CD209 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA143864
-
规格:¥2024
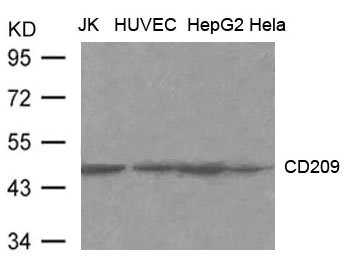
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CD209 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q9NNX6
-
基因名:CD209
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.389~393( E-Q-F-L-S )derived from Human CD209 (DC-SIGN).
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Pathogen-recognition receptor expressed on the surface of immature dendritic cells (DCs) and involved in initiation of primary immune response. Thought to mediate the endocytosis of pathogens which are subsequently degraded in lysosomal compartments. The receptor returns to the cell membrane surface and the pathogen-derived antigens are presented to resting T-cells via MHC class II proteins to initiate the adaptive immune response.; On DCs it is a high affinity receptor for ICAM2 and ICAM3 by binding to mannose-like carbohydrates. May act as a DC rolling receptor that mediates transendothelial migration of DC presursors from blood to tissues by binding endothelial ICAM2. Seems to regulate DC-induced T-cell proliferation by binding to ICAM3 on T-cells in the immunological synapse formed between DC and T-cells.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for HIV-1 and HIV-2.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Ebolavirus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Cytomegalovirus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for HCV.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Dengue virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Measles virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Herpes simplex virus 1.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Influenzavirus A.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for SARS-CoV.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Japanese encephalitis virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Lassa virus. Acts as an attachment receptor for Marburg virusn.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Respiratory syncytial virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for Rift valley fever virus and uukuniemi virus.; (Microbial infection) Acts as an attachment receptor for West-nile virus.; (Microbial infection) Probably recognizes in a calcium-dependent manner high mannose N-linked oligosaccharides in a variety of bacterial pathogen antigens, including Leishmania pifanoi LPG, Lewis-x antigen in Helicobacter pylori LPS, mannose in Klebsiella pneumonae LPS, di-mannose and tri-mannose in Mycobacterium tuberculosis ManLAM and Lewis-x antigen in Schistosoma mansoni SEA. Recognition of M.tuberculosis by dendritic cells occurs partially via this molecule.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Lewis-antigen-containing ICAM-2/3 on Jurkat leukemia cells interact with DC-SIGN to regulate DC functions PMID: 29671117
- These findings indicate that DC-SIGN plays an important role in Japanese encephalitis virus transmission from dendritic cells to T cells and provide insight into how Japanese encephalitis virus exploits the migratory and antigen-presenting capabilities of dendritic cells to gain access to lymph nodes for dissemination and persistence in the host. PMID: 28865053
- this study shows that DC-SIGN expression in Hofbauer cells may play an important role in immune tolerance in fetal chorionic villi during the development of preeclampsia PMID: 29049918
- The DC-SIGN -336G/A polymorphism significantly affects dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue fever incidence with the effect more pronounced in certain analyzed patient subgroups (Meta-Analysis). PMID: 29054571
- The results suggest that DC-SIGN SNPs rs7252229, rs4804803, and rs735240 may influence nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk in the Chinese population. PMID: 28694559
- Polymorphism of CD209 and TLR3 genes in populations of North Eurasia PMID: 29368829
- searched for the relationship between single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region of the CD209, IL-10, IL-28 and 32 base pair deletion in CCR5 coding region (Delta 32) with the human predisposition to development of various clinical presentations of tick-borne encephalitis PMID: 28894041
- These results show that DC-SIGN and TLR-4 interactions regulate inflammatory responses in renal tubular epithelial cells and participate in AKI pathogenesis. PMID: 28898406
