KCNJ2 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA003099
-
规格:¥880
-
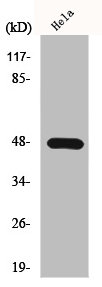
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P63252
-
基因名:KCNJ2
-
别名:KCNJ2; IRK1; Inward rectifier potassium channel 2; Cardiac inward rectifier potassium channel; Inward rectifier K(+ channel Kir2.1; IRK-1; hIRK1; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 2
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human KIR2.1.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:10000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Probably participates in establishing action potential waveform and excitability of neuronal and muscle tissues. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium or cesium.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Twelve tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from the KCNJ2 and KCNJ10 genes were genotyped. Among the 12 examined SNPs, only KCNJ10 rs1186689 was significantly associated with disease susceptibility; the variant T allele conferred a lower risk of developing ASD PMID: 30304693
- data show that hydrocinnamic acid can inhibit the currents of Kir2.1 channel in both excised inside-out and whole-cell patch with the IC50 of 5.21 +/- 1.02 and 10.08 +/- 0.46 mM, respectively. PMID: 28660286
- study confirms the pathogenicity of Kir2.1-52V in 1 patient with long-QT syndrome and also supports the use of isogenic human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes as a physiologically relevant model for the screening of variants of unknown function. PMID: 29021306
- We report a novel KCNJ2 sequence variant (p.Y145C) in a family with diagnosed Andersen-Tawil syndrome. PMID: 29017447
- Combined inhibition of IKr and IKur produced a synergistic anti-arrhythmic effect in both forms of SQT3. In conclusion, this study provides mechanistic insights into atrial proarrhythmia with SQT3 Kir2.1 mutations and highlights possible pharmacological strategies for management of SQT3-linked AF. PMID: 28609477
- Data suggest that an R204A mutation disrupts the characteristic cytoplasmic domain subunit interface salt bridges in Kir2.1 reducing apparent sensitivity of channel activity to ligand PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate). PMID: 28446610
- These findings suggest that KCNJ2 plays an important role in the pathophysiology of Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis in Korean Graves' Disease patients with Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis . PMID: 28008586
- Nav1.5 N-terminal domain binding to alpha1-syntrophin increases membrane density of human Kir2.1, Kir2.2 and Nav1.5 channels PMID: 26786162
- Kir2.1 may participate in macrophage maturation and differentiation, and play a key role in lipid uptake and foam cell formation through modulating the expression of scavenger receptors. PMID: 26689595
- a Korean family with Andersen-Tawil syndrome with a G215D mutation of the KCNJ2 gene revealed by diagnostic exome sequencing, is reported. PMID: 26927354
- Chloroethylclonidine interact with Kir2.1 channels in the cytoplasmic pore. PMID: 26922543
- Variability has been found in a three-generation family with Pierre Robin sequence, acampomelic campomelic dysplasia, and intellectual disability due to a novel approximately 1 Mb deletion upstream of SOX9, and including KCNJ2 and KCNJ16. PMID: 26663529
- Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Sustained Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Show Up-Regulation of KCNN3 and KCNJ2 Genes and CACNG8-Linked Left Ventricular Dysfunction PMID: 26710323
- Results indicate that silencing BKCa (KCa1.1) inhibits cell mobility, while silencing IKir (Kir2.1) increases cell mobility in human cardiac c-kit+ progenitor cells. PMID: 26390131
- No genetic variants were identified in the KCNJ2 gene in this cohort of Chinese thyrotoxic periodic paralysis patients. PMID: 25885757
- Kir2.1 channels exhibit a binding site determined by Cys311 that is responsible for drug-induced increases in inward rectifier Kir2.1 currents. PMID: 25205296
- Kir2.1 channel function is essential during osteoblastogenesis. PMID: 25205110
- Upregulation of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir2.1 (KCNJ2) modulates multidrug resistance of small-cell lung cancer under the regulation of miR-7 and the Ras/MAPK pathway. PMID: 25880778
- propose that Kir2.1 currents control the interspike interval, and predict that blocking Kir2.1 channels increases the action potential frequency, which should augment the rate of insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells PMID: 25727015
- Results show that K346T mutation causes gain of function of the Kir2.1 channels by altering their trafficking and stabilization suggesting that the variant has a combined effect on cardiac rhythm and neuropsychiatric phenotype. PMID: 24794859
- This study demonistrated that KCNJ2 mutations cause a variable phenotype, with dysmorphic features seen in all patients studied, a high penetrance of periodic paralysis in males and ventricular arrhythmia with a risk of sudden cardiac death. PMID: 24861851
