FOS Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA042478
-
规格:¥2024
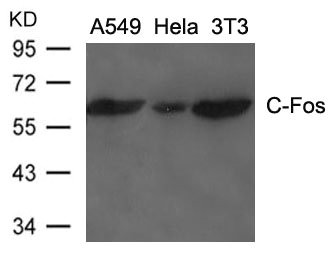
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) FOS Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P01100
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.28~32( S-Y-Y-H-S) derived from Human C-Fos.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Nuclear phosphoprotein which forms a tight but non-covalently linked complex with the JUN/AP-1 transcription factor. In the heterodimer, FOS and JUN/AP-1 basic regions each seems to interact with symmetrical DNA half sites. On TGF-beta activation, forms a multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP1/SMAD-binding site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated signaling. Has a critical function in regulating the development of cells destined to form and maintain the skeleton. It is thought to have an important role in signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. In growing cells, activates phospholipid synthesis, possibly by activating CDS1 and PI4K2A. This activity requires Tyr-dephosphorylation and association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Findings iindicate a human bone tumour defined by mutations of FOS and FOSB. PMID: 29858576
- gammadelta T cells suppressed iDCs osteoclastogenesis by downregulation of the RANK/cFos/ATP6V0D2 signaling pathway. PMID: 30066839
- Mutant cellular AP-1 proteins promote expression of a subset of Epstein-Barr virus late genes in the absence of lytic viral DNA replication. PMID: 30021895
- Low c-fos expression is associated with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PMID: 29582647
- Study demonstrated that c-Fos was highly expressed in most of ovarian epithelial carcinoma cases and was significantly correlated with Lewis y. Also, the results revealed that c-Fos interacted with the FUT1 promoter. Silencing of c-Fos prevented TGF-beta1-induced Lewis y expression. PMID: 29130097
- These findings indicate that the c-Fos/miR-22/MDC1 axis plays a relevant role in DNA repair in terminally differentiated cells, which may facilitate our understanding of molecular mechanism underlying the downregulating DNA repair in differentiated cells. PMID: 28637007
- our results strongly suggest a novel role of c-Fos as a regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell(CSC) reprogramming in Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)cells, which may hold potential as a CSC-directed therapeutic approach to improve HNSCC treatment PMID: 27965308
- High c-fos expression is associated with malignant glioma. PMID: 27602752
- Immunohistochemistry was employed to analyze cFos, cJun and CD147 expression in 41 UCB cases and 34 noncancerous human bladder tissues. PMID: 28358415
- data enforced the evidence that knockdown of c-Fos inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and promoted the apoptosis of OS cells accompanied by altered expression of Wnt2 and Fzd9 PMID: 28665975
- These findings demonstrate an essential role for the ERK pathway together with c-JUN and c-FOS in the differentiation activity of LukS-PV. PMID: 27102414
- novel function of KDM2B in the negative regulation of cell proliferation by assembling an E3 ligase to targeting c-Fos protein degradation that is antagonized by mitogenic stimulations PMID: 26725323
- NF-Y Binding Site Architecture Defines a C-Fos Targeted Promoter Class PMID: 27517874
- c-fos underexpression is associated with Myelodysplastic Syndrome. PMID: 27513856
- miR-101 is downregulated in bladder cancer cells and has an inhibitory role in the regulation of bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion via directly targeting c-FOS. PMID: 27485165
- We found that c-jun or c-fos was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, and coexpression of c-jun/c-fos, or c-jun/c-fos/p53 were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, poor differentiation and clinical stage. PMID: 27558649
- CRAC channel blockade also suppressed Oxo-M-induced c-fos and interleukin-2 expression PMID: 27474128
- The results indicate that 17beta-estradiol-induced endometrial stromal cell invasion is dependent on c-fos-mediated MMP-9 expression. PMID: 26917263
- FOS is a downstream effector of high glucose stimulation in peritoneal mesothelial cells that contributes to TGF-beta1 production. PMID: 26018137
- VEGF-induced endothelial migration is mediated primarily by induction of JunB whereas the promotion of endothelial proliferation by VEGF is mediated by JunB-independent AP-1 family members. PMID: 26860974
- c-Fos can protect against HDAC3 neurotoxicity. PMID: 25592718
- These results indicate that IL-17A enhances COX2 expression and PGE2 production via the p38/c-Fos and JNK/c-Jun signalling pathways in NP cells to mediate intervertebral disc inflammation. PMID: 26988982
- the results of this study suggest that FOS is among the candidate genes of schizophrenia and that changes in the expression of c-Fos protein may contribute to molecular mechanisms of schizophrenia-related alterations in synaptic plasticity. PMID: 25706621