- 1,25(OH)2D3 suppressed the DCSIGN expression in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected onocytes/macrophages. PMID: 27449998
- Studied the association of CD209 promoter haplotypes with risk of HIV-1 infection in a cohort of Spanish male intravenous drug users (IDU) infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). PMID: 27539513
- Upon gp120 binding to DC-SIGN, cellular NF-kappaB signaling was triggered, leading to the induction of matrix metalloproteinases, which subsequently degraded tight junction proteins and disrupted the blood-retinal barrier integrity. PMID: 27605665
- This study showed that N-glycans on the Gc and Gn surface glycoproteins redundantly support Rift Valley Fever Virus infection via DC-SIGN. PMID: 27223297
- Ligand-driven triggering of TLR-3, -4, NOD2, and DC-SIGN, despite reducing viral replication, markedly increased the capacity of infected dendritic cells to stimulate HIV-specific cytotoxic T-cells. PMID: 28266028
- CD209 polymorphisms could play a role in the susceptibility to Hepatitis C infection as well as interferon treatment response PMID: 27348632
- The activation of B cells enhances DC-SIGN expression and promotes susceptibility of B cells to the avian H5N1 infection. PMID: 28688767
- Binding of common allergens by DC-SIGN on DCs may initiate allergen sensitization of atopic dermatitis or provoke the relapse of atopic dermatitis PMID: 27554335
- These results suggest that DC-SIGN may be an alternative receptor for influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. PMID: 28493491
- The results demonstrate that DC-SIGN among the many hGBP expressed by DCs binds to alpha-fucosylated HMGs, and suggest that such interactions may be important in influencing immune responses in the developing infant. PMID: 26976925
- DC-SIGNR VNTR and DC-SIGN VNTR, were not associated with the risk of pulmonary tuberculosis in a sample of Iranian population PMID: 27309478
- CD209 gene -871A/G is associated with decreased susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis (PT) overall; -336A/G polymorphism is associated with increased susceptibility in Asians and -139G/A polymorphism is not associated with susceptibility to PT PMID: 26722430
- The high-mannose N-linked glycan at N154 of Japanese encephalitis virus E glycoprotein was shown to be crucial for binding to DC-SIGN and subsequent internalization. PMID: 26629951
- Preliminary study suggests that OAS gene cluster and CD209 gene polymorphisms influence the risk of developing clinical symptoms in Chikungunya virus-infected patients. PMID: 26398832
- DC-SIGN can promote the maturation and activation of dendritic cells on recognition of hepatitis B virus, but wild type virus can escape recognition by DC-SIGN to a certain extent with the help of demannosylated modification. PMID: 26133046
- Colorectal mucus can bind the C-type lectin DC-SIGN and block HIV-1 trans-infection of both CCR5 and CXCR4 using HIV-1 strains. PMID: 25793526
- Engagement of sIg in FL cells or normal B cells by anti-Ig led to endocytosis in vitro as expected, but DC-SIGN, even when cross-linked, did not lead to significant endocytosis of sIg PMID: 26194765
- M2 macrophages induced a DC-SIGN-dependent adhesion of highly mannosylated IgM(+) FL B cells and triggered BCR-associated kinase activation. PMID: 26272216
- selective engagement of dendritic cell-SIGN resulting in intracellular persistence in myeloid dendritic cells; however TLR2 activation can overcome autophagy evasion and pathogen persistence in dendritic cells PMID: 25679217
- High-resolution crystal structures of the SIGN-R1 carbohydrate recognition domain show 2 binding sites allowing SIGNR1 to simultaneously bind both immune glycoproteins and microbial polysaccharide components. PMID: 25450767
- Data suggest that serum amyloid P (SAP) activates CD209 DC-SIGN to regulate the innate immune system differently from C-reactive protein (CRP), and that DC-SIGN is a target for antifibrotics. PMID: 26106150
- DC-SIGN directs adaptive T helper cell type-2immunity to fucose-expressing pathogens via an IKKepsilon-CYLD-dependent signalling pathway leading to Bcl3 activation. PMID: 24867235
- Intestinal enterocytes regulate tissue-associated immune compartments under the control of DC-SIGN in inflammatory bowel disease. PMID: 25574091
