Phospho-MDM4 (Ser367) Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA975669
-
规格:¥2454
-
图片:
-
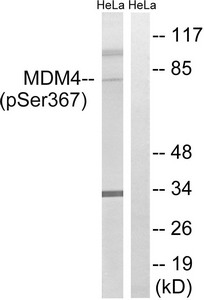
Western blot analysis of extracts from HeLa cells, treated with calyculinA (50ng/ml, 30mins), using MDM4 (Phospho-Ser367) antibody. The lane on the right is treated with the synthesized peptide.
-
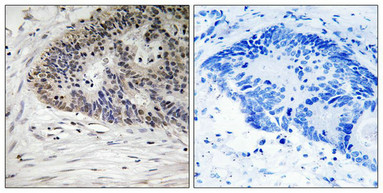
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma tissue using MDM4 (Phospho-Ser367) antibody. The picture on the right is treated with the synthesized peptide.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) MDM4 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O15151
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 367 (T-I-S(p)-A-P) derived from Human MDM4.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA,WB,IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 IHC 1:50-1:100 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Along with MDM2, contributes to TP53 regulation. Inhibits p53/TP53- and TP73/p73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Inhibits degradation of MDM2. Can reverse MDM2-targeted degradation of TP53 while maintaining suppression of TP53 transactivation and apoptotic functions.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Considering the lack of association between MDM4 rs4245739 polymorphism and breast cancer, rs4245739 polymorphism of this gene seems to have no significant role in the pathophysiology of the disease. PMID: 28164646
- We conclude that Mdm4-S overexpression is a consequence of splicing defects in tumor cells rather than a cause of tumor evolution. PMID: 28460439
- These results indicate that the rs4245739 polymorphism may contribute to a decreased cancer susceptibility and support the hypothesis that genetic variants in the MDM4 genes act as important modifiers of cancer risk. PMID: 27738340
- our study is the first to identify miR-766 as a novel p53 activator that functions by targeting MDM4 and thereby enhancing the p53 signalling axis. PMID: 28430625
- High MDM4 expression levels are associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma and influence the prognosis of patients with gastric adenocarcinoma PMID: 27626496
- MDM4 rs4245739 A > C polymorphism appears to be associated with decreased cancer risk PMID: 27687591
- analyses indicated that rs4245739 polymorphism in the MDM4 gene may play an important role in the etiology of cancer PMID: 27742919
- results revealed an allosteric ligand-binding mechanism of the N-terminal domain of MdmX in which the ligand initially interacts with a compact core, followed by augmenting intermolecular interactions with intrinsic flexible regions PMID: 29023092
- Complex alterations of HDM4 proteins, which are critical regulators of cell cycle progression, are frequent defects in AML and HG-MDS cases. The overall rates of detection of HDM4 expression in the present study, 92% in AML and 52% in MDS, respectively, indicate that HDM4 is a potential therapeutic target in patients with these diseases. PMID: 27155969
- MDM4 rs1380576 G variant is associated with gastric cancer. PMID: 28099948
- These results demonstrate that cisplatin-mediated p53(V172F) mutation regulates p53 stability at the normothermic temperature, but it is the increased recruitment of MDM4 by the homomeric or heteromeric mutant p53(V172F) complex that inhibits p53-dependent transactivation. This represents a novel cellular mechanism of p53 inhibition, and, thereby, induction of cisplatin resistance PMID: 26876197
- MDM4 protein is frequently abundant in the context of mutant p53 in basal-like breast cancer (BC) samples. MDM4 plays a critical role in the proliferation of these BC cells. MDM4 is crucial for the establishment and progression of tumours. PMID: 28097652
- Study used polymer statistics to estimate a global KD value for p53 binding to MdmX in the presence of the flexible linker and the intramolecular binding motif by assuming the flexible linker behaves as a wormlike chain. Calculations and measurements showed that the intramolecular binding motif reduces the apparent affinity of p53 for MdmX by a factor of 400. PMID: 28487147
- Data indicate that knockdown of otubain 1 protein (Otub1) reduced the levels of double minute 4 protein (MDMX). PMID: 28035068
- these data identify MDM4 as a nutrient-sensor able to inhibit mTORC1 and highlight its metabolism-related tumor-suppressing function. PMID: 28270148
- Data indicate that two single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs)rs10900598 and rs4245739, located at 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of double minute 4 protein (MDM4) gene, contribute to clinical outcome of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. PMID: 27462918
- identified a novel Her4-induced posttranslational modification on MDMX PMID: 27777309
- MDM4 SNP34091 polymorphism may function as a protective factor against cancer risk. PMID: 27646776
- Individuals harboring the MDM4 SNP34091AC/CC genotypes had a significantly elevated risk for serous ovarian cancer, particularly high-grade serous ovarian cancer. No association between SNP34091 genotypes and endometrial cancer risk was observed. PMID: 26867771
- These results suggest that secondary intermolecular interaction is important in p53 regulation by MDMX, which may represent a common phenomenon in complexes containing multidomain proteins. PMID: 27114532
