Phospho-AURKA (Thr288) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA959104
-
规格:¥2454
-
图片:
-
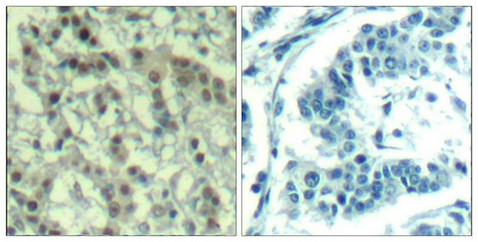
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue using Aurora A(Phospho-Thr288) Antibody(left) or the same antibody preincubated with blocking peptide(right).
-
Western blot analysis of extracts from HT29 cells, treated with Hydroxyurea or calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP), using Aurora A (phospho-Thr288) Antibody.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) AURKA Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O14965
-
基因名:AURKA
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of threonine 288 (R-T-T(p)-L-M) derived from Human Aurora A.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 IHC 1:50-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Mitotic serine/threonine kinase that contributes to the regulation of cell cycle progression. Associates with the centrosome and the spindle microtubules during mitosis and plays a critical role in various mitotic events including the establishment of mitotic spindle, centrosome duplication, centrosome separation as well as maturation, chromosomal alignment, spindle assembly checkpoint, and cytokinesis. Required for normal spindle positioning during mitosis and for the localization of NUMA1 and DCTN1 to the cell cortex during metaphase. Required for initial activation of CDK1 at centrosomes. Phosphorylates numerous target proteins, including ARHGEF2, BORA, BRCA1, CDC25B, DLGP5, HDAC6, KIF2A, LATS2, NDEL1, PARD3, PPP1R2, PLK1, RASSF1, TACC3, p53/TP53 and TPX2. Regulates KIF2A tubulin depolymerase activity. Important for microtubule formation and/or stabilization. Required for normal axon formation. Plays a role in microtubule remodeling during neurite extension. Also acts as a key regulatory component of the p53/TP53 pathway, and particularly the checkpoint-response pathways critical for oncogenic transformation of cells, by phosphorylating and destabilizing p53/TP53. Phosphorylates its own inhibitors, the protein phosphatase type 1 (PP1) isoforms, to inhibit their activity. Necessary for proper cilia disassembly prior to mitosis. Regulates protein levels of the anti-apoptosis protein BIRC5 by suppressing the expression of the SCF(FBXL7) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase substrate adapter FBXL7 through the phosphorylation of the transcription factor FOXP1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Cells lacking ARID1A show enhanced AURKA transcription, which leads to the persistent activation of CDC25C, a key protein for G2/M transition and mitotic entry. PMID: 30097580
- AURKA protein was overexpressed in nearly all dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans tissues and AURKA protein levels significantly correlated with CD34 protein levels. PMID: 29682829
- Aurora A-dependent phosphorylation of CENP-A at the inner centromere protects chromosomes against tension-induced cohesion fatigue until the last kinetochore is attached to spindle microtubules. PMID: 29760389
- Aurora A kinase regulates kinetochore-microtubule dynamics of metaphase chromosomes, and Hec1 S69, a previously uncharacterized phosphorylation target site in the Hec1 tail, is a critical Aurora A substrate for this regulation. PMID: 29187526
- Upon phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate treatment, THP-1 cells differentiated into monocytes by down-regulating AURKA, resulting in a reduction in H3S10 phosphorylation. The AURKA inhibitor alisertib accelerates the expression of the H3K27 demethylase KDM6B, dissociating AURKA and YY1 from the KDM6B promoter region and inducing differentiation. PMID: 29477140
- the two zinc fingers of BuGZ directly bind to AurA and BuGZ coacervation appears to promote AurA activation during spindle assembly. PMID: 29074706
- Findings suggest that ATP/GTP binding protein like 2 (AGBL2) plays a critical oncogenic role in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through modulation on immunity-related GTPase family, M protein (IRGM)-regulated autophagy and aurora kinase A (Aurora A) activity. PMID: 29126912
- Polymorphisms of the Aurora Kinase a Gene is associated with Breast Cancer Risk. PMID: 28647900
- Study suggests AURKA and TPX2 as potential stratification markers for taxane-based radiochemotherapy. lung adenocarcinoma cohort, high expression levels of AURKA and TPX2 were associated with specifically improved overall survival upon taxane-based radiochemotherapy. PMID: 28869599
- In all, these data suggest that Aurora A plays a pivotal role in regulation of Androgen receptor variant 7 expression and represents a new therapeutic target in castrate-resistant prostate cancer. PMID: 28205582