- Two SNPs of DC-SIGN (rs735239 and rs735240) were associated with susceptibility to fungal keratitis in the northern Han Chinese population. PMID: 25883525
- annexin A2 (ANXA2) on nasopharygeal carcinoma cells is a ligand for DC-SIGN on dendritic cells PMID: 25402728
- Our results suggest that SNPs in DC-SIGN promoter region can be associated to protection for T1DM in the Northeast Brazilian population. PMID: 25092567
- The G allele of rs4804803 is associated with symptomatic dengue (OR 2.3, p=0.08), after accounting for other biological factors including history of infection. PMID: 24911936
- CD209 polymorphisms were responsible for the susceptibility of KD, but not CAL formation and IVIG treatment responsiveness. PMID: 25148534
- Human herpesvirus 8 gB has a high mannose carbohydrate structure and binds to host DC-SIGN in a dose-dependent manner. PMID: 25018023
- Studied the possible association between CD209 rs4804803 (-336 A/G) gene polymorphism and pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) in a sample of Iranian population. PMID: 23751770
- Data obtained suggest that the OAS2 rs1293762 and CD209 rs2287886 SNPs are associated with predisposition to chronic hepatitis C in Russian population. PMID: 24594345
- data shows that immature DENV can infect imDCs through interaction with DC-SIGN, suggesting that immature and partially immature DENV particles may contribute to dengue pathogenesis during primary infection PMID: 24886790
- These findings indicate that the G allele of CD209 promoter region downregulates the spectrum of symptoms during the early acute phase of dengue fever, putatively decreasing the viremia, as suggested in the literature. PMID: 24797508
- Titration of the monomeric DC-SIGN CRD with Le(X) monitored by 2D NMR revealed significant perturbations of DC-SIGN cross-peak positions in (1)H-(15)N heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectra and identified residues near the binding site. PMID: 25121780
- Data indicate that the expression of dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN) decreases and that of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) protein increases in patients with chronic urticaria (CU). PMID: 25001940
- Monocyte-derived dendritic cells could bind efficiently enterovirus 71 viruses through viral binding to DC-SIGN molecule, and these captured-viruses could be transferred to susceptible cells for robust infection. PMID: 24620896
- These data demonstrate a new role for myelin glycosylation in the control of immune homeostasis in the healthy human brain through the MOG-DC-SIGN homeostatic regulatory axis, which is comprised by inflammatory insults that affect glycosylation. PMID: 24935259
- upregulated on dendritic cells in leprosy to induce production of IL-10 PMID: 23816300
- DC-SIGN-mediated virus entry is clathrin dependent. PMID: 23840690
- The results suggest that rs2287886 G/G genotype of CD209 gene is associated with development of dengue requiring hospitalization while A/A genotype of rs735239 is associated with thrombocytopenia in dengue cases. PMID: 23624202
- DC-SIGN has a role in lectin-EGF antibody promotion of regulatory T cells and attenuation of nephrotoxic nephritis PMID: 23627732
- These data reveal that DC-SIGN can facilitate cell entry of Lassa virus in human monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells but that its role seems distinct from the function as an authentic entry receptor reported for phleboviruses. PMID: 23966408
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 3]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 4]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 5]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Isoform 6]: Secreted.; [Isoform 7]: Secreted.; [Isoform 8]: Secreted.; [Isoform 9]: Secreted.; [Isoform 10]: Secreted.; [Isoform 11]: Secreted.; [Isoform 12]: Secreted.
-
组织特异性:Predominantly expressed in dendritic cells and in DC-residing tissues. Also found in placental macrophages, endothelial cells of placental vascular channels, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 monocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1641
OMIM: 604672
KEGG: hsa:30835
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000315477
UniGene: Hs.278694
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-