MEF2A Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA010164
-
规格:¥880
-
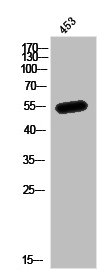
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q02078
-
基因名:
-
别名:ADCAD1 antibody; MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide A (myocyte enhancer factor 2A) antibody; MEF2 antibody; MEF2A antibody; MEF2A_HUMAN antibody; Myocyte enhancer factor 2A antibody; Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A antibody; RSRFC4 antibody; RSRFC9 antibody; Serum response factor like protein 1 antibody; Serum response factor-like protein 1 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human MEF-2 around the non-phosphorylation site of T312.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:20000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcriptional activator which binds specifically to the MEF2 element, 5'-YTA[AT](4)TAR-3', found in numerous muscle-specific genes. Also involved in the activation of numerous growth factor- and stress-induced genes. Mediates cellular functions not only in skeletal and cardiac muscle development, but also in neuronal differentiation and survival. Plays diverse roles in the control of cell growth, survival and apoptosis via p38 MAPK signaling in muscle-specific and/or growth factor-related transcription. In cerebellar granule neurons, phosphorylated and sumoylated MEF2A represses transcription of NUR77 promoting synaptic differentiation. Associates with chromatin to the ZNF16 promoter.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- PCGME1 silencing by small interfering RNA significantly induced early cell apoptosis but this effect was reduced by a miR148a inhibitor. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated a positive regulatory association between MEF2 and PCGEM1, and a reciprocal negative regulatory association between PCGEM1 and miR148a that controls cell apoptosis. PMID: 29749452
- H cordata promotes the activation of HIF-1A-FOXO3 and MEF2A pathways. PMID: 27698266
- in leiomyosarcomas (LMS), this two-faced trait of MEF2 is relevant for tumor aggressiveness. Class IIa HDACs are overexpressed in 22% of LMS, where high levels of MEF2, HDAC4 and HDAC9 inversely correlate with overall survival. The knock out of HDAC9 suppresses the transformed phenotype of LMS cells, by restoring the transcriptional proficiency of some MEF2-target loci PMID: 28419090
- The discovery of a novel MEF2A mutation in a Chinese family with premature CAD/MI suggests that MEF2A may have a significant role in the pathogenesis of premature CAD/MI. PMID: 27221044
- The findings of this study are consistent with MEF2A deregulation conferring risk of formal thought disorder. PMID: 26421691
- Variants in the 3'-UTR of MEF2A are associated with coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. PMID: 26400337
- p38 MAPK is a key regulator of canonical Wnt signaling by promoting a phospho-dependent interaction between MEF2 and beta-catenin to enhance cooperative transcriptional activity and cell proliferation. PMID: 26552705
- Mechanistically, MEF-2 was recruited to the viral promoter (LTR, long terminal repeat) in the context of chromatin, and constituted Tax/CREB transcriptional complex via direct binding to the HTLV-1 LTR. PMID: 25809782
- Our results revealed a link and interaction between MEF2A and miR-143 and suggested a potential mechanism for MEF2A to regulate H(2)O(2) -induced VSMC senescence. PMID: 25655189
- six or seven amino acid deletions and synonymous mutations (147143G-->A)in exon 11 of the MEF2A gene may be correlated with susceptibility to coronary artery disease in the Chinese population PMID: 25366733
- MEF2A is targeted to lysosomes for chaperone-mediated autophagy degradation; oxidative stress-induced lysosome destabilization leads to the disruption of MEF2A degradation as well as the dysregulation of its function PMID: 24879151
- MEF2 transcription factors promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma through TGF-beta1 autoregulation circuitry. PMID: 25087096
- MEF2 is the key cis-acting factor that regulates expression of a number of transcriptional targets involved in pulmonary vascular homeostasis, including microRNAs 424 and 503, connexins 37, and 40, and Kruppel Like Factors 2 and 4. PMID: 25336633
- SENP2 plays an important role in determining the dynamics and functional outcome of MEF2A SUMOylation and transcriptional activation. PMID: 23224591
- This study expands our understanding of the regulation of MEF2 in skeletal muscle and identifies the mAKAP scaffold as a facilitator of MEF2 transcription and myogenic differentiation. PMID: 22484155
- Correlation studies depicted two distinct groups of soft tissue sarcomas: one in which MEF2 repression correlates with PTEN downregulation and a second group in which MEF2 repression correlates with HDAC4 levels. PMID: 24043307
- Mutations in MEF2A exon12 are implicated in pathogenesis of premature coronary artery disease in the Chinese population. PMID: 23461724
- Substitution of any of the TFBS from our particular search of MEF2, CREB and SRF significantly decreased the number of identified clusters. PMID: 23382855
- DNA methylation of genes in retinol metabolism and calcium signaling pathways (P < 3 x 10-6) and with known functions in muscle and T2D including MEF2A, RUNX1, NDUFC2, and THADA decreased after exercise PMID: 23028138
- The rare 21-bp deletion might have a more compelling effect on coronary artery disease (CAD) than the common (CAG)(n) polymorphism, and MEF2A genetic variant might be a rare but specific cause of CAD/myocardial infarction. PMID: 22363637
- MEF2A dominant negative mutation enhanced cell proliferation and cell migration. PMID: 22028303
- [review] In this work, the mechanisms of regulation of MEF2 function by several well-known neurotoxins and their implications in various neurodegenerative diseases are reviewed. PMID: 21741404
- In a cohort of patients undergoing coronary angiography for suspected coronary artery disease the MEF2A exon 11 deletion occurred in 0.09%. PMID: 21450604
- HCVne particles are capable of inducing the recently discovered ERK5 pathway, in a dose dependent way. PMID: 21767578
- MEF2 positively regulates the expression of HZF1. PMID: 21468593
- No Chinese Taiwanese coronary patients had Pro279Leu & 21-bp deletion mutations in exons 7 & 11 respectively. The distribution of the allele frequencies of MEF2A exon 11 CAG repeat (CAG)n polymorphism was similar in both patients and controls. PMID: 19153100
- ZAC1 is a novel and previously unknown regulator of cardiomyocyte Glut4 expression and glucose uptake; MEF2 is a regulator of ZAC1 expression in response to induction of hypertrophy PMID: 20363751
- These results identify MEF2A gene as a susceptibility gene for coronary artery disease. PMID: 19782985
- The current structure suggests that the ligand-binding pocket is not induced by cofactor binding but rather preformed by intrinsic folding. PMID: 20132824
- TGF-beta transcriptionally upregulated MMP-10 through activation of MEF2A, concomitant with acetylation of core histones increasing around the promoter, as a consequence of degradation of the class IIa HDACs. PMID: 19935709
- MEF2A is not a susceptibility gene for coronary artery disease and premature myocardial infarction in the Italian population. PMID: 20031581
- The C-terminal region in MEF2A contains signals that are necessary to localize the histone deacetylase 4/MEF2 complex to the nucleus. PMID: 11792813
- identification of two aspects of MEF2 regulation, a highly conserved phosphoacceptor site and an indirect pathway of regulation by p38 MAPK PMID: 12586839
- MEF2a binding to HDAC5 is inhibited by HDAC5 when bound to Ca(2+)/calmodulin PMID: 12626519
- GEF and MEF2A have roles in regulating the GLUT4 promoter PMID: 14630949
- an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease/myocardial infarction (adCAD1) that is caused by the deletion of seven amino acids in transcription factor MEF2A is described PMID: 14645853
- Activation of MEF2 in skeletal muscle is regulated via parallel intracellular signaling pathways in response to insulin, cellular stress, or activation of AMPK. PMID: 14960415
- MEF2A is a candidate for chronic diaphragmatic hernia; it maps to chromosome 15. PMID: 15057983
- myogenin and myocyte enhancer factor-2 expression are triggered by membrane hyperpolarization during human myoblast differentiation PMID: 15084602
- promoter- and cell-specific functional interaction between PITX2 and MEF2A PMID: 15466416
- Myocyte enhancer factor 2 activates P2 promoter of the AbetaH-J-J locus. PMID: 15798210
- One disease-causing gene for CAD and MI has been identified as MEF2A, which is located on chromosome 15q26.3 and encodes a transcriptional factor with a high level of expression in coronary endothelium. PMID: 15811259
- A conserved pattern of alternative splicing in vertebrate MEF2 (myocyte enhancer factor 2) genes generates an acidic activation domain in MEF2 proteins selectively in tissues where MEF2 target genes are highly expressed. (MEF2) PMID: 15834131
- Results suggest that MEF2A mutations are not a common cause of coronary artery disease (CAD) in white people and argue strongly against a role for the MEF2A 21-bp deletion in autosomal dominant CAD. PMID: 15841183
- The MEF2A mutations may account for up to 1.93% of the disease population; thus, genetic testing based on mutational analysis of MEF2A may soon be available for many coronary artery disease/myocardial infarction patients. PMID: 15861005
- The genetic risk factor for myocardial infarction could be the result of a reduced transcriptional activity on MEF2A with 279Leu. PMID: 15958500
- MEF2/HAND1 interaction results in synergistic activation of MEF2-dependent promoters, and MEF2 binding sites are sufficient to mediate this synergy PMID: 16043483
- Binding of this protein to DNA resulted in significant changes of its diffusion. PMID: 16314281
- data show a dosage-dependent cardiomyopathic phenotype and a progressive reduction in ventricular performance associated with MEF2A or MEF2C overexpression PMID: 16469744
- Study demonstrates that human intestinal cell BCMO1 expression is dependent on the functional cooperation between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and myocyte enhancer factor 2 isoforms. PMID: 16504037
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Coronary artery disease, autosomal dominant, 1 (ADCAD1)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:MEF2 family
-
组织特异性:Isoform MEF2 and isoform MEFA are expressed only in skeletal and cardiac muscle and in the brain. Isoform RSRFC4 and isoform RSRFC9 are expressed in all tissues examined.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6993
OMIM: 600660
KEGG: hsa:4205
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000346389
UniGene: Hs.268675
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-