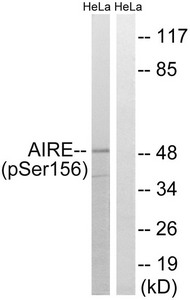
Phospho-AIRE (Ser156) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA217298
-
规格:¥2454
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) AIRE Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O43918
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Serine156 P-G-S(p)-Q-L) derived from Human AIRE.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor playing an essential role to promote self-tolerance in the thymus by regulating the expression of a wide array of self-antigens that have the commonality of being tissue-restricted in their expression pattern in the periphery, called tissue restricted antigens (TRA). Binds to G-doublets in an A/T-rich environment; the preferred motif is a tandem repeat of 5'-ATTGGTTA-3' combined with a 5'-TTATTA-3' box. Binds to nucleosomes. Binds to chromatin and interacts selectively with histone H3 that is not methylated at 'Lys-4', not phosphorylated at 'Thr-3' and not methylated at 'Arg-2'. Functions as a sensor of histone H3 modifications that are important for the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Mainly expressed by medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs), induces the expression of thousands of tissue-restricted proteins, which are presented on major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) and MHC-II molecules to developing T-cells percolating through the thymic medulla. Also induces self-tolerance through other mechanisms such as the regulation of the mTEC differentiation program. Controls the medullary accumulation of thymic dendritic cells and the development of regulatory T-cell through the regulation of XCL1 expression. Regulates the production of CCR4 and CCR7 ligands in medullary thymic epithelial cells and alters the coordinated maturation and migration of thymocytes. In thimic B-cells, allows the presentation of licensing-dependent endogenous self-anitgen for negative selection. In secondary lymphoid organs, induces functional inactivation of CD4(+) T-cells. Expressed by a distinct bone marrow-derived population, induces self-tolerance through a mechanism that does not require regulatory T-cells and is resitant to innate inflammatory stimuli.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- this review shows the role of AIRE in peripheral tolerance PMID: 30255105
- AIRE contributes to autoimmunity in more common organ-specific autoimmune disorders than autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type-1 (Review) PMID: 27504588
- Rs3761389 variant is associated with the susceptibility of myasthenia gravis in Chinese patients. PMID: 28262400
- Our findings suggest that AIRE does not have a role in the induction and function of monocyte-derived tolerogenic DC in humans, but these findings do not exclude a role for AIRE in peripheral tolerance mediated by other cell types. PMID: 26912174
- Estrogen induces decreased thymic AIRE expression by epigenetic modifications through increased number of methylation sites within the AIRE promoter.[review] PMID: 28240208
- Whole exome sequencing followed by Sanger sequencing revealed that all three subjects affected by hypoparathyroidism were compound heterozygous for two previously reported mutations, c.967_979delCTGTCCCCTCCGC:p.(L323SfsX51) and c.995+(3_5)delGAGinsTAT, in AIRE, which encodes the autoimmune regulator protein that is defective in autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1 (APS-1). PMID: 28323927
- Aire exerts multi-faceted autoimmune control that extends to a population of innate-like T cells. PMID: 27851927
- Homozygote Mutation in the AIRE gene is associated with APECED syndrome. PMID: 28222032
- the presence of AIRE can trigger molecular events leading to an altered chromatin landscape and the enhanced transcription of low-expressed genes PMID: 28242760
- These data are the first to identify AIRE expression in breast cancer and an association with prognosis. PMID: 27753538
- AIRE, which is phosphorylated on two specific residues near its N terminus, then binds to the F-box protein 3 (FBXO3) E3 ubiquitin ligase. In turn, this SCF(FBXO3) (SKP1-CUL1-F box) complex ubiquitylates AIRE, increases its binding to the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), and potentiates its transcriptional activity. PMID: 27365398
- this paper shows that genetic polymorphisms in AIRE do not contribute to the Graves' disease in Spain PMID: 27266815
- This study supports the notion that AIRE mutation could specifically affect human insulin gene expression in thymic epithelial cells through INS-VNTR and subsequently induce either insulin tolerance or autoimmunity. PMID: 27048654
- androgen control of an intrathymic Aire-mediated tolerance mechanism contributes to gender differences in autoimmunity. PMID: 27072778
- results indicate that in females, estrogen induces epigenetic changes in the AIRE gene, leading to reduced AIRE expression under a threshold that increases female susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. PMID: 26999605
- The rs2075876 and rs760426 loci of the AIRE gene are associated with increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis among ethnic Han Chinese from ShaanXi. PMID: 27264825
- The novel mutation of c.622G>T (p.G208W) in AIRE gene is associated autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type I. PMID: 26903062
- AIRE-655GAIRE-230T haplotype could dramatically alter AIRE transcription. PMID: 25978041
- In the current study, we demonstrate that AIRE activates the expression of transiently transfected luciferase reporters that lack defined promoter regions, as well as intron and poly(A) signal sequences. PMID: 26607109
- These results suggest that Aire expression is inherent to all medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) but may occur at particular stage(s) and/or cellular states during their differentiation, thus accounting for the broad impact of Aire on the promiscuous gene expression of mTECs. PMID: 26503950
