COL8A2 Antibody
-
中文名称:COL8A2兔多克隆抗体
-
货号:CSB-PA068096
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
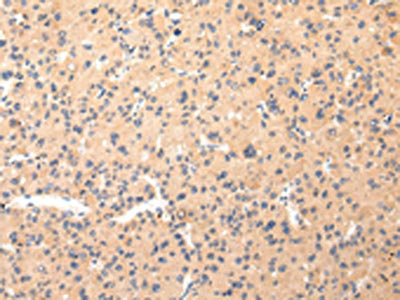
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using CSB-PA068096(COL8A2 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
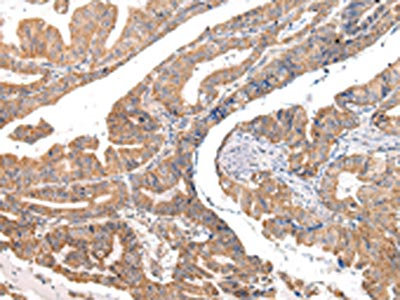
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human esophagus cancer tissue using CSB-PA068096(COL8A2 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P25067
-
基因名:COL8A2
-
别名:COL8A2Collagen alpha-2(VIII) chain antibody; Endothelial collagen antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human COL8A2
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:2000-1:5000 IHC 1:25-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Macromolecular component of the subendothelium. Major component of the Descemet's membrane (basement membrane) of corneal endothelial cells. Also component of the endothelia of blood vessels. Necessary for migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and thus, has a potential role in the maintenance of vessel wall integrity and structure, in particular in atherogenesis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Analysis of SLC4A11, ZEB1, LOXHD1, COL8A2 and TCF4 gene sequences in a multi-generational family with late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy found no evidence for found polymorophisms causing the disease in this specific pedigree. PMID: 27121161
- Peripheral, anterior microcystic corneal edema represents a characteristic aspect of the phenotype associated with the p.(Leu450Trp) substitution in COL8A2, in at least 2 of 3 known affected families worldwide. PMID: 26989952
- No mutations were identified in COL8A2, in neither the late-onset cohort nor the early-onset family, suggesting genetic heterogeneity in this Late-onset Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) family. PMID: 25007886
- mutations in the COL8A2 gene do not contribute to all cases of early-onset early-onset Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy . PMID: 23601356
- Variation in the COL8A2, SLC4A11, and ZEB1 genes is present in only a small fraction of African American cases and as such does not appear to significantly contribute to the genetic risk of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. PMID: 24348007
- Esophageal transcript profiling identified a distinct subset of genes, including COL8A2, in patients with Eosionophilic esophagitis and inherited connective tissue disorders. PMID: 23608731
- Association of central corneal thickness with TCF4 was also significant (p = 6.1x10(-7)), but was abolished with adjustment for FECD grade (p = 0.92). PMID: 23110055
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms in COL8A2 gene is not associated with central corneal thickness in glaucoma. PMID: 22814818
- Report cellular model in which collagen VIII mutations, which clinically result in Fuchs' dystrophy, are associated with abnormal cellular accumulation of collagen VIII. PMID: 22020132
- These data constitute the first report of a heterozygous Q455V mutation of the COL8A2 gene in Korean patients with Fuchs' corneal dystrophy and Q455V may be the causative defect in the development and progression of Korean FECD patients. PMID: 18464802
- COL8A2, SLC4A11 genes may not be responsible for Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy in patients examined in this study. PMID: 20144242
- The R155Q and T502M mutations of COL8A2 may not be the causative defect in the Japanese Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy and posterior polymorphous dystrophy patients examined in this study. PMID: 15175909
- No pathogenic mutations were identified in the COL8A2 gene or in several positional candidate genes in a series of patients, indicating that other genetic factors are involved in the development of this autosomal dominant corneal dystrophy. PMID: 15851557
- A novel pathogenic L450W COL8A2 mutation was identified and its highly distinctive pathology characterized. This indicates that COL8A2 mutations give rise to a rare subtype of FCD (Fuchs corneal dystrophy). PMID: 15914606
- Alpha2(VIII) collagen supported endothelial cell attachment in a dose-dependent manner, with an 18-fold higher affinity for endothelial cells. PMID: 16908762
- Microscopic and electron microscopic examination revealed pathological changes in Descemet's membrane of L450W COL8A2 mutants that were consistent with several-fold increased growth of the extracellular matrix. PMID: 17471329
- description of the phenotype of early-onset Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy in a British family, which is caused by a point mutation (resulting in p.L450W substitution) in COL8A2 PMID: 18024822
- The previously reported mutations in the COL8A2 gene were not found in the 92 samples tested. PMID: 18502986
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Corneal dystrophy, Fuchs endothelial, 1 (FECD1); Corneal dystrophy, posterior polymorphous, 2 (PPCD2)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix, basement membrane.
-
组织特异性:Expressed primarily in the subendothelium of large blood vessels. Also expressed in arterioles and venules in muscle, heart, kidney, spleen, umbilical cord, liver and lung and is also found in connective tissue layers around hair follicles, around nerve b
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2216
OMIM: 120252
KEGG: hsa:1296
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000305913
UniGene: Hs.353001
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-