24864
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human Cyclin E1.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC,IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 IHC 1:50-1:100 IF 1:100-1:500 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Essential for the control of the cell cycle at the G1/S (start) transition.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- miR-874 inhibits CCNE1 expression during growth factor deprivation and that miR-874 down-regulation in osteosarcomas leads to CCNE1 up-regulation and more aggressive growth phenotypes. PMID: 29109143
- Amplified/cyclin E1(hi) and non-amplified/cyclin E1(hi) tumors have different pathological and biological characteristics and clinical outcomes indicating that they are separate subsets of cyclin E1(hi) HGSOC. PMID: 30209015
- Breast cancer recurrence-free interval was significantly worse in patients with cyclin E (LMW-E)-positive tumors who received aromatase inhibitor (AI) neoadjuvant therapy, compared with those with LMW-E negative tumors. PMID: 28947566
- in a series of human biopsies, non-metastatic SCCs displayed a higher degree of chromosomal alterations and higher expression of the S phase regulator Cyclin E and the DNA damage signal gammaH2AX than the less aggressive, non-squamous, basal cell carcinomas. However, metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma lost the gammaH2AX signal and Cyclin E, or accumulated cytoplasmic Cyclin E. PMID: 28661481
- Cytoplasmic cyclin E identifies patients with the highest likelihood of recurrence consistently across different patient cohorts and subtypes. These patients may benefit from alternative therapies targeting the oncogenic isoforms of cyclin E. PMID: 27881578
- our results validate the assumption that CBX7 is a tumor suppressor of gliomas. Moreover, CBX7 is a potential and novel prognostic biomarker in glioma patients. We also clarified that CBX7 silences CCNE1 via the combination of CCNE1 promoter and the recruitment of HDAC2. PMID: 28460453
- Our findings suggest that gene copy-number gain and upregulation of CCNE1 occur in ovarian clear cell carcinoma and are associated with a worse clinical outcome, dictating the survival of early-stage patients. PMID: 27767100
- YAP/ TAZ pathways contribute to the proliferation/quiescence switch during colon cancer 5FU treatment according to the concerted regulation of Cyclin E1 and CREB PMID: 27527859
- Silencing of CDCA5 suppresses proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inducing G1-phase arrest via downregulating CCNE1. PMID: 29326043
- Analysis of genomic data from TCGA demonstrated coamplification of CCNE1 and AKT2 Overexpression of Cyclin E1 and AKT isoforms, in addition to mutant TP53, imparted malignant characteristics in untransformed fallopian tube secretory cells, the dominant site of origin of high-grade serous ovarian cancer PMID: 27663592
- Finding suggest that amplification of CCNE1 serves as one mechanism for the development of some serous tubal intraepithelial carcinomas. PMID: 27443516
- Prognostic gene sets based on the 13 genes were developed, and their prognostic values were verified in three independent patient cohorts (n=501). Among them, a signature of CCNE1 and its coexpressed genes was significantly associated with disease progression and validated in the independent cohorts. PMID: 28082741
- Cyclin E1 mRNA and protein expressions were suppressed. PMID: 26603262
- The opposing effects of ORC1 (represor) and CDC6 (gene activator) in controlling the level of Cyclin E ensures genome stability and a mechanism for linking directly DNA replication and cell division commitment. PMID: 27458800
- High cyclin E expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 28760857
- High CCNC1 expression is associated with inflammatory breast cancer. PMID: 28107181
- Inhibition of cell division cycle associated 2 (CDCA2) suppressed the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) cells via G1 phase arrest by downregulating cyclin E1(CCNE1), while overexpression of CDCA2 promoted LAC cells proliferation by upregulating CCNE1. PMID: 28423619
- a PI3K/PKCiota/cyclin E signaling pathway as a therapeutic target during ovarian tumorigenesis PMID: 26279297
- Amplification of 19q12 CCNE1/URI was found in 10.4% (28/270) and was significantly associated with type II endometrial cancer (EC) high grade, advanced FIGO stage, and aberrant tumor supressor p53 expression. PMID: 27582547
- Results show that cyclin E1 and CDK2 participate in STC1 promoting cell proliferation of prostate neoplasm cells. PMID: 28350121
- cyclin E is specifically dephosphorylated at S384 by the PP2A-B56 phosphatase, thereby uncoupling cyclin E degradation from cyclin E-CDK2 activity PMID: 28137908
- These results provide evidence that ARTD1 regulates cell cycle re-entry and G1/S progression via cyclin E expression and p27(Kip 1) stability independently of its enzymatic activity, uncovering a novel cell cycle regulatory mechanism. PMID: 27295004
- These results demonstrate a repressor role for NFAT1 in cell cycle progression and Cyclin E expression in B lymphocytes, and suggest a potential function for NFAT1 protein in B cell malignancies. PMID: 27399331
- High CCNE1 amplification and expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 26810187
- CCNE1/REL gene interaction might play pivotal roles in the occurrence and development of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. PMID: 26676054
- These results indicate that miR-25 has anti-apoptosis roles in AGS cells, possibly via inhibiting FBXW7 and thus promoting oncogenes, such as CCNE1 and MYC. PMID: 27120728
- Cyclin E-driven OvCa cells appeared addicted to glucose metabolism via TCA. Combined CDKi with modalities targeting TCA, like SDHA inhibition showed promising effects for this genotype. Combined blockade of CDK and SDH, both genetically and pharmaceutically, showed synergy and resulted in inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion and migration in A2780 cells PMID: 26826064
- Over-expression of CCNE1 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. PMID: 26771237
- High levels of cyclin E are a predicator of poor prognosis among patients with gastrointestinal cancer. [meta-analysis] PMID: 25627202
- The effects of CCNE1 knockdown were dependent on the CCNE1 expression status. PMID: 26647729
- Data show that melanoma antigen, family C, 2 protein (MAGE-C2) binds with RING-box protein 1 (Rbx1) and Cullin 1, and regulates cyclin E stability in melanoma cells. PMID: 26540345
- The findings suggest that the role of cyclin E and tumor specific low molecular weight isoforms as mediators of tumorigenesis is in part dependent on p53 context. PMID: 26625764
- Ad-cycE can target cyclin E overexpression in cancer cells and repress tumor growth in syngeneic mouse models. PMID: 26475304
- ovary tumors with elevated CCNE1 expression may be staged for Cdk2-targeted therapy PMID: 26204491
- our findings identify a novel mechanism of cyclin E-mediated Mcl-1 regulation in human cancer PMID: 26219338
- miR-15b might be involved in termination of osteoblastic cells proliferation by arresting them at G0/G1 phase through direct targeting cyclin E1. PMID: 26007664
- A significant correlation between cyclin E1 amplification and deletions at a number of the genomic loci in breast cancer. PMID: 25959964
- These results indicate cyclin E1 is downregulated by both miR-497 and miR-34a, which synergistically retard the growth of human lung cancer cells. PMID: 25909221
- MicroRNA-30c-2-3p negatively regulates NF-kappaB signaling and cell cycle progression through downregulation of TRADD and CCNE1 in breast cancer. PMID: 25732226
- Results show that miR-16 and HuR co-regulate the cyclin E1 mRNA without influencing each other's binding or expression. miR-16 regulation predominates, blocking upregulation of cyclin E1 by HuR. PMID: 25830480
- Expression of Notch1, -2, and -3, CDK2, and CCNE1 was significantly decreased by upregulation of ALDH1A1 in A549 cells, but increased by its interruption in A549s cells. PMID: 24671051
- Results show that CCNE1 and BRD4 on chromosome 19 were amplified/overexpressed in a substantial cases of epithelial ovarian cancer with no involvement of BRCA genes. PMID: 25892415
- This study indicates that CCNE1 rs1406 polymorphism may contribute to BC risk PMID: 25159285
- Suppression of NF90 caused a decrease in the half-life of cyclin E1 mRNA PMID: 25399696
- miR-144-5p functions as tumour suppressor in BC cells. CCNE1 and CCNE2 were directly regulated by miR-144-5p and might be good prognostic markers for survival of bladder cancer patients PMID: 26057453
- HOXA7 promotes cell proliferation, and these changes are mediated by cyclin E1/CDK2 PMID: 25501982
- Aurora-A/HURP relays cell transforming signal to NF-kappaB, and the HURP/NF-kappaB complex is engaged in the regulation of cyclin E1 expression. PMID: 25289861
- Contrary to previous literature, we found a correlation between cyclin E expression and prognosis. Further large-scale studies are required to confirm our findings. PMID: 26026100
- Global gene expression profiling identifies ALDH2, CCNE1 and SMAD3 as potential prognostic markers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. PMID: 25408144
- The cell cycleassociated proteins cyclin E and p27kip1 may have contributed to this antitumor effect. PMID: 25310086
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Cyclin family, Cyclin E subfamily
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in testis and placenta. Low levels in bronchial epithelial cells.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1589
OMIM: 123837
KEGG: hsa:898
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000262643
UniGene: Hs.244723
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-