DISC1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA580837
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
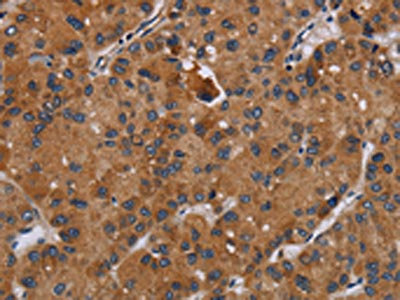
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using CSB-PA580837(DISC1 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
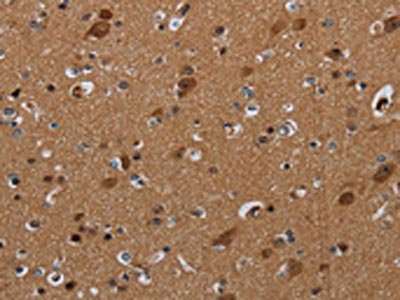
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human brain tissue using CSB-PA580837(DISC1 Antibody) at dilution 1/20, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q9NRI5
-
基因名:DISC1
-
别名:C1orf136 antibody; DISC1 antibody; DISC1_HUMAN antibody; Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 antibody; Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 protein antibody; KIAA0457 antibody; RP4-730B13.1 antibody; SCZD9 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide of Human DISC1
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:1000-1:2000 IHC 1:25-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in the regulation of multiple aspects of embryonic and adult neurogenesis. Required for neural progenitor proliferation in the ventrical/subventrical zone during embryonic brain development and in the adult dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Participates in the Wnt-mediated neural progenitor proliferation as a positive regulator by modulating GSK3B activity and CTNNB1 abundance. Plays a role as a modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Inhibits the activation of AKT-mTOR signaling upon interaction with CCDC88A. Regulates the migration of early-born granule cell precursors toward the dentate gyrus during the hippocampal development. Inhibits ATF4 transcription factor activity in neurons by disrupting ATF4 dimerization and DNA-binding. Plays a role, together with PCNT, in the microtubule network formation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Significant effect of truncated hDISC1 on glial identity cells along the rostrocaudal axis and their oligodendrocytes specification; appearance of hindbrain oligodendrocyte lineage cells and their premature differentiation may affect cerebrocortical organization and contribute to the pathophysiology of SZ. PMID: 28981898
- Study shows that DISC1-mutant cerebral organoids display disorganized structural morphology and impaired proliferation, which is phenocopied by WNT agonism and rescued by WNT antagonism. PMID: 29643329
- Results suggest that DISC1 may be involved in the regulation of lactate production in astrocytes to support neuronal activity and associated behaviors. PMID: 29643356
- This study showed several gene expression profiles, including DISC1, are associated with age-related changes in White Matter disconnectivity. PMID: 28946750
- DISC1 overexpression and misassembly is associated with deficits in long-term memory and attention-related behavior in a tgDISC1 rat model. PMID: 29107702
- Findings showed that NOS1AP (rs348624, rs12742393 and rs1415263), DISC1 (rs821633 and rs1000731), DAOA (rs2391191) and GSK3B (rs6438552) SNPs had no association with development of early-onset schizophrenia; however, our finding suggested statistically significant role of the interaction of NOS1AP, DISC1, DAOA and GSK3B polymorphisms in schizophrenia susceptibility. PMID: 29100974
- Meta-analysis found that DISC1 polymorphisms increased a risk of schizophrenia, especially in the Chinese population. PMID: 29031911
- DISC1 a key molecular lead in psychiatry and neurodevelopment. PMID: 27595595
- The nervous system developmental pathway is a potential pathogenesis of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, among them, the polymorphism of rs3737597 in DISC1 might play some roles. PMID: 27052956
- meta-analysis analyzed the association between DISC1 SNPs rs3738401 and rs821616 with schizophrenia. We found that rs3738401 did not show association with schizophrenia in the Caucasian, Asian or Japanese subgroups PMID: 29410289
- DISC1 affects glioblastoma cell development via mitochondria dynamics partly by down regulation of Drp1. PMID: 27852062
- In combination with molecular modeling, data support predictions regarding the three-dimensional fold of a DISC1 segment as well as its steric arrangement in complex with a llama heavy chain antibody. PMID: 29324815
- s found that three pathways that include the homologs of Drosophila Dys, Trio, and Shot were downregulated by introducing a C-terminal truncated mutant DISC1. PMID: 28472294
- disrupting DISC1/Ndel1 complex formation prolongs mitotic length and interferes with cell-cycle progression in human cells, and it causes cell-cycle deficits of radial glial cells in the embryonic mouse cortex and human forebrain organoids PMID: 29103808
- Study reports sex-specific influence of common disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 variants on volumes of the basal ganglia, the amygdala and on the cortical surface area. PMID: 27369464
- Study found a significant association between the DISC1 gene polymorphism rs6675281 alone, and the combination of rs6675281 and rs821616, and differences in long-term cortical thickness growth in patients with a first-episode of psychosis; and observed an overall difference in cortical thickness, as well as heightened disparities in the frontal and temporal brain regions. PMID: 26209938
- HTT forms a ternary protein complex with the scaffolding protein DISC1 and cAMP-degrading phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) to regulate PDE4 activity. PMID: 28263187
- This theme highlights the importance of understanding precisely how DISC1 can regulate intracellular trafficking, and suggests that a novel approach to the treatment of psychiatric disorders could be provided by targeting this protein and the trafficking machinery with which it interacts. PMID: 27121900
