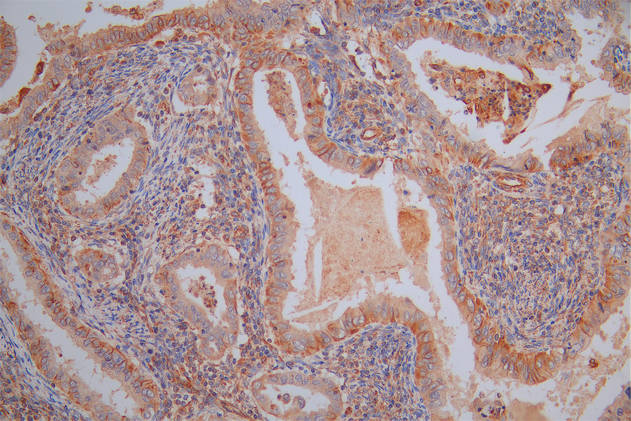
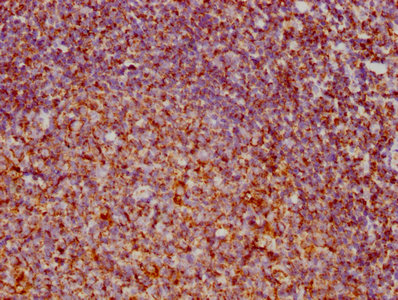
CDT1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA005125GA01HU
-
规格:¥3,900
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q9H211
-
基因名:CDT1
-
别名:CDT 1 antibody; cdt1 antibody; CDT1_HUMAN antibody; Chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1 antibody; DNA replication factor antibody; DNA replication factor Cdt1 antibody; Double parked antibody; Double parked Drosophila homolog of antibody; Double parked homolog antibody; DUP antibody; Retroviral integration site 1 antibody; Retroviral integration site 2 antibody; Retroviral integration site1 antibody; Retroviral integration site2 antibody; RIS 2 antibody; RIS2 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Human CDT1
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Required for both DNA replication and mitosis. DNA replication licensing factor, required for pre-replication complex assembly. Cooperates with CDC6 and the origin recognition complex (ORC) during G1 phase of the cell cycle to promote the loading of the mini-chromosome maintenance (MCM) complex onto DNA to generate pre-replication complexes (pre-RC)(PubMed:14672932). Required also for mitosis by promoting stable kinetochore-microtubule attachments. Potential oncogene.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results show that both Cdc6 and Cdt1, when expressed in a high level, alone or in combination, were significantly associated with poorer survival in the breast cancer patient cohort. In line with this finding, the expression of Cdc6 and Cdt1 was upregulated in breast cancer cells compared to normal breast epithelial cells. Expression of Cdc6 and Cdt1 was significantly higher in ER negative breast cancer. PMID: 28428557
- CDT1, MCM7, and NUDT1 were shown to be up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and provide a more accurate diagnosis than alpha-fetal protein alone. PMID: 29442275
- PPP2R3B codes for the PR70 protein, a regulatory substrate-recognizing subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. PR70 decreased melanoma growth by negatively interfering with DNA replication and cell cycle progression through its role in stabilizing CDC6-chromatin licensing and CDT1 interaction PMID: 27974665
- mismatch repair (MMR) proteins are also involved in the degradation of Cdt1 after ultraviolet irradiation in the G1 phase PMID: 28278049
- Cdt1-binding protein GRWD1 promotes chromatin fluidity by influencing nucleosome structures, e.g., by transient eviction of H2A-H2B, and thereby promotes efficient MCM loading at replication origins. PMID: 27552915
- ATM silencing induced partial reduction in levels of Skp2, a component of SCF(Skp2) ubiquitin ligase that controls Cdt1 degradation. PMID: 24280901
- Protein levels of Geminin and Cdt1 are tightly regulated through the cell cycle, and the Cdt1-Geminin complex likely acts as a molecular switch that can enable or disable the firing of each origin of replication. PMID: 22918581
- These results demonstrate an important role for Cdt1 in human papillomavirus E7-induced rereplication and shed light on mechanisms by which human papillomavirus induces genomic instability. PMID: 23152514
- ATR, activated after DNA damage, phosphorylates Cdt2 and promotes the rapid degradation of Cdt1 after UV irradiation in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. PMID: 23029527
- A lethal phenotype was seen in four individuals with compound heterozygous CDT1 mutations PMID: 22333897
- results support the conclusion that Cdt1 binding to Hec1 is essential for an extended Ndc80 configuration and stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment PMID: 22581055
- Genes in the erythroid differentiation and cell cycle regulation pathways influence interindividual variation in RBC indices. Our results provide insights into the molecular basis underlying variation in RBC traits. PMID: 22560525
- FOXO3 is a binding partner of Cdt1. PMID: 22451935
- The over-expression of geminin and cdt1 may play an important role in pathogenesis of acute leukemia. PMID: 21729526
- Cdt1- and SNF2H-mediated promotion of MCM loading may be biologically relevant for the regulation of DNA replication. PMID: 21937426
- JNK1 phosphorylation of Cdt1 inhibits recruitment of HBO1 histone acetylase and blocks replication licensing in response to stress PMID: 21856198
- findings support a model in which MAP kinase activity in G(2) promotes reaccumulation of a low-activity Cdt1 isoform after replication is complete. PMID: 21930785
- p97 is an essential regulator of DNA damage-dependent CDT1 destruction PMID: 21981919
- Studies suggest that DNA damage-induced ubiquitination or sumoylation of PCNA prevents CRL4Cdt2-dependent degradation by inhibiting binding of Cdt1 to PCNA. PMID: 21846465
- study reports that UBCH8 and UBE2G1 and UBE2G2 cooperate with CRL4Cdt2 in promoting the polyubiquitylation and subsequent degradation of p21 and Cdt1, respectively PMID: 21628527
- Cdt1 is recruited onto damaged sites in G1 phase cells, within seconds of DNA damage induction by ultraviolet laser PMID: 21224399
- Results indicate that the interaction between hCdt1 and hMcm6 through their interacting domains is key for hCdt1 in facilitating the MCM hetero-hexamer to load onto chromatin for replication licensing. PMID: 21099365