- The inverse correlation between the VHL gene expression profile and alisertib sensitivity was further confirmed in human cancer xenografts models. Taken together, these results suggested that VHL loss could potentially serve as a biomarker for predicting the efficacy of AURKA inhibitors. PMID: 29845253
- LKB1 undergoes AURKA-mediated phosphorylation, which largely compromises the LKB1/AMPK signaling axis, in turn leading to the elevation of non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration. PMID: 28967900
- Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cell apoptosis rate was repressed after treatment with lncRNA TUG1 mimic and promoted after treatment with lncRNA TUG1 inhibitor. AURKA expression but not CLDN3, SERPINE1, or ETS1 expression was adversely regulated by lncRNA TUG1 mimic and inhibitor. In conclusion, lncRNA TUG1 promotes cells proliferation and inhibits cells apoptosis through regulating AURKA in EOC cells. PMID: 30200102
- Metformin disrupts malignant behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma via a novel signaling involving Late SV40 factor/Aurora-A. Findings showed that a novel Late SV40 Factor and Aurora-A-signaling inhibition supports the rationale of using metformin as potential oral squamous cell carcinoma therapeutics. PMID: 28465536
- The present study confirmed that pAURKA is important in the development of gastric adenocarcinoma and revealed a novel functional link between PTEN, AURKA and pAURKA activation. PMID: 29512701
- The role of four AURKA single nucleotide polymorphisms on hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility PMID: 29333101
- AURKA overexpression is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. PMID: 29387948
- The data suggest that AKA is the vertebrate ancestral gene, and that AKB and AKC resulted from gene duplication in placental mammals. PMID: 29283376
- expression of AURKA and CHEK1 was linked with detrimental outcome in patients. Our data describe a synthetic lethality interaction between CHEK1 and AURKA inhibitors with potential translation to the clinical setting PMID: 28847989
- these findings suggest that Aurora A SNP at codon 57 may predict disease outcome and response to alisertib in patients with solid tumors PMID: 29122619
- lncRNA TUG1 associates with advanced disease and worse prognosis in adult AML patients, and it induces AML cell proliferation and represses cell apoptosis via targeting AURKA PMID: 29654398
- Aurora A is able to individually shorten cilia when cilia are growing but requires interaction with never in mitosis-kinase 2 (Nek2) when cilia are being absorbed. Inhibition of Aurora A increases cilia number. PMID: 29141582
- In patients who received alisertib for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma, longer progression-free survival was observed in carriers of the minor allele A of rs2273535 in AURKA than in patients who were homozygous for the major allele T. PMID: 28155045
- The combination also reduces the growth of PDAC xenografts in vivo Mechanistically, it was found that inhibiting methyltransferases of the H3K9 pathway in cells, which are arrested in G2-M after targeting AURKA, decreases H3K9 methylation at centromeres, induces mitotic aberrations, triggers an aberrant mitotic check point response, and ultimately leads to mitotic catastrophe PMID: 28442587
- Prostate cancer cells expressing an S273A mutant of CHIP have attenuated AR degradation upon 2-ME treatment compared with cells expressing wild-type CHIP, supporting the idea that CHIP phosphorylation by Aurora A activates its E3 ligase activity for the AR PMID: 28536143
- Our results indicate that AURKA plays an important role in the activation of EIF4E and cap-dependent translation. Targeting the AURKA-EIF4E-c-MYC axis using alisertib is a novel therapeutic strategy that can be applicable for everolimus-resistant tumors and/or subgroups of cancers that show overexpression of AURKA and activation of EIF4E and c-MYC PMID: 28073841
- Aurora-A may serve as a predictive biomarker of radiation response and a therapeutic target to reverse radiation therapy resistance. PMID: 28404933
- We also propose a model for the stabilization mechanism in which binding to Aurora-A alters how N-Myc interacts with SCF(FbxW7) to disfavor the generation of Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chains PMID: 27837025
- Results identified AURKA to be significantly upregulated in the lung squamous cell carcinoma tissues of smoking patients and may play an important role in diagnosis and prognosis. PMID: 28949095
- s conclude that AURKA may revive dormant tumor cells via FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway activation, thereby promoting migration and invasion in laryngeal cancer. PMID: 27356739
