F9 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA574453
-
规格:¥880
-
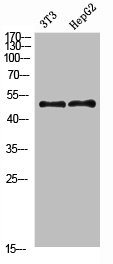
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P00740
-
基因名:
-
别名:Christmas Disease antibody; Christmas factor antibody; Coagulant factor IX antibody; Coagulation factor 9 antibody; Coagulation factor IX antibody; Coagulation factor IXa heavy chain antibody; F9 antibody; FA9_HUMAN antibody; Factor 9 antibody; Factor IX Deficiency antibody; FactorIX antibody; FIX antibody; Haemophilia B antibody; HEMB antibody; MGC129641 antibody; MGC129642 antibody; P19 antibody; Plasma Thromboplastic Component antibody; Plasma thromboplastin component antibody; PTC antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Factor IX at AA range: 412-461
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB,ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-2000 ELISA 1:10000-20000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca(2+) ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- available to predict the inhibitory activity on FIXa. On the basis of pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking, and 3D-QSAR modeling screening, six molecules are PMID: 29724133
- Report induced pluripotent stem cell model characterizing mutated F9 mRNA in hemophilia B. PMID: 28834196
- genetic association studies in cohort of patients in Switzerland: Data suggest that F9 propeptide mutation-associated hypersensitivity to vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants is rare phenomenon; F9 propeptide mutation Ala37Thr confers high sensitivity to warfarin. PMID: 29450643
- Higher FIX antigen levels are associated with incident coronary heart disease in blacks but not in whites; the association of FXI levels with ischemic stroke is slightly attenuated after adjusting for stroke risk factors. PMID: 28393470
- a computational approach was conducted to select suitable location(s) for introducing new N-glycosylation sites into the human coagulation factor IX. PMID: 27356208
- The pathogenic basis for one synonymous mutation (Val107Val) in the F9 gene associated with haemophilia B was determined. PMID: 28007939
- caspase-3 inhibitors also suppressed the attenuation of cell adhesion and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK by EGF-F9. Our data indicated that EGF-F9 activated signals for apoptosis and induced de-adhesion in a caspase-3 dependent manner. PMID: 27129300
- Specific factor IX mRNA and protein features that favor drug-induced readthrough over recurrent nonsense mutations have been reported. PMID: 28196793
- Here we optimize the transient transfection of HEK293T/17 cells for the production of AAV human factor IX in a disposable fixed-bed bioreactor, the iCELLis((R)) Nano (PALL Corporation). PMID: 27229773
- Thus, splicing and protein alterations contribute to define at the molecular level the disease-causing effect of a number of exonic mutations in coagulation FIX exon 5. In addition, our results have a significant impact in the development of splicing-switching therapies in particular for mutations that affect both splicing and protein function PMID: 27227676
- This study confirms the high heterogeneity of molecular defects leading to hemophilia B in Belgium. Six missense variants and 1 in-frame deletion, previously unreported, were predicted to affect FIX protein function. PMID: 27865967
- this study shows that targeted high-throughput sequencing is an effective technique to detect the F9 gene mutations in hemophilia patients PMID: 27292088
- Patient 1 had a 149-kb deletion with breakpoints 90-kb upstream and 30-kb downstream from F9. Patients 2 and 3 showed 273-kb and 1.19-Mb deletions respectively. Patient 4 had two deleted regions: a 1663-bp deletion 1.34-Mb upstream from F9 and a 7.2-Mb deletion including F9. PMID: 26686734
- Factor IX mutation was found in every family: eight had large deletions, three had small deletions (<10 base pair) and 102 had single base pair substitutions (69 missense, 26 nonsense, four splice site and three promoter). PMID: 26612714
- Data suggest that coagulation factor IX (hFIX) minigene containing beta-globin (hBG) introns could represent a particular interest in stem cell-based gene therapy of hemophilias. PMID: 26928674
- miR-128 and miR-125 could help to increase the nonsense-mutant F9 levels by repressing nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. PMID: 27133073
- In 293T cells, the addition of 0.5 mM Ca(+2) and 1 mM Mg(+2) resulted in higher recombinant human Factor IX concentration. SK-Hep-1 cell line proved to be very effective in rhFIX production, and it can be used as a novel biotechnological platform for the production of recombinant proteins. PMID: 26802680
- Mutations were revealed in 56 unrelated patients with hemophilia B in this study by using direct sequencing of factor IX gene functionally important fragments. PMID: 27529981
- The Cys109Tyr F9 mutation found in two siblings and their mother, is a missense mutation previously described in two patients with hemophilia B, but first in Korea. PMID: 25402191
- Differentiation studies demonstrated osteogenic (but not chondrogenic or adipogenic) differentiation capability and efficient FIX secretion of the enclosed MSCs in the fibronectin-alginate suspension culture. PMID: 24564349
- Selective disruption of exosite-mediated regulation of factor IX by heparin and antithrombin can be achieved with preserved or enhanced thrombin generation capacity. PMID: 25851619
