KCNJ1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA012047LA01HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
Western blot
All lanes: KCNJ1 antibody at 2µg/ml
Lane 1: HepG2 whole cell lysate
Lane 2: Hela whole cell lysate
Secondary
Goat polyclonal to rabbit IgG at 1/10000 dilution
Predicted band size: 45, 43 kDa
Observed band size: 45 kDa -
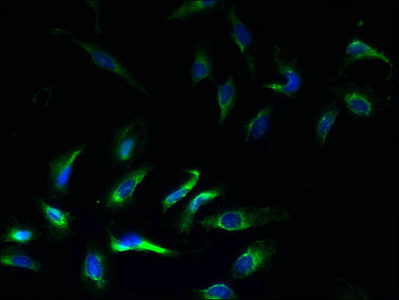
Immunofluorescent analysis of Hela cells using CSB-PA012047LA01HU at dilution of 1:100 and Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) KCNJ1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:P48048
-
基因名:KCNJ1
-
别名:ATP regulated potassium channel ROM K antibody; ATP sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 1 antibody; ATP-regulated potassium channel ROM-K antibody; ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 1 antibody; Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.1 antibody; inwardly rectifying K+ channel antibody; inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 1 antibody; IRK1_HUMAN antibody; KCNJ 1 antibody; KCNJ antibody; Kcnj1 antibody; Kir 1.1 antibody; Kir1.1 antibody; OTTHUMP00000045938 antibody; Potassium channel antibody; Potassium channel inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 1 antibody; potassium inwardly-rectifying channel J1 antibody; ROMK 1 antibody; ROMK 2 antibody; ROMK antibody; ROMK1 antibody; ROMK2 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 1 protein (178-391AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
本页面中的产品,KCNJ1 Antibody (CSB-PA012047LA01HU),的标记方式是Non-conjugated。对于KCNJ1 Antibody,我们还提供其他标记。见下表:
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, WB, IF
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:1000-1:5000 IF 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:In the kidney, probably plays a major role in potassium homeostasis. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. This channel is activated by internal ATP and can be blocked by external barium.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- We replicated the methods in a previous study to detect rare and potentially loss-of-function variants in SLC12A3, SLC12A1, and KCNJ1 reducing blood pressure in variant carriers as compared with noncarriers using whole exome sequencing data. Our study confirmed that SLC12A3, SLC12A1, and KCNJ1 are indeed genes protective of hypertension in the general population. PMID: 30113482
- The presence of ROMK protein was observed in the inner mitochondrial membrane fraction. Moreover, colocalization of the ROMK protein and a mitochondrial marker in the mitochondria of fibroblast cells was shown by immunofluorescence. PMID: 29458000
- Data suggest underlying pathology for some patients with type II Bartter syndrome is linked to stability of ROMK1 in ERAD pathway; using a yeast expression system, cells can be rescued by wild-type (rat) ROMK1 but not by ROMK1 containing any one of four mutations found in (human) type II Bartter syndrome; mutant ROMKs are significantly less stable than wild-type ROMK. (ERAD = endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) PMID: 28630040
- WNK4 is a substrate of SFKs and the association of c-Src and PTP-1D with WNK4 at Tyr(1092) and Tyr(1143) plays an important role in modulating the inhibitory effect of WNK4 on ROMK PMID: 25805816
- knockdown of KCNJ1 in HK-2 cells promoted cell proliferation. Collectively, these data highlight that KCNJ1, low-expressed in ccRCC and associated with poor prognosis, plays an important role in ccRCC cell growth and metastasis PMID: 25344677
- The association between polymorphisms in KCNJ1, SLC12A1, and 7 other genes and calcium intake and colorectal neoplasia risk was studied. PMID: 25165391
- A KCNJ1 SNP was associated with increased FG during HCTZ treatment. PMID: 22907731
- Molecular analysis revealed a compound heterozygous mutation in the KCNJ1 gene, consisting of a novel K76E and an already described V315G mutation, both affecting functional domains of the channel protein. PMID: 23782368
- Findings suggest that 11q24 is a susceptible locus for openness, with KCNJ1 as the possible candidate gene. PMID: 23211697
- no mutation in the KCNJ1 gene, among patients suffering from bartter and Gitelman syndromes PMID: 21631963