- our identification of the novel interaction between Aurora A and H-Ras as a mechanism by which Aurora A can activate Ras-MAPK signaling opens the way for studies into perturbation of the Aurora A/H-Ras interaction and the effect on Ras-MAPK signaling. PMID: 28177880
- MiR-124-3p has significant impact on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells by targeting AURKA PMID: 28269755
- Taken together, our data suggest that Aurora-A plays an important role in the suppression of autophagy by inhibiting the phosphorylation of Akt, which in turn prevents autophagy-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer PMID: 28269749
- Results show that overexpression of Aurora-A and PTGS2 occurs in colon polyps and has a reverse correlation with miR-137 in both colon polyps and colorectal cancer tissue suggesting that AURKA and PTGS2 expression is under the regulation of mir-137. PMID: 27764771
- SIX3 is a novel negative transcriptional regulator and acts as a tumor suppressor that directly represses the transcription of AURKA and AURKB in astrocytoma. PMID: 28595628
- this report provides clear evidence that overexpression of the AURKA, SKA3, and DSN1 genes strongly correlates with the progression of colorectal adenomas to colorectal cancer PMID: 27329586
- Although research biopsies were obtained on only a few patients, they did confirm pharmacodynamic effects of the drug. These effects though suggest inhibition of Aurora B rather than Aurora A, which consistent with pre-clinical data that show dose-dependent effects on both PMID: 27502708
- Aurora A kinase is hyperphosphorylated in early mitosis under oxidative stress, which may disturb the function of Aurora A in mitotic spindle formation. PMID: 28017898
- Our findings suggested that AURKA (rs911160) and AURKB (rs2289590) polymorphisms could affect GC risk. Further validation studies in larger and multi-ethnical populations are needed to elucidate their functional impact on the development of GC PMID: 28843004
- Possible models of regulation of Lck by Aurora-A during T cell activation are described in the review. PMID: 27910998
- our study demonstrate that KCTD12 binds to CDC25B and activates CDK1 and Aurora A to facilitate the G2/M transition and promote tumorigenesis and that Aurora A phosphorylates KCTD12 at serine 243 to trigger a positive feedback loop, thereby potentiating the effects of KCTD12. Thus, the KCTD12-CDC25B-CDK1-Aurora A axis has important implications for cancer diagnoses and prognoses. PMID: 28869606
- Our findings showed novel regulatory mechanisms of p53 in regulating Aurora-A gene expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. PMID: 28884479
- HIP2 regulates mitotic spindle alignment. SHIP2 is expressed in G1 phase, whereas Aurora A kinase is enriched in mitosis. SHIP2 binds Aurora A kinase and the scaffolding protein HEF1 and promotes their basolateral localization at the expense of their luminal expression connected with cilia resorption. PMID: 27926875
- Aurora kinase inhibitor CCT137690 induces necrosis-like death in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells, via RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL signaling. PMID: 28764929
- our data indicate that hnRNP Q1 is a novel trans-acting factor that binds to Aurora-A mRNA 5'-UTRs and regulates its translation, which increases cell proliferation and contributes to tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer PMID: 28079881
- A central role of Aurora kinase A (AURKA) in promoting Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotypes via ALDH1A1. PMID: 28193222
- Switching Aurora-A kinase on and off at an allosteric site has been documented. (Review) PMID: 28342286
- This is the first report of F31I and V57I polymorphisms in AURKA gene in breast cancer in Iran PMID: 28906374
- High Aurora A kinase expression is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. PMID: 27593935
- Results provide evidence that AURKA is a target for the VHL E3 ligase ubiquitination. PMID: 28114281
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole. Cell projection, neuron projection.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, Ser/Thr protein kinase family, Aurora subfamily
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in testis and weakly in skeletal muscle, thymus and spleen. Also highly expressed in colon, ovarian, prostate, neuroblastoma, breast and cervical cancer cell lines.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11393
OMIM: 603072
KEGG: hsa:6790
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000216911
UniGene: Hs.250822
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-