BTLA Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
货号:CSB-RA773799MA1HU
-
规格:¥1320
-
图片:
-
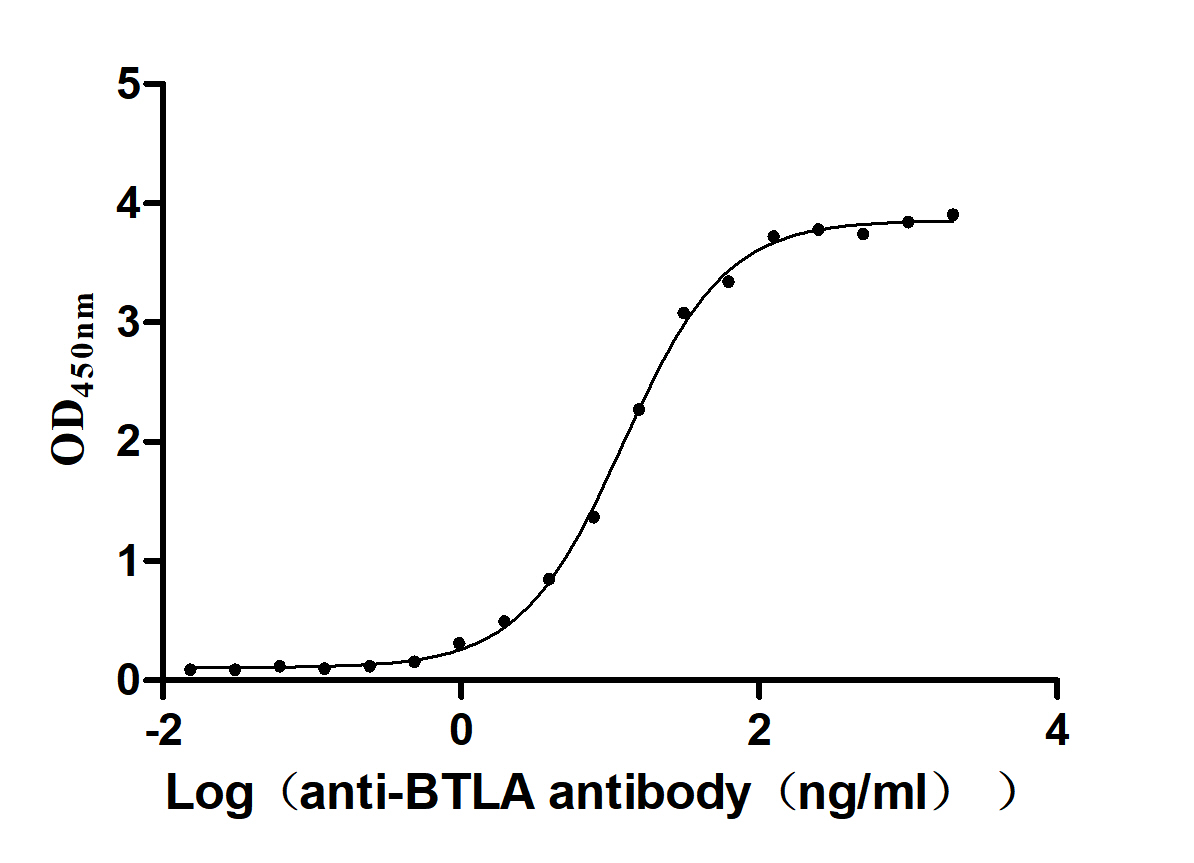
The Binding Activity of Human BTLA with Anti-BTLA Recombinant Antibody
Activity: Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human BTLA(CSB-MP773799HU1)at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-BTLA recombinant antibody , the EC50 is 11.56-13.00 ng/mL. -
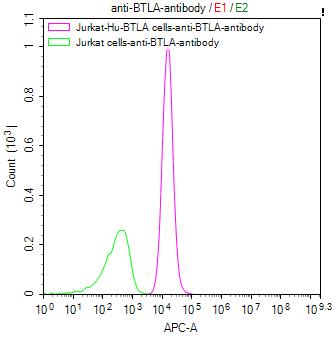
Untransfected Jurkat cells surface (green line) and transfected Human BTLA Jurkat stable cells surface (red line) were stained with anti-BTLA antibody (2µg/1*106cells), washed and then followed by APC-conjugated anti-Human IgG Fc antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry.
-
Untransfected CHO-K1*106cells), washed and then followed by FITC-conjugated anti-Human IgG Fc antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:Q7Z6A9
-
基因名:
-
别名:BTLA Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human BTLA protein
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Monoclonal
-
抗体亚型:Human IgG4
-
纯化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆号:10A10
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 -
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, FC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution FC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Inhibitory receptor on lymphocytes that negatively regulates antigen receptor signaling via PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with TNFRSF14. In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that both HVEM and UL144 bind a common epitope of BTLA, whether engaged in trans or in cis; these studies were conducted in cell lines representing B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. (HVEM = human herpes virus entry mediator; UL144 = membrane glycoprotein UL144 of Human herpesvirus 5; BTLA = human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator) PMID: 29061848
- our data suggested that the BTLA/HVEM pathway contributes to peripheral T cell suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients PMID: 30116751
- data provide the first evidence that increased BTLA predicts poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and blockade of BTLA with other checkpoints may potentially represent a new strategy for immunotherapy of DLBCL. PMID: 29353075
- The genetic variants of rs76844316 in BTLA influence the susceptibility to severe chronic hepatitis B and might play a protective role against the progression of chronic hepatitis B. PMID: 29558758
- The impairment of Bregs and CD19+/BTLA+ cells could play an important pathogenic role in multiple sclerosis (MS). PMID: 27412504
- Our data portrays BTLA as a molecule with the singular ability to provide both costimulatory and coinhibitory signals to activated CD8(+) T cells, resulting in extended survival, improved tumor control, and the development of a functional recall response. PMID: 28754817
- results indicate that polymorphisms rs1982809 situated in 3' UTR nearby region of BTLA gene might be considered as low-penetrating risk factor for RCC, but results have to be confirmed in further studies PMID: 27234378
- The percentage of circulating BTLA+CD4+ lymphocytes was significantly higher in patients with severe community acquired pneumonia. PMID: 28164546
- Plasma concentrations of soluble BTLA were increased early in sepsis/septic shock and correlated to severity of disease. A baseline concentration >21ng/mL was associated with a poor prognosis. PMID: 28056053
- this study shows that in chronic hepatitis B virus patients, a subset of inefficient interferon-gamma producing antigen-specific CD8+ T cells recruited to the liver expressed high BTLA levels PMID: 27743606
- this study shows that BTLA expression is likely associated with positive rather than conventional negative regulation of CD11c antigen-presenting cell stimulatory capacity PMID: 27717503
- rs1982809 BTLA gene polymorphism is associated with mRNA expression level and variations in the BTLA gene might be considered as potentially low-penetrating chronic lymphocytic leukemia risk factor PMID: 27933341
- Study showed a decreased expression of BTLA in ocular Behcet's disease suggesting that it may be involved in the development and recurrence of this disease. PMID: 26841832
- BTLA expression declines on B cells of the aged and is associated with low responsiveness to the trivalent influenza vaccine. PMID: 26277622
- our study confirms that CD200/BTLA deletions are recurrent genetic lesions in the biology of BCP-ALL PMID: 26137961
- Focal deletions of the BTLA were associated with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PMID: 25261097
- high BTLA expression levels in gastric cancer, identified by IHC, are an independent biomarker for the poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. PMID: 25334051
- Data indicate taht lung function and the expressions of B, T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and Treg cells were lower in patients with rheumatism than those in normal controls. PMID: 24909289
- BTLA is a coreceptor that negatively regulates human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cell proliferation and has a role in immune escape for lymphoma cells PMID: 23692853
- BTLA and HVEM may have roles in graft rejection after kidney transplantation PMID: 23375291
- BTLA regulates human B cell responses and has implications for future development of therapies modulating B cells. PMID: 22903545
- The expression of BTLA has been observed on the surface of several kinds of cells within synovial tissues of RA patients, which indicates this signal might be involved in the regulation of local T cell activation and the pathogenesis of RA. PMID: 22691359
- These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. PMID: 22459947
- study described the expression and spatial distribution of HVEM and BTLA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues, and results indicated that HVEM/BTLA may be involved in regulating the progress of joint inflammation PMID: 22179929
- BTLA-HVEM interactions impair minor histocompatibiility antigen-specific T cell functionality, providing a rationale for BTLA signaling blockade in post-stem cell transplantation. PMID: 22634623
- Added with PD-1 and Tim-3 blockades, BTLA blockade enhanced the expansion, proliferation, and cytokine production of NY-ESO-1-specific CD8(+) T cells. PMID: 22205715
- HVEM-BTLA cis complex provides intrinsic regulation in T cells serving as an interference mechanism silencing signals coming from the microenvironment. PMID: 21920726
- The results of a mutagenesis study of HVEM suggest that the CD160 binding region on HVEM was slightly different from, but overlapped with, the BTLA binding site. PMID: 21959263
- 590C single-nucleotide polymorphism of B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator was significantly associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, but not to systemic lupus erythematosus or Sjogren's syndrome. PMID: 21403914
- BTLA expression on overall CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells was progressively decreased in HIV-1 infection, which was directly correlated with disease progression and CD4(+) T-cell differentiation and activation PMID: 21592997
- In vitro blockade of the BTLA pathway augments allogeneic as well as cytomegalovirus-specific CD8-positive T cell proliferation, thereby enhancing the functional capacity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in viral infections. PMID: 20693422
- BTLA gene polymorphisms may affect the sporadic breast cancer risk and prognosis in Chinese women in northeast of Heilongjiang Province PMID: 19585237
- Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. PMID: 15647361
- distinct herpesviruses target the HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway, suggesting the importance of this pathway in regulating T cell activation during host defenses. PMID: 16131544
- 2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface PMID: 16169851
- BTLA is constitutively expressed on most CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and its expression progressively decreases upon T cell activation. PMID: 16643847
- Cross-linking of BTLA with mAb 7D7 suppressed T lymphocyte proliferation, downregulated the expression of T cell activation marker CD25, and inhibited the production of interferon (IFN)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-2, IL-4, and IL-10. PMID: 17257317
- BTLA is an inhibitory coreceptor of the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway that attenuates B cell activation by targeting the downstream signaling molecules Syk and B cell linker protein (BLNK). PMID: 19155498
- this study did not find any genetic contribution of the BTLA gene to the development of T1D and SLE in Japanese population. PMID: 19207938
- results suggest that down-regulation of the BTLA-HVEM pathway may be involved in germinal center B-cell activation. PMID: 19762537
- the HVEM-BTLA cis-complex competitively inhibits HVEM activation by ligands expressed in the surrounding microenvironment, thus helping maintain T cells in the naive state. PMID: 19915044
- HVEM binds to B T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an Ig family member, which inhibits T cell proliferation. PMID: 15568026
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 21087
OMIM: 607925
KEGG: hsa:151888
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000333919
UniGene: Hs.445162
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-