- s show that the EMT phenotype in multiple cellular models and in clinical prostate and breast cancer samples is associated with a decrease in MDM2 and increase in MDMX expression. PMID: 26416355
- MDM4 SNP34091 status to be associated with reduced risk of breast cancer, in particular in individuals carrying the MDM2 SNP309GG genotype, but not to be associated with either lung-, colon- or prostate cancer. PMID: 26471763
- The phosphate group of pTyr99 imposes extensive steric clashes with the C-terminus of p53 peptide and induces a significant lateral shift of the peptide ligand, decreasing the binding affinity of MDMX for p53. PMID: 26148237
- MDM4/HIPK2/p53 cytoplasmic assembly uncovers coordinated repression of molecules with anti-apoptotic activity during early DNA damage response. PMID: 25961923
- MDM4 rs4245739 single nucleotide polymorphism contributes to small cell lung cancer risk and support the notion that gene 3'-UTR genetic variants, impacting miRNA-binding, might modify small cell lung cancer susceptibility. PMID: 26274820
- These results identify Mdmx growth dependency in wt p53 expressing breast cancer across a range of subtypes. Based on our findings, we propose that Mdmx targeting is an attractive strategy for treating breast cancer harboring wt p53 PMID: 26181202
- MDM4 overexpression is related to complex karyotype-acute myeloid leukemia with wild-type TP53 and might play a pathogenic role by inhibiting p53-signal pathway. PMID: 25405759
- MDMX exerts oncogenic activity via suppression of RB. PMID: 25703327
- We show using reporter gene assays and endogenous MDM4 expression analyses that miR-191-5p and miR-887 have a specific affinity for the rs4245739 SNP C-allele in prostate cancer PMID: 25670033
- MDM4 mutation identified in a glioma patient was associated with loss of the putative MDM4 target site. Therefore, let-7 binding to MDM4 is implicated in the DNA damage response PMID: 26028311
- Finally, a strong association between the expression of EEF1A2, phosphorylated AKT and MDM4 was observed in human HCC samples. Strong activation of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 signaling pathway was observed in HCC patients. PMID: 25394965
- Confirmation that the residue Tyr99 in MDMX can generate a steric clash with the inhibitors due to energy and structure. PMID: 22408446
- The HDMX polymorphism is unlikely to contribute to individual susceptibility to sarcoma. PMID: 24972690
- The results indicate a putative role for the MDM4 gene in predicting local recurrence of bladder cancer. PMID: 25026175
- Endogenously high levels of Mdm4 inhibit and sequester p53 in AML. High levels of Mdm4 do not block function of Mdm2 inhibitors in AML. PMID: 24659749
- in the absence of p53 or in the presence of MdmX overexpression, FL118 promotes p53-independent apoptosis PMID: 25512388
- Downregulation of Mdm4 by miR-661 augments p53 activity and inhibits cell cycle progression in p53-proficient cells. PMID: 24141721
- Loss of MDM4 expression is associated with glioblastoma. PMID: 24445145
- the novel variant MDM4-B may play a role in glioma tumorigenesis or cancer progression PMID: 23994448
- The activation level of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 axis significant influences the survival probability of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. PMID: 24285179
- Functional MDM4 rs4245739 SNP, alone and in combination with P53 Arg72Pro genetic variant, was associated with a significantly decreased risk of breast cancer in Chinese populations. PMID: 23793604
- MDMX contains a regulatory element (the "WWW element") that binds to its own N-terminal domain and prevents MDMX from binding to p53. PMID: 24127580
- The MDM4 rs4245739 (miR-191 target site) AC and CC genotypes were significantly associated with decreased esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk PMID: 23724042
- Mdm4 is upregulated in a substantial proportion of stage I-IV human melanomas. It promotes the survival of metastatic melanoma by antagonizing p53. In xenografts, inhibition of the MDM4-p53 interaction restored p53 function. PMID: 22820643
- The interaction of nutlin with MDMX is very short-lived compared with MDM2 and does not show such direct initial interactions with the binding site. PMID: 23324352
- The rs1563828(C > T) polymorphism in MDM4 gene may not confer risk to breast cancer, especially for early-onset breast cancer patients. Homozygous TT of rs1563828 is associated with younger age of onset of breast cancer. PMID: 22490292
- FULL length-MDM4 and a splicing variant of MDM4 overexpression are indicators of p53 aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, suggesting that those patients have a poor prognosis. PMID: 22937789
- MicroRNA-34a modulates MDM4 expression via a target site in the open reading frame. PMID: 22870278
- The results of this study showed that strong association between MDM4 gene alternation and high-grade oligodendroglial tumors. PMID: 22825724
- DNA damage activates p53 in part by disrupting CK1a-MDMX interaction and reducing MDMX-p53 binding affinity. PMID: 23028042
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:MDM2/MDM4 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in all tissues tested with high levels in thymus.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6974
OMIM: 602704
KEGG: hsa:4194
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000356150
UniGene: Hs.497492
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-