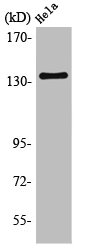-
货号:CSB-PA003200
-
规格:¥880
-
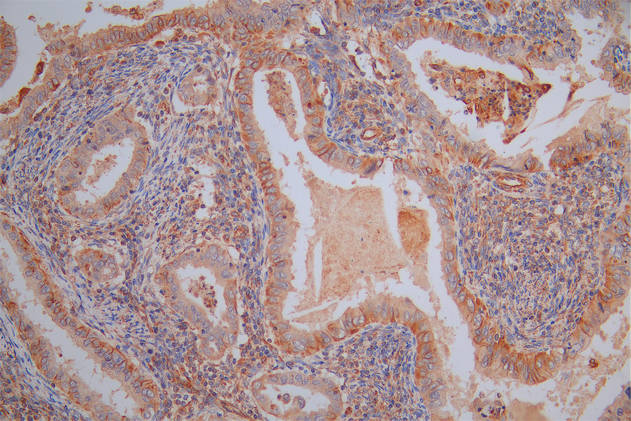
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q12791
-
基因名:
-
别名:subfamily M subunit alpha-1 antibody; BK channel antibody; BKCA alpha antibody; BKCA alpha subunit antibody; BKTM antibody; Calcium-activated potassium channel antibody; Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 antibody; Drosophila slowpoke like antibody; hSlo antibody; K(VCA)alpha antibody; KCa1.1 antibody; KCMA1_HUMAN antibody; KCNMA antibody; KCNMA1 antibody; Maxi K channel antibody; Maxi Potassium channel alpha antibody; MaxiK antibody; SAKCA antibody; SLO alpha antibody; SLO antibody; Slo homolog antibody; Slo-alpha antibody; Slo1 antibody; Slowpoke homolog antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human MaxiKα.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:40000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
引用文献
- The role of potassium current in the pulmonary response to environmental oxidative stress R Canella,Archives of biochemistry and biophysics,2023
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) that mediates export of K(+). It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg(2+). Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca(2+), caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin (IbTx) and charybdotoxin (CTX).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that BKCa channels play important role in cell cycle progression and cell self-renewal in cardiac stem cells. PMID: 29211342
- KCNMA1 mutation causes epilepsy and changes voltage gating but not calcium sensitivity. PMID: 29330545
- Data suggest that large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels, alpha subunit (BK channel) mutations affect the Ca2 +-sensing more than the voltage- sensing mechanism. PMID: 28966112
- An important role of BKCa in proliferation and migration of endometrial cancer HEC-1-B cells. PMID: 29477869
- Study identified a novel tumor suppressive gene, KCNMA1, which is frequently inactivated in gastric cancer because of promoter methylation. KCNMA1 exerts a tumor suppressive function by regulating the PTK2 expression to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway. PMID: 28231797
- High BKCA expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 26993604
- Heme-independent activation of the CFTR channel and the Slo1 BKCa channel by carbon monoxide (CO) may represent two different modes of gating regulation of ion channels by CO. In the case of CFTR, Fe3+ is bound to the R-ICL3 interface.15,16 This interfacial Fe3+ site is formed by traditional coordination ligands such as H950 and H954 from ICL3 and C832 and D836 from the R domain.[Review] PMID: 28474046
- High BK channel is associated with glioblastoma. PMID: 26893360
- Oxidant signaling underlies PKGIalpha modulation of Ca2+ sparks and BKCa in myogenically active arterioles PMID: 27729549
- These results provide further insights into the mechanism of modulation of the different N-terminal regions of the BKCa channel by beta-subunits. PMID: 28750098
- Thiourea derivative, compound 326, stimulates the activity of large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels. PMID: 28075010
- Implicating both KCa1.1 and KCa3.1 channels. PMID: 28028617
- These results identify KCa1.1 channels as crucial regulators of skeletal myogenesis. PMID: 27763639
- Results show that reduced miR-17 expression is correlated with increased expression of KCNMA1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Computational analysis identified KCNMA1 gene is a direct target of miR-17. PMID: 27245839
- These findings provide significant new evidence that BKalphaDeltae2 can modulate cellular responses to physiological stimuli in human chondrocyte and contribute under pathophysiological conditions, such as osteoarthritis. PMID: 27758860
- Our report defines a novel autosomal recessive KCNMA1-related epileptic phenotype that encompasses cerebellar atrophy without paroxysmal dyskinesia, and highlights the sensitivity of the developing brain to both increased and decreased activity of the KCNMA1-encoded channels PMID: 27567911
- A directed proteomic approach discovered the novel interaction of BKCa with Tom22, a component of the mitochondrion outer membrane import system, and the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT). PMID: 27592226
- GSK3b may up-regulate BK channels, an effect disrupted by lithium or additional expression of AKT and possibly participating in the regulation of cell volume and excitability. PMID: 27537208
- MiR-31 represses KCNMA1 expression. PMID: 26386726
- By introducing lanthanide binding tags in the extracellular region of the alpha- or beta1-subunit, we determined (i) a basic extracellular map of the BK channel, (ii) beta1-subunit-induced rearrangements of the voltage sensor in alpha-subunits, and (iii) the relative position of the beta1-subunit within the alpha/beta1-subunit complex. PMID: 27217576
- Suggest that BK channel modulation by auxiliary gamma subunits depends on intra- and/or juxta-membrane mechanisms. PMID: 26009545
- Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid enhanced the expression of malignant genes such as KCNMA1 in lung cancer cells remaining after treatment, creating a more drug-resistant state. PMID: 25796627
