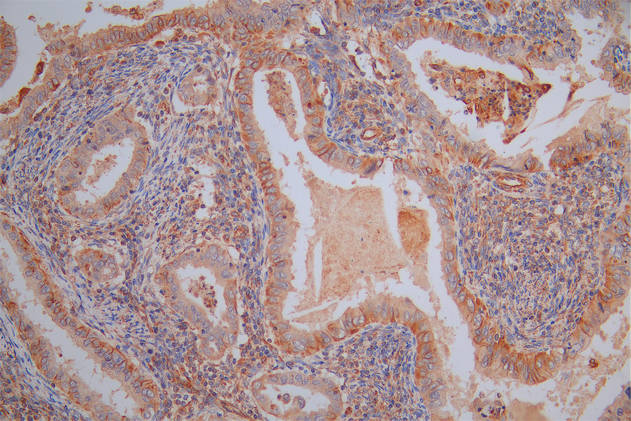
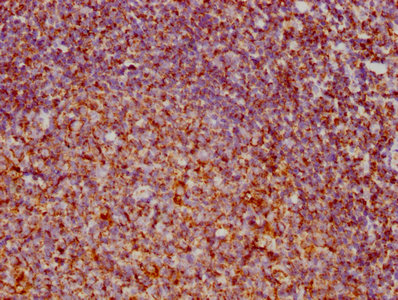
CKAP4 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA005453GA01HU
-
规格:¥3,900
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q07065
-
基因名:
-
别名:63 kDa membrane protein antibody; CKAP 4 antibody; Ckap4 antibody; CKAP4_HUMAN antibody; Cytoskeleton associated protein 4 antibody; Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 antibody; ERGIC 63 antibody; ERGIC63 antibody; MGC99554 antibody; p63 antibody; Transmembrane protein 63kD endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment antibody; Type II transmembrane protein p63 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Human CKAP4
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC,IF
-
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Mediates the anchoring of the endoplasmic reticulum to microtubules.; High-affinity epithelial cell surface receptor for the FZD8-related low molecular weight sialoglycopeptide APF/antiproliferative factor. Mediates the APF antiproliferative signaling within cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Both DKK1 and CKAP4 are frequently expressed in pancreatic and lung tumours, and their simultaneous expression is negatively correlated with prognosis. PMID: 28514532
- CKAP4 has a role as a Dickkopf1 receptor and in pancreatic and lung tumor progression PMID: 27322059
- Human Prostate Basal cell hyperplasia is an expansion of p63. PMID: 28795417
- APF binds specifically to sites within the cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) extracellular domain PMID: 28893174
- The still rudimentary information of how CLIMP-63 fulfills these different roles, what these are exactly and how post-translational modifications control them, will be discussed. PMID: 25849921
- Although VIMP can interact with CLIMP-63 and Syn5L, it does not interact with MT-binding ER proteins (such as Reep1) that shape the tubular smooth ER PMID: 25008318
- revealed that CKAP4 could associate with EGFR at basal status and the complex was reduced upon EGF stimulation, leading to release EGFR into cytoplasm PMID: 24838946
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms in p63 are implicated in the etiology of nonsyndromic bladder-exstrophy-epispadias complex. PMID: 23913486
- Here we report that the combination of p63, a master regulator of epidermal development and differentiation, and KLF4, a regulator of epidermal differentiation, is sufficient to convert dermal fibroblasts to a keratinocyte phenotype. PMID: 23921950
- CKAP4 was correlated with favorable clinical outcome and was an independent predictor for overall survival in hepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients. PMID: 23665508
- p63 positively regulates desmosome adhesion by directly controlling the expression of several desmosome genes, including Dsp, Dsc3 and Dsg1. PMID: 23108156
- CLIMP63 regulates the luminal diameter within the endoplasmic reticulum and may play a role in regulating the formation of endoplasmic reticulum sheets. PMID: 21111237
- The results define CLIMP-63 as a novel protein interactor and regulator of Dicer function, involved in maintaining Dicer protein levels in human cells. PMID: 23047949
- Treatment of airway epitheial cells (AEC) with SP-A, monoclonal antibodies to CKAP4/P63, or CKAP4/P63-specific small interfering RNA decreased the binding of purified alginate exopolysaccharide to AEC. PMID: 22966120
- This study identifies specific changes in skin structural biology and signalling pathways that result from mutant p63 and provides new molecular insight into the AEC syndrome phenotype PMID: 22329826
- CCN2 regulation by antiproliferative factor involves CKAP4 nuclear translocation and binding to the CCN2 promoter. PMID: 22438586
- Tumor markers, p63 and high molecular weight cytokeratin, may be utilised in the distinction between urothelial carcinoma with prostatic stromal invasion and urothelial carcinoma with colonisation of prostatic ducts and acini. PMID: 22406481
- These findings strongly support the routine use of p40 in place of p63 for the diagnosis of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma. PMID: 22056955
- This study found a consistent expression profile and localization analysis of p63 and GM1 in primary keratinocytes and in human epidermal biopsies. PMID: 21820419
- Telomere length in Sjogren syndrome is shorter and associated with lower levels of expression of p63 and nucleostemin than in non-Sjogren syndrome. PMID: 21655359
- Synthetic as-antiproliferative factor inhibits cell proliferation in T24 bladder carcinoma cells via the CKAP4 receptor PMID: 21143984
- Data demonstrate an important role for the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway in intracellular transport of surfactant protein A receptor P63. PMID: 20870746
- p63 binds to an enhancer element in the SHFM1 locus and this element controls expression of DLX6 and DLX5 which are important for limb development. PMID: 20808887
- p63 was not found to be highly sensitive for squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 20184665
- I510T mutation of p63 was detected in both RHS and AEC syndrome patients and mutation of S541 residue can lead to either RHS (S541Y) or AEC syndrome (S541F). PMID: 20156774
- evidence to support the hypothesis that p63 is the functional tPA binding site on VSMC PMID: 12913003
- The ectrodactyly, absence of radius side part palm and split foot malformation are caused by the mutation of base pair at number 665 of the exon 5 of P63. PMID: 15476176
- CLIMP-63-mediated stable anchoring of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to microtubules is required to maintain the spatial distribution of the ER during interphase. PMID: 15703217
- is not responsible for autosomal-dominant amelogenesis imperfecta PMID: 16546853
- cytoskeleton-associated protein 4/p63 (CKAP4/p63), a type II transmembrane receptor, binds with high affinity to APF PMID: 17030514
- Olomoucine, a CDK inhibitor, up-regulates CKAP4, a cytoskeleton-linking membrane protein. PMID: 17975794
- Identification of CKAP4/p63 as a substrate of DHHC2, a putative tumor suppressor. PMID: 18296695
- CK MNF116 and p63 were useful in identifying squamous cell carcinomas with single cell infiltration. PMID: 18333895
- Results substantiate the role of P63 as a lung surfactant protein-A receptor protein localized on the surface of lung type II cells. PMID: 18708633
- DHHC2-mediated palmitoylation of CKAP4 has a role in opposing cancer-related cellular behaviors. PMID: 19144824
- p73 and p63, but not p53, are modulated during the cell cycle PMID: 19861536
- The p62/p63 protein was first identified because it is palmitoylated during mitosis. PMID: 1730740
- Purification and cloning of p62/p63. PMID: 8566419
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Note=Translocates to the perinuclear region upon APF-stimulation.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 16991
KEGG: hsa:10970
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000367265
UniGene: Hs.74368
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-
VDAC1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat