GGCX Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA181894
-
规格:¥1100
-
图片:
-
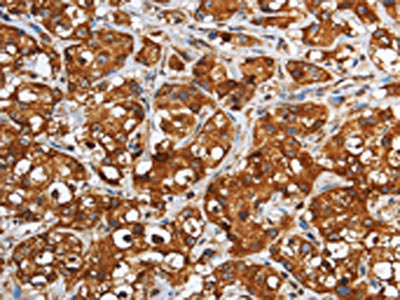
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human breast cancer tissue using CSB-PA181894(GGCX Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
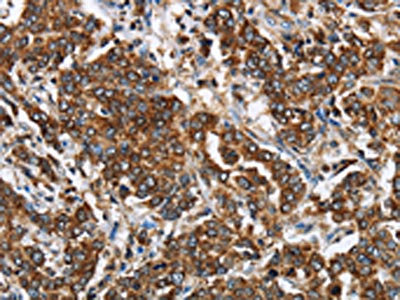
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using CSB-PA181894(GGCX Antibody) at dilution 1/60, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P38435
-
基因名:
-
别名:GGCX; GC; Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase; Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase; Peptidyl-glutamate 4-carboxylase; Vitamin K gamma glutamyl carboxylase
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Fusion protein of Human GGCX
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:2000-1:10000 IHC 1:100-1:300 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Mediates the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of glutamate residues to calcium-binding gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues with the concomitant conversion of the reduced hydroquinone form of vitamin K to vitamin K epoxide.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The risk for ischemic atherothrombotic stroke in patients with the gamma-glutamyl carboxylase T/T genotype was higher than in major C-allele carriers. PMID: 29975826
- unlike the traditional in vitro GGCX activity assay, allows us to assess the functionality of GGCX using its natural protein substrates in a cellular milieu PMID: 27394683
- 2 causative GGCX mutations ( c.1889-6G>A and c.1657delA) from the first reported clinical case of a VKCFD patient. The intronic mutation c.1889-6G>A affects GGCX splicing. Functional characterization of these 2 mutations suggests that truncation of GGCX from its C-terminus affects not only substrate binding but also protein stability. PMID: 28679738
- impact of CYP4F2, ABCB1, and GGCX polymorphisms on bleeding episodes associated with acenocoumarol in Russian patients with atrial fibrillation PMID: 27662649
- this systematic review suggests that there indeed may be genotype-phenotype correlations for GGCX-related phenotypes, which can guide patient counseling and management. PMID: 28125048
- GGCX c.2084+45G polymorphisms has a moderate effect on VKAs dose requirements in Slavic population from Central-Eastern Europe. PMID: 25042728
- Detected are ten mutations in the gamma-glutamyl carboxylase gene in patients with hereditary deficiency of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. PMID: 25151188
- The allele frequency for GGCX 12970 C > G is 1.43 in north Indians and did not have a significant bearing on the maintenance dose of acenocoumarol oral anticoagulant in cardiac valve replacement patients. PMID: 24927344
- GGCX mutation found in families with pseudoxanthoma elasticum with retinitis pigmentosa and cutis laxa. PMID: 24739904
- These findings indicate that individuals carrying the CYP2C19 rs3814637CC or CYP2C9 rs1057910AA or GGCX rs699664AA genotype needed higher warfarin doses in the Chinese population. PMID: 23941071
- In atrial fibrillation population in Xinjiang, patients with CT and TT genotypes in the gamma-glutamyl carboxylase gene rs259251 loci required significantly higher warfarin dose than those with CC genotype. PMID: 24148610
- evaluation of urinary Gla excretion in relation with apo E genotype PMID: 23817635
- study demonstrated the effects of SNP (974G>A) in the GGCX gene on the correlation between dietary vitamin K intake and gamma-carboxylation of serum osteocalcin PMID: 24231026
- there may be no significant association between the low activity and mutation of GGCX in calcium oxalate urolithiasis PMID: 19821094
- Quantitative PCR assays for VKORC1, CYP4F2, GGCX and CALU identified two copies in all populations. PMID: 22188360
- GGCX polymorphism appeared to have an influence over the reduction of undercarboxylated osteocalcin, especially in older women (age >/=65). PMID: 21344298
- no association between haplotypes and venous thrombosis PMID: 21800014
- no effects of genetic variants on maintenance warfarin dose in a multi-ethnic Asian population PMID: 21475774
- Molecular analysis of the gamma-glutamylcarboxylase gene revealed a heterozygous single nucleotide polymorphism, which decreases carboxylase activity and induces VK-dependent coagulation deficiency. PMID: 21704322