- Findings indicate that disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) and close homolog of L1 may engage in physical and functional interaction in neural development, supporting the notion that DISC1 regulates neurite outgrowth with a receptor belonging to the neural cell adhesion molecules. PMID: 27346367
- DISC1 increased the risk for late-onset Alzheimer's disease in northern Han Chinese population. PMID: 27023224
- Findings suggest that synapse-associated protein of 97-kDa molecular weight and disrupted in schizophrenia 1 contribute to maintaining Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activity within a homeostatic range by regulating glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta phosphorylation. PMID: 27026592
- DISC1 has distinctly folded regions, which are bisected by mental illness-related mutations PMID: 28249940
- These results should contribute to reveal DISC1 physiological function and potential pathogenic role in severe mental illnesses PMID: 27466199
- This population-based case-control study was carried out to determine whether polymorphisms in DISC1 and NRG1 genes could be associated with schizophrenia in the Chinese population. PMID: 27236031
- This study demonstrated that the Increased density of DISC1-immunoreactive oligodendroglial cells in fronto-parietal white matter of patients with paranoid schizophrenia. PMID: 26315603
- The present findings, at least in part, provide some clues for further investigating the association of DISC1 variants with SCZ susceptibility PMID: 26945459
- DISC1 may be involved in sleep regulation PMID: 27354230
- Polymorphisms in DISC1 play a role in vulnerability to opioid dependence in a Polish sample. PMID: 26997180
- Hypoxic preconditioning decreases NF-kappaB activity via DISC1. PMID: 26615762
- It is anterogradely transported to the neurite tips, together with Lis1, and functions in neurite extension via suppression of GSK3beta activity. PMID: 27333658
- DISC1 disruption affects expression of neural cell fate markers and Wnt signaling. PMID: 26299970
- These results uncover an unexpected role for DISC1 in normal beta-cell physiology and suggest that DISC1 dysregulation contributes to T2D independently of its importance for cognition. PMID: 26546129
- DISC1 gene variations may affect the course of cognitive deficits found in patients suffering from the first episode of non-affective psychosis PMID: 26443054
- DISC1 acts as an important regulator of mitochondrial dynamics in both axons and dendrites. PMID: 26553875
- An association was found with DISC1 genetic variants and susceptibility to schizophrenia in a Han Chinese population. PMID: 26162659
- Results with immature neurons from patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder showed common alterations in DISC1 levels and its cellular distribution, cAMP homeostasis, and cell migration PMID: 25620115
- results demonstrate that DISC1 protein levels in human lymphocytes are correlated with the diagnosis of schizophrenia independent of smoking and thus present a potential biomarker PMID: 25218871
- The results of this student findings provide consistent evidence that the DISC1 Ser704Cys polymorphism influences the thalamic-prefrontal circuits in humans. PMID: 24146131
- Transient neonatal disruption of signaling via the C-terminal domain of "disrupted in schizophrenia 1" (DISC1)-a molecule implicated in psychiatric disorders-resulted in a lack of long-term potentiation (LTP) (persistent strengthening of synapses) and experience-dependent potentiation in adulthood. PMID: 26206934
- We demonstrated that Ser704Cys-genotype of DISC1 influences (para)hippocampal structure and functioning the dorsal PFC during executive planning, most prominently in unaffected controls PMID: 25533973
- Our results revealed association between rare haplotypes and affective disorder providing further support to the hypothesis that DISC1 sequence variations may be related to AD susceptibility PMID: 24090488
- These results suggested a possible role of the DISC1 genotype in the early neurodevelopment of human brains, but failed to show its specific role in the neurodevelopmental pathology of schizophrenia. PMID: 25092219
- In Disc1-knockout mice, recombinant human DISC1 regulates the dendritic transport of Itpr1 mRNA by directly interacting with its mRNA. PMID: 25821909
- In the adult mammalian brain DISC1 plays a critical role in neurite outgrowth and neuronal migration, particularly in the hippocampus. PMID: 25043320
- DISC1 knockdown leads to a reduction of VGF in neurons. PMID: 24934694
- These findings highlight the importance of the coordinated expression of DISC1-interactome genes for normal cognitive function. PMID: 24940743
- This study provided that DISC1 genetic variants reveals a relationship with the structure and functional connectivity of the precuneus in schizophrenia. PMID: 24909300
- Expression of the DB7 fusion gene may reduce protein translation to impair brain functions and thereby contribute to the pathogenesis of major psychiatric disorders. PMID: 24908665
- DISC1 forms a complex with dysbindin and increases its stability in association with a reduction in ubiquitylation. PMID: 25635053
- The results reinforce the role of DISC1 in the association of schizophrenia PMID: 23855403
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Schizophrenia 9 (SCZD9)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic density.
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous. Highly expressed in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Also expressed in the temporal and parahippocampal cortices and cells of the white matter.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2888
OMIM: 604906
KEGG: hsa:27185
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000355593
UniGene: Hs.13318
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-