- Keratopathy can be an early and severe manifestation of APS1, which contributes to the global prognosis of the disease. Its mechanisms remain to be elucidated. PMID: 26114819
- Molecular characterization of the functional domains of Aire has revealed multiple binding partners that assist Aire's function in altering gene transcription and chromatin remodeling. PMID: 26579596
- study identified a novel AIRE mutation which alters the intracellular location and transcription activity of AIRE, and has implications in the pathogenesis of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy PMID: 25064028
- genetic polymorphism is associated with development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in China PMID: 25637666
- Data indicate that autoimmune regulator Aire mRNA transcripts are regulated in a keratin 17 (K17) dependent manner in skin tumor keratinocytes. PMID: 26168014
- The study reports a new homozygous splicing mutation in the AIRE intron 5 acceptor (c.653-1G>A, in two patients of a consanguineous Spanish family with different phenotypes of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. PMID: 24988226
- disease-causing mutations are more common than previously appreciated and cause more variable autoimmune phenotypes PMID: 26084028
- Deficiency of AIRE partner, PRKDC, can present as an inflammatory disease with organ-specific autoimmunity, suggesting a role for PRKDC in regulating autoimmune responses and maintaining AIRE-dependent tolerance in human subjects. PMID: 25842288
- The disease is caused by a homozygous mutation in the AIRE gene mapped to chromosome 21q22.1. PMID: 25367057
- Our findings suggest that the AIRE gene is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the Spanish population PMID: 23320549
- a model in which lysines acetylation increases the stability of AIRE in the nucleus. PMID: 25158603
- Mutations in the AIRE gene is associated with polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type I. PMID: 24945421
- APECED was confirmed by molecular analysis of AIRE gene, which showed two mutations. PMID: 24703644
- The findings provide strong evidence for the fundamental role of AIRE and promiscuous gene expression, namely, central tolerance, in the predisposition to autoimmunity of Down syndrome individuals. PMID: 25217160
- the increased AIRE gene dose in DS could contribute to an autoimmune phenotype through multiple AIRE-mediated effects on homeostasis and function of thymic epithelial cells that affect thymic selection processes. PMID: 25038256
- AIRE rs2075876 and rs760426 polymorphisms were involved in the genetic background of rheumatoid arthritis in the Chinese population. PMID: 24170308
- these findings implicate AIRE in the promiscuous expression of thyroid proteins in fibrocytes. PMID: 24708100
- We demonstrated the importance of Aire's interaction with the ATF7ip-MBD1 protein complex in maintaining central tolerance PMID: 24464130
- Studies indicate that the plant homeodomain 2(PHD2) of autoimmune regulator (AIRE) protein plays a critical role in the activation of gene transcription. PMID: 24275490
- Eight patients were identified with APECED and all patients were found to be homozygous for the c.964dell3 mutation. A wide clinical variation is apparent within APECED syndrome. PMID: 23620608
- in patients with autoimmune non-APECED polyendocrinopathies, heterozygous mutations of the AIRE gene were not detected; however a trend of association was observed, heterozygous polymorphisms S278R and IVS9+6G>A were detected in patients without statistically significant prevalence than in controls PMID: 23643663
- it was concluded that miR-220b inhibited the AIRE gene translation through the 3'UTR region of AIRE gene, indicating that miR-220b could serve as a regulator for human AIRE gene translation. PMID: 23954874
- There are a limited number of cases linking autoimmune retinopathy with a mutation in the AIRE gene. PMID: 23697860
- These findings reveal a mutual interdependence of miRNA and Aire in the regulation of promiscuous gene expression in purified mouse and human thymic epithelial cells PMID: 23589212
- functional characterization of the alternatively spliced AIRE mutation that may explain the pathogenetic role in APS-1 PMID: 23342054
- Alterations of the autoimmune regulator transcription factor and failure of central tolerance: APECED as a model. PMID: 23256763
- AIRE gene mutations are associated with autoimmune-polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal-dystrophy in patients from Apulia and Sicily. PMID: 22104652
- [review] The C terminus of AIRE does not share obvious homology with functional domains in other proteins but is highly conserved between human and mouse AIRE proteins, serving as a transcriptional activation domain. PMID: 23456700
- Data indicate that PHD2 domain is required for Aire to interact with a subset of its partners PMID: 23319629
- Mutations in heterozygosity of the AIRE gene are not associated with major findings of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis-ectodermal-dystrophy (APECED), also known as autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. PMID: 22024611
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 1, with or without reversible metaphyseal dysplasia (APS1)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Expressed at higher level in thymus (medullary epithelial cells and monocyte-dendritic cells), pancreas, adrenal cortex and testis. Expressed at lower level in the spleen, fetal liver and lymph nodes. In secondary lymphoid organs, expres
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 360
OMIM: 109100
KEGG: hsa:326
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000291582
UniGene: Hs.129829
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-