CHEK2 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA187496
-
规格:¥1100
-
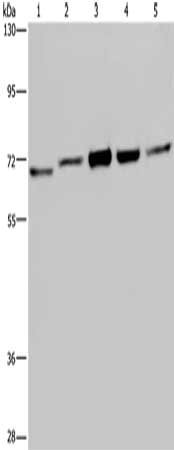
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:O96017
-
基因名:
-
别名:CDS 1 antibody; Cds1 antibody; Cds1 homolog antibody; Checkpoint kinase 2 antibody; Checkpoint like protein CHK2 antibody; CHEK 2 antibody; Chek2 antibody; Chk 2 antibody; CHK2 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe) antibody; CHK2 checkpoint homolog antibody; CHK2_HUMAN antibody; hCds1 antibody; HuCds 1 antibody; LFS 2 antibody; LFS2 antibody; PP1425 antibody; RAD 53 antibody; RAD53 antibody; Rad53 homolog antibody; Serine/threonine protein kinase Chk2 antibody; Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human CHEK2
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:1000-1:2000 WB 1:200-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis in response to the presence of DNA double-strand breaks. May also negatively regulate cell cycle progression during unperturbed cell cycles. Following activation, phosphorylates numerous effectors preferentially at the consensus sequence [L-X-R-X-X-S/T]. Regulates cell cycle checkpoint arrest through phosphorylation of CDC25A, CDC25B and CDC25C, inhibiting their activity. Inhibition of CDC25 phosphatase activity leads to increased inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDK-cyclin complexes and blocks cell cycle progression. May also phosphorylate NEK6 which is involved in G2/M cell cycle arrest. Regulates DNA repair through phosphorylation of BRCA2, enhancing the association of RAD51 with chromatin which promotes DNA repair by homologous recombination. Also stimulates the transcription of genes involved in DNA repair (including BRCA2) through the phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor FOXM1. Regulates apoptosis through the phosphorylation of p53/TP53, MDM4 and PML. Phosphorylation of p53/TP53 at 'Ser-20' by CHEK2 may alleviate inhibition by MDM2, leading to accumulation of active p53/TP53. Phosphorylation of MDM4 may also reduce degradation of p53/TP53. Also controls the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes through phosphorylation of the transcription factor E2F1. Tumor suppressor, it may also have a DNA damage-independent function in mitotic spindle assembly by phosphorylating BRCA1. Its absence may be a cause of the chromosomal instability observed in some cancer cells. Promotes the CCAR2-SIRT1 association and is required for CCAR2-mediated SIRT1 inhibition.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- present study aimed to molecularly define and determine the contribution of two rare, apparently novel CHEK2 Large Genomic Rearrangements, among Greek breast cancer patients. PMID: 29785007
- CHEK2 Y390C mutation induced the drug resistance of triple negative breast cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. PMID: 29761796
- CHEK2 Germ Line Mutation is not associated with Familial and Sporadic Breast Cancer. PMID: 29479983
- Chk1 and Chk2 are significantly expressed in human sperm. In case of sperm DNA damage, up-regulated Chk1 expression may enhance sperm apoptosis and lead to asthenospermia, while increased Chk2 expression may inhibit spermatogenesis and result in oligospermia. PMID: 29658237
- CHK1 and CHK2 and their activated forms are frequently expressed in HGSC effusions, with higher expression following exposure to chemotherapy, and their expression is related to survival. PMID: 29804637
- first article to report that identical germline mutation of CHEK2 gene, p.R180C, exists in both NF1 and NF2 patients. PMID: 29879026
- Results suggested that there was a correlation between mutation of the CHEK2 gene and gastric cancer. PMID: 29067458
- Truncating variants in PALB2, ATM and CHEK2 , but not XRCC2 were associated with increased breast cancer risk. PMID: 28779002
- our results identify a novel link between XRRA1 and the ATM/CHK1/2 pathway and suggest that XRRA1 is involved in a DNA damage response that drives radio- and chemoresistance by regulating the ATM/CHK1/2 pathway. PMID: 29082250
- BRCA2 and CHEK2 play an important role in the genetic susceptibility to urinary tract cancers. PMID: 27632928
- Checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2) inhibition suppressed C-terminal acetylation of p53 and delayed the induction of p53-target genes under heat stress (HS). Chk2 inhibition failed to inhibit apoptosis induced by HS, indicating that Chk2 was dispensable for p53-dependent apoptosis under HS. Chk2 inhibition abrogated G2/M arrest and promoted cell death induced by HS in cells with p53 defects. PMID: 28733865
- The inhibition CHK2 expression reduced detachment-induced apoptosis but did not influence the ability of cells to migrate and invade, which illustrates that CHK2 could inhibit tumor progression and metastatic potential by enhancing anoikis. PMID: 29486482
- These data suggest that the CHEK2 c.1100delC mutation is associated with an increased risk for MBC in the Finnish population. PMID: 28874143
- Data suggest that mediator complex subunit 1 (Med1/TRAP220) is a target for checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2)-mediated phosphorylation and may play a role in cellular DNA damage responses by mediating proper induction of gene transcription upon DNA damage. PMID: 28430840
- this report conceives a novel strategy of Twist1 suppression through Chk2 induction, which prevents metastatic dissemination and promotes premature senescence in p53-defective invasive cancer cells. PMID: 28498365
- we have provided evidence in this study that hepatocarcinogenesis with lagging chromosomes elicits the expression of DNA damage response protein Chk2. Thus, the overexpression of Chk2 and its mislocalisation within structures of the mitotic spindle contribute to sustain cell division and chromosomes missegregation. PMID: 28360097
- PI3K kinase activity is necessary for maintaining 4E-BP1 stability. Our results also suggest 4E-BP1 a novel biological role of regulating cell cycle G2 checkpoint in responding to IR stress in association with controlling CHK2 phosphorylation PMID: 28539821
- Data show that the checkpoint kinase 1/2 (Chk1/Chk2) inhibitor prexasertib (LY2606368) inhibits cell viability in B-/T-ALL cell lines. PMID: 27438145
- Results confirm the predicted multiplicative relationship between CHEK2*1100delC and the common low-penetrance susceptibility variants for breast cancer. PMID: 27711073
- Results show that Chk2 expression is regulated by 14-3-3s in G2-M arrest for non-homologous end joining repair probably via PARP1. PMID: 28087741
- Results indicate that CHEK2 possesses non-cell-autonomous tumor suppressor functions, and present the Chk2 protein as an important mediator in the functional interplay between breast carcinomas and their stromal fibroblasts through repressing the expression/secretion of SDF-1 and IL-6. PMID: 27484185
- variants in CHEK2 were associated with moderate risks of breast cancer. PMID: 28418444
- In this paper, we describe an extension to the BOADICEA model to incorporate the effects of intermediate risk variants for breast cancer, specifically loss of function mutations in the three genes for which the evidence for association is clearest and the risk estimates most precise: PALB2, CHEK2 and ATM PMID: 27464310
- SIAH2 regulates CHK2 basal turnover, with important consequences on cell-cycle control and on the ability of hypoxia to alter the DNA damage-response pathway in cancer cells. PMID: 26751770
- CHECK2 rare variants were associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and prostate cancer. PMID: 27595995
- MCM2-MCM6 complex is required for CHK2 chromatin loading and its phosphorylation to DNA damage response in squamous cell carcinoma cells. PMID: 27964702
- On the basis of analyses of approximately 87,000 controls and patients with breast cancer from population- and hospital-based studies, our best estimate for the relative risk of invasive breast cancer for carriers of the 1100delC mutation in CHEK2, compared with noncarriers, was 2.26 (95% CI, 1.90 to 2.69). PMID: 27269948
- the G2 damage checkpoint prevents stable recruitment of the chromosome-packaging-machinery components condensin complex I and II onto the chromatin even in the presence of an active Cdk1. PMID: 27792460
- data suggest that cancer risks reported for founder mutations may be generalizable to all CHEK2 + s, particularly for breast cancer PMID: 27751358