- study revealed six unique and unreported changes in the F9 gene among haemophilia B patients from Macedonia and Bulgaria PMID: 25582609
- We conclude that the nature of the F9 gene mutation may be an important risk factor for the development of inhibitors. PMID: 25470321
- Activatable bioengineered FIX molecules with FVIII-independent activity might be a promising tool for improving hemophilia A treatment, especially for patients with inhibitors. PMID: 25224783
- Data suggest that Gly317 plays role in normal catalytic function for FIX/FIXa in the clotting cascade; mutations in Gly317 (G317R, G317E) result in variable severity of bleeding in hemophilia B patients. PMID: 26023895
- repetitive elements and non-B DNA forming motifs contribute to deletion mutations in severe haemophilia B PMID: 24816826
- Various factor IX mutations have been identified in Chinese hemophilia B patients. PMID: 24261420
- 11 FIX gene mutations (8 point mutations, 2 small deletions/insertions, and 1 large deletion), including two novel mutations (exon6 c.687-695, del 9 mer and c.460-461, ins T) were found. PMID: 24656159
- Report oral FIX gene transfer strategy for hemophilia B. PMID: 24679056
- This review discuss structural features of factor XIa that are required for factor IX activation, and the importance of the protease's dimeric structure. [review] PMID: 24759143
- Circulating contact-pathway-activating microparticles together with factors IXa and XIa induce spontaneous clotting in plasma of hematology and cardiologic patients. PMID: 24498168
- Thrombin-mediated, TAFI-dependent down-regulation of fibrinolysis provides new clues for explaining the heightened thrombotic risk in subjects carrying the FIX-Padua mutation. PMID: 24136406
- 87 unique mutations (9 novel) were found in 225 American hemophilia B patients. c.316G>A, c.1025C>T, and c.1328T>A accounted 37.1%. Only those with large deletions and nonsense mutations had inhibitors. PMID: 24375831
- The allosteric mechanism of activation of antithrombin as an inhibitor of factor IXa and factor Xa: heparin-independent full activation through mutations adjacent to helix D. PMID: 24068708
- The results suggest the Omega-loop of FIX binds to an area on FXIa composed of residues from the N-terminus and C-terminus of the A3 domain. These residues are buried in zymogen FXI, and must be exposed upon conversion to FXIa to permit FIX binding. PMID: 23617568
- Report interactive database providing insights into mechanisms of hemophilia B. PMID: 23617593
- Data indicate that five nanofilters can be used interchangeably to yield a high purity Coagulation Factor IX product. PMID: 23410583
- Elevated factor IX activity is associated with an increased odds ratio for both arterial and venous thrombotic events. PMID: 24124147
- Letter: report factor IX activity/antigen ratio in relation to risk of first unprovoked venous thromboembolism. PMID: 23446552
- Mutations at the -5/-6 site (nucleotides -5 and -6 relative to the transcription start site, designated 1) of the F9 promotor account for the majority of hemophilia B Leyden cases and disrupt the binding of ONECUT transcription factors. PMID: 23472758
- Results demonstrate the role of plasticity in regulating FIXa function with respect to discrimination of extended substrate sequences. PMID: 22212890
- structural features within residues of the 39-loop contribute to the resistance of FIXa to inhibition by plasma inhibitors ZPI and TFPI. PMID: 23530052
- Report causative F9 mutations in Argentine families with hemophilia B and determine mutation-associated FIX inhibitor risks. PMID: 23093250
- The effect of surface contact activation and temperature on plasma coagulation with an RNA aptamer directed against factor IXa. PMID: 23054460
- investigated the contribution of the NH2-terminal EGF-domain (EGF1) to the recognition specificity of intrinsic tenase by constructing an EGF1 deletion mutant and characterising the properties of the mutant in kinetic, direct binding and FRET assays PMID: 23014580
- The results suggest that information at the mRNA level as well as conservation of amino acids of coagulation factor IX correlate well with disease severity. PMID: 22639855
- Results indicate that fXIa activates fIX by an exosite- and Ca(2+)-mediated release-rebind mechanism. PMID: 22961984
- Western blotting of plasma from FIX deficient (Hemophilia B) patients revealed traces of full-length FIX for the p.R294* and p.R298* mutations, but not for the p.L103* mutation that triggered major FIX mRNA decay. PMID: 22618954
- factor IX mutations were identified in either the exon or intronic regions in haemophilia B patients in Malaysia; one novel mutation, 6660_6664delTTCTT was identified in siblings with moderate form of haemophilia B PMID: 22870602
- The F9 mutations were heterogenous and the missense mutations were the most prevalent gene defects in Chinese haemophilia B patients. PMID: 22544209
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Hemophilia B (HEMB); Thrombophilia, X-linked, due to factor IX defect (THPH8)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Peptidase S1 family
-
组织特异性:Detected in blood plasma (at protein level). Synthesized primarily in the liver and secreted in plasma.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3551
OMIM: 300746
KEGG: hsa:2158
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000218099
UniGene: Hs.522798
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-