- Increased c-Fos expression is through TRPM3-mediated stimulation of the c-Fos promoter. PMID: 26493679
- A novel AP-1 binding site at -1363 bp of the human TF promoter region was identified. PMID: 26631725
- Simultaneous high expression of ID1 and c-Jun or c-Fos was correlated with poor survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. PMID: 26858249
- miR-146a has a role in targeting Fos expression in human cardiac cells PMID: 26112171
- The translocation causes truncation of the FOS protein, with loss of the transactivation domain, which is thereby a novel mechanism involved in tumorigenesis. PMID: 26173738
- ERK1 and ERK2 regulated the expression of c-Fos and c-Jun proteins in human cervical cancer cells. PMID: 25647783
- O-GlcNAcylation of MLL5beta at T440 residue is critical for MLL5 recruitment to the HPV16/18-long control region through its interaction with AP-1. PMID: 25670814
- The RNA binding complexes NF45-NF90 and NF45-NF110 associate dynamically with the c-fos gene and function as transcriptional coactivators. PMID: 26381409
- Data show that interleukin-1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) forms a complex with c-Fos proto-oncogene protein and activates the interleukin-6 (IL-6) and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) promoters. PMID: 26209639
- Data indicate that deregulation of transcription factor AP-1 and microRNA-21-mediated axis led to an enhanced cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). PMID: 25544773
- These results establish c-Fos homodimers as a novel form of the AP-1 complex that may be an autonomous transcription factor in c-Fos-overexpressing tissues and could contribute to tumor development. PMID: 26303532
- Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates the hepatic AP-1 complex via MAPK-dependent signaling pathways. PMID: 25077945
- co-expression of c-Fos or Fra1 was able to cooperate with TAp73 in potentiating cellular growth, similarly to c-Jun. These data together suggest that TAp73 plays a vital role in activation of AP-1 target genes via direct binding to c-Jun PMID: 26018080
- The light-induced FOS response in melanopsin expressing HEK-293 cells is correlated with melanopsin quantity and dependent on light duration and irradiance. PMID: 24909488
- c-Fos promotes the progression of viral transcription from early to late stages and accelerates viral lytic replication upon sustained ORF45-ERK-RSK activation during the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus lytic life cycle. PMID: 25903346
- By targeting the proto-oncogene Fos, miR-101 is involved in G1-to-S phase transition in cervical cancer cells in vitro. PMID: 24987920
- Data suggest that p38 MAP kinase regulates c-Fos/cellular oncogene fos mRNA stability/decay by affecting state of phosphorylation of ELAVL1/HuR (Hu antigen R). PMID: 25588078
- CDK12 plays an important role in cotranscriptional processing of c-FOS transcripts PMID: 25384976
- We found significant negative correlations regarding the expression of the genes COMT, MAOB, DRD4, DRD5 and FOS, indicating that increased schizotypy coincides with higher levels of dopaminergic dysregulation on the mRNA-level. PMID: 24630741
- results support the proposal that cooperative signaling of both NF-kappaB and AP1 (via p38alpha) amplifies STIM1 expression in ECs and, thereby, contributes to the lung vascular hyperpermeability response during sepsis PMID: 25016017
- SMAR1 has a role in repressing c-Fos-mediated HPV18 E6 transcription through alteration of chromatin histone deacetylation PMID: 25157104
- This study indicates that increased expression of c-Fos, p-c-Jun, members of AP-1 transcriptional factor and p-JNK is associated with neuronal degeneration in the ganglion cell layer of retinas in diabetic patients. PMID: 24073601
- S100A4, FOS and CXCR4, playing a major role in tumor progression and metastasis, are downregulated by sorafenib. PMID: 24378831
- the IL-1beta/p38/AP-1(c-fos)/MMP2 & MMP9 pathway play an important role in metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma PMID: 24479681
- the distinct requirement of NF-kappaB for mouse and human c-fos regulation PMID: 24386331
- c-Fos, a well known AP-1 transcription factor, has emerged as a unique protein with the capacity to associate to specific enzymes of the pathway of synthesis of phospholipids at the endoplasmic reticulum and activate their synthesis. (Review) PMID: 24886961
- Inflammation mediators act through c-Fos to increase VEGF production in peritoneal mesothelium. PMID: 23760290
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Note=In quiescent cells, present in very small amounts in the cytosol. Following induction of cell growth, first localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and only later to the nucleus. Localization at the endoplasmic reticulum requires dephosphorylation at Tyr-10 and Tyr-30.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, Fos subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3796
OMIM: 164810
KEGG: hsa:2353
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000306245
UniGene: Hs.25647
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-