- genetic polymorphism affects therapeutic dose of warfarin PMID: 20694283
- The activity and expression of GGCX are decreased in renal tissues of patients with calcium oxolate urolithiasis. PMID: 20332604
- Subtle polymorphisms, including those in GGCX, NQO1, and VKORC1 genes, influence individual susceptibility to the development of atherosclerotic stroke. PMID: 20193673
- Effect of vitamin K-dependent protein precursor propeptide, vitamin K hydroquinone, and glutamate substrate binding on the structure and function of {gamma}-glutamyl carboxylase. PMID: 20716530
- Gene polymorphisms of VKORC1 significantly associated with the variation of interindividual warfarin dose requirement variation, and the effects are different in ethnicities. PMID: 19942260
- characterization of vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase internal propeptide PMID: 12034728
- Cys-99 and Cys-450 form the only disulfide bond in carboxylase PMID: 12963724
- mutations in residues between 393 and 404 in gamma-glutamyl carboxylase cause impaired glutamate binding PMID: 12968027
- A 14-base deletion was found in intron 1 (bases 1056-1069) of the gamma-carboxylase gene. It destroys a reverse palindromic sequence (TTGAGGCAA) of the type often associated with cis-acting elements. This element may regulation the enzyme's expression. PMID: 14567538
- GGCX SNP showed a small but significant effect on warfarin dose. PMID: 15883587
- Crystallization of human GGCX. PMID: 16979907
- report demonstrates the different activities of GGCX between the common genotypes and their association with bone mineral density PMID: 17029979
- In addition to polymorphisms in VKORC1 and CYP2C9, we identified GGCX 8016G>A, resulting in the missense mutation R325Q, as a genetic determinant of warfarin maintenance dose in Japanese patients. PMID: 17049586
- Mass spectrometric results show that the N-linked glycosylation in carboxylase occurs at positions N459, N550, N605, and N627. PMID: 17144668
- identified 37 SNPs in GGCX. The GGCX-12970 SNP had a small, but significant effect, on warfarin maintenance dose PMID: 17764537
- There is no significant association between the polymorphisms in GGCX and the warfarin dose requirement. PMID: 17786385
- GGCX R325Q genotype did not provide significant differences in acenocoumarol dose requirements in patients PMID: 18234294
- A homology model of gamma-glutamyl carboxylase transmembrane domains 2 and 5 suggests that not only do these two domains associate but that transmembrane domain 2 may interact with another transmembrane domain. PMID: 18498174
- analysis of GGCX and ABCC6 mutations in a family with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like phenotypes [case report] PMID: 18800149
- Our findings also confirm GGCX as the second gene locus causing Pseudoxanthoma elasticum PMID: 19116367
- heterozygous carriers of GGCX rs10187424 and rs7568458 had significantly lower percent undercarboxylated osteocalcin relative to either homozygous group. PMID: 19436136
- Polymorphisms in VKORC1 and GGCX are not major genetic determinants of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor activity in Western Germans. PMID: 19652895
- Cys-99 and Cys-450 are free sulfhydryls in the gamma-glutamyl carboxylase active site. The free sulfhydryls were mapped by isolating a native carboxylase-factor IX enzyme substrate complex, modification with NEM and mass spectral mapping. PMID: 11087858
- An activated amine initiates the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation reaction, while the Cys-99 and Cys-450 free sulfhydryls play other important roles in the carboxylase reaction PMID: 15365175
- Quantitative radiolabeled N-ethylmaleimide modification of a carboxylase with all Cys residues changed to Ala supports the identification of Cys-99 and Cys-450 as the free sulfhydryls in the active site. PMID: 15365175
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors 1 (VKCFD1); Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with multiple coagulation factor deficiency (PXEL-MCFD)
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 4247
OMIM: 137167
KEGG: hsa:2677
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000233838
UniGene: Hs.77719
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-