FOXJ1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA979139
-
规格:¥2024
-
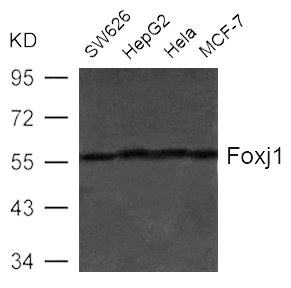
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) FOXJ1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q92949
-
基因名:FOXJ1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.413~417( D-W-A-S-V) derived from Human Foxj1 (HFH4).
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor specifically required for the formation of motile cilia. Acts by activating transcription of genes that mediate assembly of motile cilia, such as CFAP157. Binds the DNA consensus sequences 5'-HWDTGTTTGTTTA-3' or 5'-KTTTGTTGTTKTW-3' (where H is not G, W is A or T, D is not C, and K is G or T). Activates the transcription of a variety of ciliary proteins in the developing brain and lung.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Downregulation and aberrant localization of FOXJ1 may be crucial characteristics of the allergic nasal mucosa. PMID: 29635245
- Our findings provide clues regarding the role of FOXJ1 as a tumor inducer in bladder cancer and an enhancer in glycolysis. Targeting FOXJ1 could be a potential therapeutic strategy in bladder cancer. PMID: 29129693
- Findings demonstrate that increased FOXJ1 contributes to the progression of CRC, which might be associated with the promotion effect of b-catenin nuclear translocation. PMID: 28209947
- In ependymomas and choroid plexus tumours, reduced expression of FOXJ1 and its ciliogenesis programme are markers of poor outcome PMID: 26690880
- Decreased FOXJ1 expression was correlated with clinic stage, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis, and lower FOXJ1 expression independently predicted shorter survival time in gastric carcinoma. PMID: 24809300
- Both protein and mRNA levels of ciliogenesis-associated markers CP110, Foxj1, TAp73 were significantly increased in patients with nasal polyps versus those seen in control subjects and were positively correlated with cilia length PMID: 25201258
- By stimulating ciliogenesis with the transcription factor FOXJ1, it may be possible to maintain close to normal cilia length despite the stress of cigarette smoking. PMID: 24828273
- Nanog-mediated cell migration and invasion involved its regulation of E-cadherin and FOXJ1. PMID: 22945654
- FOXJ1 is an important regulator of cilia gene expression during ciliated cell differentiation, with RFX3 as a transcriptional co-activator to FOXJ1. PMID: 23822649
- FOXJ1 was overexpressed in HCCs and associated with histological grade and poor prognosis. PMID: 22488567
- Rer1p depletion reduced ciliary length and function by increasing gamma-secretase complex assembly and activity and, consequently, enhancing Notch signaling as well as reducing Foxj1a expression. PMID: 23479743
- goblet cells formed in response to IL-13 treatment are in part or wholly derived from progenitors that express the ciliated cell marker, FOXJ1 PMID: 20539013
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified in FOXJ1 and a significant association was found with allergic rhinitis. PMID: 16518568
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Allergic rhinitis (ALRH)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:FOXJ1 family
-
组织特异性:Testis, oviduct, lung and brain cortex.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 3816
OMIM: 602291
KEGG: hsa:2302
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000323880
UniGene: Hs.651204
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-