- K373E mutation of CHK2 in tumorigenesis PMID: 27716909
- Checkpoint kinase 1 and 2 signaling is important for apoptin regulation. PMID: 27512067
- High CHEK2 expression is associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma. PMID: 28373435
- High expression of pCHK2-Thr68 was associated with decreased patient survival (p = 0.001), but was not an independent prognostic factor. Our results suggest that pCHK2-Thr68 and pCDC25C-Ser216 play important roles in breast cancer and may be potential treatment targets PMID: 27801830
- Our study reports the first case of Li-Fraumeni syndrome-like in Chinese patients and demonstrates the important contribution of de novo mutations in this type of rare disease. PMID: 27442652
- hese findings confirmed that 53BP1 loss might be a negative factor for chemotherapy efficacy, promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis by suppressing ATM-CHK2-P53 signaling, and finally inducing 5-FU resistance. PMID: 27838786
- All 14 exons of CHEK2 were amplified and sequenced. PMID: 27510020
- All 14 exons of CHEK2 were amplified. PMID: 27039729
- CHEK2 mutation is associated with Pancreatic Cancer. PMID: 26483394
- Data suggest that nitroxoline induces anticancer activity through AMP-activated kinase (AMPK)/mTOR serine-threonine kinase (mTOR) signaling pathway via checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2) activation. PMID: 26447757
- CHEK2 mutation carriers were characterized by older age, a history of gastric cancer in the family, locally advanced disease, lower histologic grade and luminal B type breast cancer. PMID: 26991782
- The germline mutations of the CHEK2 gene are associated with an increased risk of polycythaemia vera. PMID: 26084796
- loss of CHK2 or PP6C-SAPS3 promotes Aurora-A activity associated with BRCA1 in mitosis PMID: 26831064
- we observed a great degree of heterogeneity amongst the CHEK2*1100delC breast cancers, comparable to the BRCAX breast cancers. copy number aberrations were mostly seen at low frequencies in both the CHEK2*1100delC and BRCAX group of breast cancers. PMID: 26553136
- The aim of this study was to determine the frequency and spectrum of germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 and to evaluate the presence of the CHEK2 c.1100delC allele in these patients. PMID: 26577449
- germ-line CHEK2 mutations affecting protein coding sequence confer a moderately-increased risk of NHL, they are associated with an unfavorable NHL prognosis, and they may represent a valuable predictive biomarker for patients with DLBCL. PMID: 26506619
- Mutations in CHEK2 were most frequent in patients with hereditary non-triple-negative breast cancers. PMID: 26083025
- s propose that CHK2 is a negative regulator of androgen sensitivity and prostate cancer growth, and that CHK2 signaling is lost during prostate cancer progression to castration resistance. PMID: 26573794
- These data provide a rationale for further evaluation of the combination of Wee1 and Chk1/2 inhibitors in malignant melanoma. PMID: 26054341
- Variants at the CHEK2 locus are associated with risk of invasive epithelial ovarian cancer. [meta-analysis] PMID: 26424751
- CHEK2 H371Y mutation carriers are more likely to respond to neoadjuvant chemotherapy than are non-carriers PMID: 25884806
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2 (LFS2); Prostate cancer (PC); Osteogenic sarcoma (OSRC); Breast cancer (BC)
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 2]: Nucleus. Note=Isoform 10 is present throughout the cell.; [Isoform 4]: Nucleus.; [Isoform 7]: Nucleus.; [Isoform 9]: Nucleus.; [Isoform 12]: Nucleus.; Nucleus, PML body. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Note=Recruited into PML bodies together with TP53.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CHK2 subfamily
-
组织特异性:High expression is found in testis, spleen, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes. Low expression is found in other tissues.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 16627
OMIM: 114480
KEGG: hsa:11200
UniGene: Hs.291363
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-