- PI3K-activating hormones inhibit ROMK by enhancing its endocytosis via a mechanism that involves phosphorylation of WNK1 by Akt1 and SGK1. PMID: 21355052
- THGP modulation of ROMK function confers a new role of THGP on renal ion transport and may contribute to salt wasting observed in FJHN/MCKD-2/GCKD patients. PMID: 21081491
- KCNJ1 mutations are associated with Bartter syndrome. PMID: 20219833
- ROMK1 is a substrate of PKC and that serine residues 4 and 201 are the two main PKC phosphorylation sites that are essential for the expression of ROMK1 in the cell surface PMID: 12221079
- One disease-causing mutation in the ROMK channel truncates the extreme COOH-terminus and induces a closed gating conformation. PMID: 12381810
- In a heterozgous Bartter syndrome patient, AA exchanges Arg338Stop & Met357Thr in ROMK exon 5 alter the C-terminus of the ROMK protein & can affect channel function. PMID: 12589089
- Findings support the proposed role of ROMK channels in potassium recycling and in the regulation of K+ secretion and present a rationale for the phenotype observed in patients with ROMK deficiency. PMID: 15895241
- NH(2)-terminal phosphorylation modifying a COOH-terminal ER retention signal in ROMK1 could serve as a checkpoint for proper subunit folding critical to channel gating. PMID: 15987778
- ROMK is antagonistically regulated by long and kidney-specific WNK1 isoforms PMID: 16428287
- molecular mechanism for stimulation of endocytosis of ROMK1 by WNK kinases PMID: 17380208
- A novel mutation in KCNJ1 in a Bartter syndrome case diagnosed as pseudohypoaldosteronism. PMID: 17401586
- CD63 plays a role in the regulation of ROMK channels through its association with RPTPalpha, which in turn interacts with and activates Src family PTK, thus reducing ROMK activity. PMID: 18211905
- Members of the Framingham Heart Study were screened for variation in three genes-SLC12A3, SLC12A1 and KCNJ1 causing rare recessive diseases featuring large reductions in blood pressure. PMID: 18391953
- Five polymorphisms in the KCNJ1 gene coding for the potassium channel, ROMK, showed associations with mean 24-hour systolic or diastolic blood pressure. PMID: 18443236
- Multiple intra- and/or intermolecular interactions of WNK1 domains are at play for regulation of ROMK1 by WNK1 in the kidney. PMID: 18550644
- These results confirm the important role of the acidic motif of WNK4 in its protein-protein interaction with the ROMK channel. PMID: 18755144
- In a large cohort of ante/neonatal Bartter syndrome, deafness, transient hyperkalaemia and severe hypokalaemic hypochloraemic alkalosis orientate molecular investigations to BSND, KCNJ1 and CLCNKB genes, respectively. PMID: 19096086
- hydrophobic leucines at the cytoplasmic end of the inner transmembrane helices comprise the principal pH gate of Kir1.1, a gate that can be relocated from 160-Kir1.1b to 157-Kir1.1b. PMID: 19170254
- KS-WNK1 is an important physiological regulator of renal K(+) excretion, likely through its effects on the ROMK1 channel. PMID: 19244242
- These results suggest that the conformation of the cytoplasmic pore in the Kir1.1 channel changes in response to pHi gating such that the N- and C-termini move apart from each other at pHi 7.4, when the channel is open. PMID: 19272129
- Regulation of renal outer medullary potassium channel and renal K(+) excretion by Klotho. PMID: 19349416
- c-Src inhibits SGK1-mediated phosphorylation hereby restoring the WNK4-mediated inhibition of ROMK channels thus suppressing K secretion. PMID: 19706464
- POSH inhibits ROMK channels by enhancing dynamin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis and by stimulating ubiquitination of ROMK channels. PMID: 19710010
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Bartter syndrome 2, antenatal (BARTS2)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Phosphorylation at Ser-44 by SGK1 is necessary for its expression at the cell membrane.
-
蛋白家族:Inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family, KCNJ1 subfamily
-
组织特异性:In the kidney and pancreatic islets. Lower levels in skeletal muscle, pancreas, spleen, brain, heart and liver.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6255
OMIM: 241200
KEGG: hsa:3758
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000376432
UniGene: Hs.527830
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-