- in human cancer cells, RBX1 silencing causes the accumulation of DNA replication licensing proteins CDT1 and ORC1, leading to DNA double-strand breaks, DDR, G(2) arrest, and, eventually, aneuploidy PMID: 21115485
- Cdt1 degradation following UV irradiation occurs rapidly at damaged sites due to PCNA chromatin loading and the recruitment of Cdt1 and CRL4(Cdt2), before DNA damage repair is completed PMID: 20929861
- Cdt1 promote MCM loading in vivo involves the stimulation of large-scale chromatin decondensation to allow access to the underlying DNA substrate. PMID: 20980834
- Data show that the Cdt1:Geminin complex can exist in two distinct forms, a "permissive" heterotrimer and an "inhibitory" heterohexamer. PMID: 19906994
- human CDT1 is essential for DNA replication and chromatin licensing PMID: 11896191
- Results show that geminin, cdt1 and cdc6 are differentially regulated during megakaryocytic differentiation and suggest an active role of cdc6 in endomitosis. PMID: 12429841
- SCF(Skp2)-mediated ubiquitination pathway may play an important role in the cell cycle-dependent Cdt1 degradation in mammalian cells. PMID: 12840033
- Cdt1 function is negatively regulated by the Cdk phosphorylation independent of geminin binding PMID: 14993212
- Cdt1 is phosphorylated and its degradation induced by Cdk2 and Cdk4 PMID: 15004027
- Geminin is both a negative and positive regulator of pre-replicative complex formation in human cells, playing a positive role in allowing CDT1 accumulation in G2-M PMID: 15257290
- in proliferating HeLa cells geminin and Cdt1 are co-expressed during a relatively short time at the G(1)-to-S phase transition; Cdt1 is rapidly degraded early in S phase, but geminin remains bound to the chromatin sites PMID: 15284237
- a Skp2-independent pathway that requires the N-terminal 32 residues of Cdt1 is critical for the degradation of Cdt1 in S phase- this degradation is necessary for the optimum progression of cells through S phase PMID: 15855168
- Cdt1 overexpression contributes to tumorigenecity by causing genomic instability in transgenic p53 knockout mice. PMID: 16261166
- Cdt1 expression is severely downregulated upon differentiation of Caco-2 cells, an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial differentiation. PMID: 16273206
- PCNA is involved in mediating Cdt1 degradation by the Cul4-Ddb1 ligase in response to DNA damage. PMID: 16407242
- Data from several different systems strongly indicate that unregulated Cdt1 overexpression at pathophysiological levels can induce chromosomal damage other than rereplication in non-transformed cells. PMID: 16835273
- L2DTL and PCNA interact with CUL4/DDB1 complexes and are involved in CDT1 degradation after DNA damage. PMID: 16861906
- Results suggest that DDB1 prevents DNA lesions from accumulating in replicating human cells, in part by regulating Cdt1 degradation. PMID: 16940174
- These studies uncover diverse substrate receptors for Cul4 and identify Cdt2 as a conserved component of the Cul4-Ddb1 E3 that is essential to destroy Cdt1 and ensure proper cell cycle regulation of DNA replication. PMID: 16949367
- Findings suggest that the CDT1 838G/A and GMNN 387C/A polymorphisms may not play a major role in the etiology of breast cancer, but CDT1 variant may have a potential role only in genetically susceptible women. PMID: 17029205
- DTL promotes genomic stability through two distinct mechanisms. First, it is an essential component of the CUL4-DDB1 complex that controls CDT1 levels, thereby preventing rereplication. Second, it is required for the early G2/M checkpoint. PMID: 17085480
- we discuss how these dynamic Cdt1-chromatin interactions and the local recruitment of Geminin onto origins of replication by Cdt1 may provide a tight control of the licensing process in time and in space. PMID: 17598984
- hCdt1 and hCdc6 expression promote malignant behavior PMID: 18006835
- Human Cdt1-binding proteins were identified by a combination of Cdt1 affinity chromatography and liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry analysis. PMID: 18162579
- exogenous Cdt1 induces re-replication by de-repressing endogenous Cdt1 through the titration of PCNA and cyclin; Cdt1 lacking the evolutionarily conserved region that interacts with MCM2-7 is capable of inducing re-replication PMID: 18184650
- These results suggested that, at least in vitro, oleic acid-containing cell membranes of the lipid bilayer inhibit Cdt1-geminin complex formation by binding to Cdt1 and thereby liberating Cdt1 from inhibition by geminin. PMID: 18288374
- Cdt1 and Geminin expression is deregulated in human tumor specimens and may represent novel markers useful for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. PMID: 18508524
- rereplication-associated DNA damage triggers Cdt1 and Cdc6 ubiquitination and destruction; this pathway represents an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that minimizes the extent of rereplication PMID: 18617514
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Meier-Gorlin syndrome 4 (MGORS4)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore.
-
蛋白家族:Cdt1 family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 24576
OMIM: 605525
KEGG: hsa:81620
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000301019
UniGene: Hs.122908
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
VDAC1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat