FCGR1A Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA936888
-
规格:¥880
-
图片:
-
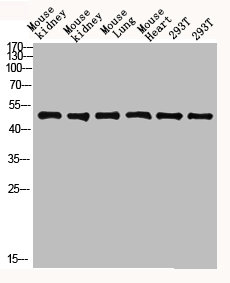
Western blot analysis of mouse-kidney lysate, antibody was diluted at 2000. Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:20000
-
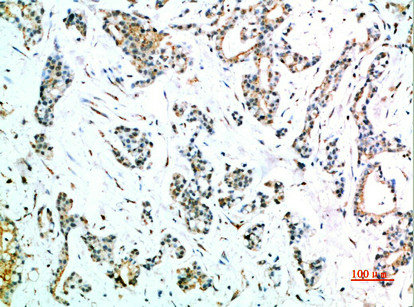
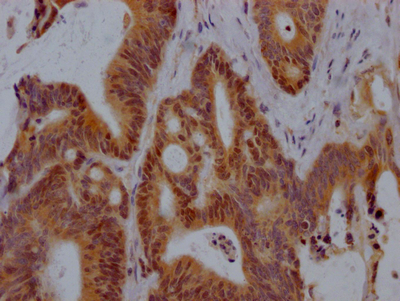
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-stomach-cancer, antibody was diluted at 1:200
-
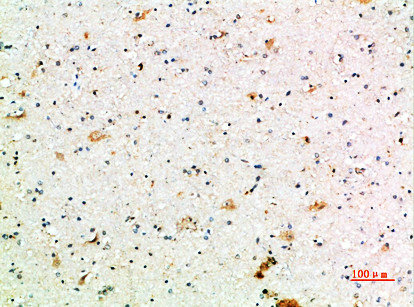
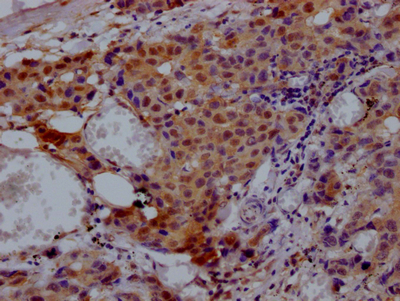
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human-brain, antibody was diluted at 1:200
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P12314
-
基因名:
-
别名:FCGR1A; FCG1; FCGR1; IGFR1; High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I; IgG Fc receptor I; Fc-gamma RI; FcRI; Fc-gamma RIA; FcgammaRIa; CD antigen CD64
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthetic peptide from Human protein at AA range: 230-280
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit serum by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide as Preservative and 50% Glycerol.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-2000 IHC 1:50-300 ELISA 1:10000-20000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:High affinity receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulins gamma. Functions in both innate and adaptive immune responses.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is a better addition to C-reactive protein than CD64 index as a marker for infection in COPD. PMID: 28185443
- FcgammaRI functions as a regulator for immune inflammation via acceleration of NF-kappaB regulating NLRP3 inflammasome signaling PMID: 29920250
- HIV infection and HIV replication are associated with up-regulation of neutrophil CD64. PMID: 27221825
- Neutrophil CD64 distinguished sepsis and non-septic ICU patients. PMID: 28898742
- These results suggest that tyrosine phosphorylation may be critical in FcgammaRI-dependent endocytosis/phagocytosis that may be regulated by LILRB4 by triggering dephosphorylation of key signalling proteins. PMID: 27725776
- neutrophil CD64 elevated in septic neonates PMID: 27578316
- Neutrophil CD64 expression could be a good predictor as an immune parameter with high sensitivity and a negative predictive value for bacteremia in febrile neutropenic patients. PMID: 27348760
- investigated consequences of 3 nonsynonymous SNPs for FcgammaRI; only SNP V39I reduces immune-complex binding of FcgammaRI whereas monomeric IgG binding is unaffected; SNPs I301M and I338T have no influence on monomeric IgG or immune complex binding, but FcRgamma signaling is decreased for both SNPs PMID: 28814603
- Studies show that neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) is a reliable biomarker for diagnosing neonatal sepsis. PMID: 28791853
- Data revealed that Erythema Nodosum Leprosum neutrophils express CD64, presumably contributing to the immunopathogenesis of the disease. PMID: 27556927
- Our findings demonstrate that remarkable CD64 expression during Kawasaki dsease flare-ups may serve as a biomarker for diagnosis. PMID: 27020279
- Both activation by Fcgamma-receptor (FcgammaR) dependent and independent stimuli were inhibited by inactive pepsin, indicating inhibition occurs in a downstream signaling pathway used for releasing granules. PMID: 27368805
- FCGR1A expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing PMID: 28005267
- This study demonstrated that CD64 discriminates between critically ill patients with culture positive and negative sepsis and correlates with severity of disease. However, CD64 index is not a good predictor for 28-day mortality in the critically ill patient. PMID: 27565453
- CD64 seems to be a promising marker of infection in the intensive care setting, with Leuko64 showing a slight advantage PMID: 28097142
- An elevated neutrophil CD64 index was a reliable prognostic biomarker for both short-term and long-term mortality in patients admitted for acute exacerbation of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PMID: 26922686
- Monocyte HLA-DR and neutrophil CD64 expression in critically ill infants with sepsis are related to age and infection. PMID: 26322411
- The three-dimensional structure of a human IgG1 Fc fragment bound to wild-type human Fc-gamma RI is reported PMID: 26527150
- Combinatorial immunophenotypic analyses showed that loss of PTEN expression with concomitant IGFR-1 expression correlated with poor disease-free survival PMID: 22759273
- Early RA patients display increased membrane and soluble CD64 and an impaired FcgammaR function correlating with joint disease activity. PMID: 26406605
- CD64 index, CRP and sCD14-ST served as good parameters to determine possible infection in patients that needed intensive care after major procedures. PMID: 25854904
- GZMA, GBP5 and CD64 genes show promise as a rapid diagnostic markers separating tuberculosis from other pulmonary diseases. PMID: 26025597
- hydrophobic pocket at the surface perfectly suited for residue Leu235 of Fc PMID: 25925696
- we address of monocytes functional status through assessment of the patterns of expression of Fcgamma receptors CD64, CD32, CD16 and CD180 receptor on monocytes from CLL patients and healthy individuals using specific mAbs and flow cytometry. PMID: 25802446
- FcgammaRI levels were found to not be associated with vascular leakage in dengue patients. PMID: 25566870
- The results indicate that conformational plasticity, as well as the openness of the upper CH2 region, is critical for FcgammaR binding and therapeutic effector functions of IgG antibodies. PMID: 26153451
- Neutrophil CD64 is a highly sensitive marker for suspected early-onset sepsis in preterm neonates. PMID: 25033045
- neutrophil CD64 expression tends to be low in the healthy state and increases in patients with advanced cancer even in the absence of active infection PMID: 26147145
- diagnostic accuracy of CD64 index to predict sepsis in critically ill patients PMID: 25324452
- Data show that the recombinant Fc gamma receptors FcgammaRIa, FcgammaRIIa, FcgammaRIIb, FcgammaRIIIa(Phe158/Val158), and FcgammaRIIIb glycosylation is complex and varied between receptors. PMID: 25345863
- Acute alcohol exposure decreased neutrophil CD64 expression in critically ill nontrauma patients. PMID: 24827394
- Data show that IgG4 is capable of transducing signal through FC gamma RI (FcgammaRI). PMID: 25484046
- Data indicate that monoclonal antibody Hu 15C1 simultaneously interacts with both Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) and Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaRI or FcgammaRIIA) at the cell surface. PMID: 25484053
- Data suggest that the specific blocking of immunoglobulin G receptor CD64 by H22(scFv) could be used a possible anti-inflammatory mechanism for potentiating the effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antibodies. PMID: 25517313
- high expression of CD64 is an indicator important in the diagnosis of infection and sepsis. PMID: 25180450
- An elevated neutrophil CD64 index is associated with both mucosal inflammation and an increased risk for clinical relapse in pediatric Crohn disease. PMID: 24788216
- CD64 is expressed on neutrophils and monocytes in periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and cervical adenitis (PFAPA) syndrome during flares PMID: 24623459
- FCGR1A (high-affinity IgG Fc receptor 1 (CD64)) was the only marker expressed at significantly higher levels in participants with active tuberculosis. PMID: 24205913
- Describe biosensing techniques to evaluate the glycosylation pattern of monoclonal antibodies using the extracellular domains of CD64a. PMID: 24810583
- CD64 expression on neutrophils increases significantly in neonates with sepsis and is a useful diagnostic marker for early diagnosis of neonatal infection. PMID: 24463977
- As a surveillance biomarker, neutrophil CD64 detected LOS/NEC 1.5 days before clinical presentation, but at the expense of performing 41% additional sepsis evaluations PMID: 24046202
- Neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) expression was higher in patients with severe sepsis/septic shock (81.2%) and sepsis(78.8%) as compared to those with traumatic brain injury (5.5%) or controls (0.9%, p < 0.0001). PMID: 23452299
- FcgammaRI (CD64) promotes IgG-mediated inflammation, anaphylaxis, and antitumor immunotherapy. PMID: 23293080
- Screening identified 19 amino acid mutations contributing to the thermal stability and production rate of rhFcgammaRI PMID: 22967788
- Data indicate a tool for measuring antibodies triggering activation of FcgammaRIIIA, FcgammaRIIA or FcgammaRI receptors. PMID: 23023090
- Simultaneous quantitative analysis of CD64 and CD35 expression on neutrophils might be useful to distinguish between bacterial and viral infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients. PMID: 22237765
- observations suggest that serum amyloid P, at least in part, uses FcgammaRI and FcRgamma to inhibit fibrocyte differentiation PMID: 22493081
- Data indicate the simultaneous analysis of CD64 together with CD304 (Neuropilin-1) or the combination of CD11b and CD38 was suitable for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)patients with high current activity in synovitis. PMID: 22251373
- Neutrophil CD64 appears to be a better diagnostic test than traditional hematological assays. PMID: 22420242
- Expression of CD64 (FcgammaRI) in skin of patients with acute GVHD. PMID: 21243031
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Stabilized at the cell membrane through interaction with FCER1G.
-
蛋白家族:Immunoglobulin superfamily, FCGR1 family
-
组织特异性:Monocyte/macrophage specific.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3613
OMIM: 146760
KEGG: hsa:2209
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000358165
UniGene: Hs.534956
Most popular with customers
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
VCP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP
Species Reactivity: Human, Rat