- We conclude that arachidonic acid itself selectively activates the beta1-associated BKCa channel, destabilizing its closed state probably by interacting with the beta1-subunit, without modifying the channel voltage sensitivity PMID: 24375290
- The present study revealed that 11,12-EET targets the TRPV4-TRPC1-KCa1.1 complex to induce smooth muscle cell hyperpolarization and vascular relaxation in human LIMAs. PMID: 25511389
- DS-201 selectively targets the pore-forming alpha subunit of human BKCa channels, thus enhancing the channel activities and increasing the subunit expression and trafficking. PMID: 25345746
- Bisphenol A activates BK alpha via an extracellular site and that Bisphenol A-sensitivity is increased by the beta1 subun PMID: 24476761
- show that Slo1 is localized to the sperm flagellum and is inhibited by progesterone. Inhibition of hKSper by progesterone may depolarize the spermatozoon to open the calcium channel CatSper PMID: 24137539
- our results strongly suggest that AT1R regulates BK channels through a close protein-protein interaction involving multiple BK regions and independent of G-protein activation. PMID: 25070892
- hSlo1c associates with Cav-1 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells.A 57-amino acid (966-1022) fragment in hSlo1c was identified to be critical for hSlo1c/Cav-1 interaction. PMID: 24705869
- Recombinant martentoxin selectively blocks KCNMA1/KCNMB4 channels. PMID: 24759175
- HIV and methamphetamine -induced elevated miR-9 lead to suppression of miR-response element-containing splice variants of KCNMA1 PMID: 23508624
- Overexpression of JAK2 in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells significantly enhanced BK channel mRNA and protein abundance. PMID: 24696148
- The reduced KCa1.1 channel protein expression was also observed. PMID: 24260325
- Here we examined the action of docosahexaenoic acid on the Slo1 channel without any auxiliary subunit and sought to elucidate the biophysical mechanism and the molecular determinants of the DHA sensitivity. PMID: 24127525
- N-terminal isoforms of the large-conductance Ca(2)-activated K channel are differentially modulated by the auxiliary beta1-subunit. PMID: 24569989
- Overexpression of KCNMA1, the pore-forming subunit of BK, overcame the reduction of airway surface liquid volume induced by IFN-gamma. PMID: 24414257
- The SLO1 gating ring is not required for voltage activation but is required for Ca2+ and Mg2+ activation. PMID: 24067659
- A novel Cav3-KCa1.1 signaling complex has been identified where Cav3-mediated calcium entry enables KCa1.1 activation over a wide range of membrane potentials. PMID: 23626738
- BK-IS1 (44-113) alpha subunit has been over-expressed using a bacterial system and purified in the presence of detergent micelles for multidimensional heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structural studies. PMID: 23831469
- BK(Ca) as a crucial part of the signaling cascade of LH/hCG in Leydig cells. PMID: 23267835
- These results strongly suggest that cav3 possesses direct interaction with KCa1.1, presumably at the same domain for cav1 binding. PMID: 23237801
- whole-cell current, spontaneous transient outward current, and Ca(2+) sensitivity of BK(Ca) channels are reduced in human vascular smooth muscle cells. This may account for the dysfunction of artery relaxation in primary hypertension. PMID: 23232643
- enhanced expression of KCNMA1 correlates with and contributes to high proliferation rate and malignancy of breast cancer. PMID: 22899999
- Phosphodiesterase blockade causes relaxation of human urinary bladder smooth muscle by increasing transient K(Ca)1.1 channel current activity, hyperpolarizing cell membrane potential, and decreasing the global intracellular Ca(2+). PMID: 22896041
- TM1 of the beta2-subunit physically binds to the transmembrane S1 domain of the alpha-subunit of BK potassium channels PMID: 22710124
- The effects of protein kinase C on Slo surface expression might be indirect; when clustered on hair cell membranes, Slo contributes to increasing amounts of channel clusters on high-frequency responsiveness of hair-cell membranes. PMID: 22538239
- Multiple cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motifs in cytosolic C tail of Slo1 subunit determine cholesterol sensitivity of Ca2+- and voltage-gated K+ (BK) channels. PMID: 22474334
- These studies identify for the first time a central role for beta-catenin in mediating Slo surface expression. PMID: 22194818
- BK(Ca) channels are involved in the response of podocytes to chronic hypoxia via the upregulation of the beta4-subunit. PMID: 22446331
- Cym04 reversibly left-shifts the Slo1 half-activation voltage. It interacts with the S6/RCK linker & mimics site-specific shortening of this passive spring, transmiting force from the cytosolic gating ring structure opening the channel's gate. PMID: 22331907
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia, 3, with or without generalized epilepsy (PNKD3)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, Calcium-activated (TC 1.A.1.3) subfamily, KCa1.1/KCNMA1 sub-subfamily
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Except in myocytes, it is almost ubiquitously expressed.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6284
OMIM: 600150
KEGG: hsa:3778
UniGene: Hs.144795
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-