- R67Q-Kir2.1 is associated with an adrenergic-dependent clinical and cellular phenotype with rectification abnormality enhanced by increased calcium. PMID: 24561538
- genetic variation in the KCNJ2 gene is a significant locus for thyrotoxic periodic paralysis PMID: 23803013
- Mutations in KCNJ2 has been shown to cause familial atrial fibrillation. PMID: 24460807
- SGK3 is a novel regulator of K(ir)2.1. PMID: 24556932
- Thus multiple proteolytic pathways control Kir2.1 levels at the plasma membrane PMID: 24227888
- This review describes the loss-of-function mutations in KCNJ2 associated with type 1 Anderson-Tawil syndrome. PMID: 24383070
- Despite a severe clinical presentation with a very high rate of ventricular arrhythmias, the arrhythmic prognosis of the Andersen-Tawil syndrome patients with KCNJ2 mutations is relatively good under treatment. PMID: 23867365
- Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS) is a rare inherited multisystem disorder associated with mutations in KCNJ2. PMID: 24047492
- This review compiles clinical, genetic, biochemical, electrophysiological, and molecular evidence that identifies Kir2.1 as a molecular target for FASD development and possibly therapeutic treatment. PMID: 23756044
- Genetic background of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in Japan. PMID: 23595086
- Report pentamidine analogue which specifically blocks cardiac KIR2.1 channel, lengthening action potential duration. PMID: 23625347
- Kir2.1 gene expression inhibits motor neuron activity by resisting depolarization to the action potential threshold. PMID: 23277370
- Energetics and location of phosphoinositide binding in human Kir2.1 channels. PMID: 23564459
- Overexpression of Kir2.1 channel aTTENUATES POSTTRANSPLANTATION PROARRHYthmic risk in myocardial infarction. PMID: 23041574
- Kir2.1 loss of function is additive to the increase in late sodium current, prolonging repolarization and leading to arrhythmia generation in Cav3-mediated long qt syndrome 9. PMID: 23640888
- Identify two novel, heterozygous KCNJ2 mutations (p.N318S, p.W322C) located in the C-terminus of the Kir2.1 subunit in Andersen-Tawil syndrome. PMID: 23644778
- the present observations show that PKB in conjunction with PIKfyve activates Kir2.1 channels. PMID: 23188060
- miR-26 controls the expression of KCNJ2 and may have a role in atrial fibrillation PMID: 23543060
- KCNJ2 mutation in short QT syndrome 3 results in atrial fibrillation and ventricular proarrhythmia. PMID: 23440193
- Mutations of two distant Kir2.1 cytosolic residues, Leu-222 and Asn-251, form a two-way molecular switch that controls channel modulation by cholesterol. PMID: 22995912
- The targeting of the K(ir)2.1 3'UTR at bp 2677-2683 by miR-212 results in a decrease in the red/green fluorescence intensity ratio as determined by automated image analysis confirmed the mutations at this site alter the binding. PMID: 22880819
- The common variant rs7219669 is associated with the TPE interval(EKG). It is a candidate to modify repolarization-related arrhythmia susceptibility. PMID: 22342860
- Expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analysis identified SNPs in the region flanking rs312691 (+/-10 kb) that could potentially affect KCNJ2 expression in thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. PMID: 22863731
- Mutation-positive rates of KCNJ2 were 75% in typical ATS, 71% in cardiac phenotype alone, 100% in periodic paralysis, and 7% in CPVT. PMID: 22589293
- KCNJ2-D172N mutation leads to accelerated ventricular repolarization and QT interval shortening, facilitating initiation and maintenance of re-entrant circuits. PMID: 22308236
- Characterization of a novel, dominant negative KCNJ2 mutation associated with Andersen-Tawil syndrome. PMID: 22186697
- The C-terminal region is a vital motif of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) binding and channel trafficking, and defects in PIP2 binding have been reported to constitute a pathogenic mechanism in ATS.5 PMID: 21875779
- bacterial Kir channels (KirBac1.1 and KirBac3.1) and human Kir2.1 are all inhibited by cholesterol, most likely by locking the channels into prolonged closed states, whereas the enantiomer, ent-cholesterol, does not inhibit these channels PMID: 21559361
- tetrad complex shows the close association of the Kir2.1 cytoplasmic domains and the influence of PSD-95 mediated self-assembly on the clustering of these channels PMID: 21756874
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Long QT syndrome 7 (LQT7); Short QT syndrome 3 (SQT3); Atrial fibrillation, familial, 9 (ATFB9)
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:Inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family, KCNJ2 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Heart, brain, placenta, lung, skeletal muscle, and kidney. Diffusely distributed throughout the brain.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6263
OMIM: 170390
KEGG: hsa:3759
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000243457
UniGene: Hs.1547
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-