Recombinant Drosophila melanogaster Protein decapentaplegic (dpp)
-
货号:CSB-YP357184DLU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP357184DLU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP357184DLU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP357184DLU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP357184DLU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:dpp
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:dpp; CG9885Protein decapentaplegic; Protein DPP-C
-
种属:Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:457-588
-
氨基酸序列DVSG GEGGGKGGRN KRQPRRPTRR KNHDDTCRRH SLYVDFSDVG WDDWIVAPLG YDAYYCHGKC PFPLADHFNS TNHAVVQTLV NNMNPGKVPK ACCVPTQLDS VAMLYLNDQS TVVLKNYQEM TVVGCGCR
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Required during oogenesis for eggshell patterning and dorsal/ventral patterning of the embryo. Acts as a morphogen during embryogenesis to pattern the dorsal/ventral axis, specifying dorsal ectoderm and amnioserosa cell fate within the dorsal half of the embryo; this activity is antagonized by binding to sog and tsg. Induces the formation of visceral mesoderm and the heart in early embryos. Required later in embryogenesis for dorsal closure and patterning of the hindgut. Also functions postembryonically as a long-range morphogen during imaginal disk development; is responsible for the progression of the morphogenetic furrow during eye development. Patterns the wing imaginal disk along its anterior/posterior axis and has a role in positioning pro-veins. Also required to subdivide the wing disk along the proximal/distal axis into body wall (notum) and wing. Ensures the correct architecture of wing epithelial cells. Has multiple roles in the developing tracheal system, controlling directed tracheal cell migration during embryogenesis and later specifying the fate of fusion cells in the tracheal branches. Required for viability of larvae. Essential for the maintenance and division of germline stem cells in the ovary. Signals via the type I receptor tkv, the type II receptor punt, and in some tissues via the type I receptor sax, in a signaling cascade that leads to activation and repression of target genes.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- analysis of phenotype caused by misexpression of Wg, a negative regulator of eye development, using GMR17E04-Gal4, GMR18D08-Gal4 with existing dpp-Gal4 driver, which suggests the need for revisiting misexpression studies with Gal4 drivers PMID: 29702674
- Loss of Pngl results in a severe decrease in the level of Dpp homodimers and abolishes BMP autoregulation in the visceral mesoderm mediated by Dpp and Tkv homodimers. Loss of Pngl results in developmental midgut defects reminiscent of midgut-specific loss of BMP signaling. PMID: 28826503
- The s find that both arms of the TFGb signaling pathways specifically instruct the pale photoreceptor subset in R8. The Activin arm utilizes the three ligands dActb, Daw, and Myo non-redundantly to activate Babo and downstream dSmad2 in R8, while the BMP arm signals by way of Dpp and Gbb to Tkv and Mad. PMID: 28853393
- Dpp regulates growth and proliferation rates equally in central and lateral regions of the developing wing appendage and reduced levels of Dpp affects similarly the width and length of the resulting wing. PMID: 28675372
- Here, by removing dpp from the stripe at different time points, the s show that the dpp stripe source is indeed required for wing disc growth, also during third instar larval stages. PMID: 28675373
- With two independent conditional alleles of dpp, the s find that the stripe of Dpp is essential for wing growth. The s then show that this requirement, but not patterning, can be fulfilled by uniform, low level, Dpp expression. Thus, the stripe of Dpp ensures that signalling remains above a pro-growth threshold, while at the same time generating a gradient that patterns cell fates. PMID: 28675374
- Study provide evidence of yet another mechanism by which Dpp regulates the expression of its target retinal retinal determining (RD) genes independent of its bona fide transcriptional regulator specifically during induction of ectopic eyes. Apart from previously known transcriptional activation of the RD genes, Dpp simultaneously triggers another signaling cascade that involves dTak1-mediated activation of JNK. PMID: 27270790
- we found that the Dpp target gene sal is only expressed in peripodial epithelium (DP, also known as pseudostratified columnar epithelia) , not in PE cells, also known as squamous epithelia, although pMad is present in the PE. PMID: 27452716
- Here we provide evidence that although wild type CtBP negatively and dominantly influences Dpp signaling in fly presumptive wings, mutant CtBP unable to form dimer does not, indicating that dimerization is required for the repression role of CtBP in Dpp signaling in vivo. PMID: 29225171
- Dpp activates signaling cascade involving dTak1 and JNK, to induce ectopic Mmp1 expression. PMID: 28696218
- ECM over planar cell polarity mutant cells had reduced levels of laminin, Dally and Dlp, and whereas Dpp-receiving ASP cytonemes navigated in the Dally layer and required Dally (but not Dlp), FGF-receiving ASP cytonemes navigated in the Dlp layer, requiring Dlp (but not Dally). PMID: 27591355
- The s show that Pent internalises the Dpp co-receptors, the glypicans Dally and Dally-like protein (Dlp), and propose that this internalisation is important in the establishment of a long range Dpp gradient. PMID: 27269283
- The expression of optix is activated by Dpp and repressed by the Spalt proteins, becoming restricted to the most anterior region of the wing blade. PMID: 28760811
- En forms a complex with Nejire (Nej), the Drosophila ortholog of histone acetyltransferase CBP/p300, and directs Nej to this cis-regulatory region where Nej functions as the co-activator for dpp expression. PMID: 28928281
- Basement membrane elimination, in contrast, attenuated signaling by bone morphogenetic protein/transforming growth factor beta ligand Dpp, which was not efficiently retained within the tissue and escaped to the body cavity. PMID: 28697337
- This report provides a genetic analysis of primary nociceptive neuron mechanisms that promote sensitization in response to injury. Drosophila melanogaster larvae whose primary nociceptive neurons were reduced in levels of specific components of the BMP signaling pathway, were injured and then tested for nocifensive responses to a normally subnoxious stimulus. PMID: 28855331
- Dad and Dpp activity is dynamically regulated in the adult Drosophila middle midgut. PMID: 27570230
- Here we uncover a cell non-autonomous requirement for the Epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) pathway in the lateral epidermis for sustained dpp expression in the LE. Specifically, we demonstrate that Egfr pathway activity in the lateral epidermis prevents expression of the gene scarface (scaf), encoding a secreted antagonist of JNK signaling PMID: 28628612
- In this work, we have explored the disc autonomous function of TGFbeta that promotes wing imaginal disc growth. We have studied the genetic interactions between TGFbeta signaling and other pathways regulating wing disc growth, such as the Insulin and Hippo/Salvador/Warts pathways, as well as cell cycle regulators. PMID: 28315837
- During normal development, Dpp represses hth and tsh ensuring that the progenitor state is transient. However, cells in which Hth+Tsh expression is forcibly maintained use Dpp to enhance their proliferation. PMID: 27502436
- Here we demonstrate that each prostate-like secondary cell (SC) in the paired adult Drosophila melanogaster male accessory glands contains approximately ten large DCGs, which are loaded with the Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) ligand Decapentaplegic (Dpp). PMID: 27727275
- disruption of dpp expression causes apoptosis in peripodial cells and underlying disc proper cells PMID: 26500262
- we elucidate the genetic network elicited by Snoo and Dpp activity. These results illustrate a regulatory mechanism that translates intrinsic potential and extrinsic cues into the facultative stem cell features of differentiated progenitors. PMID: 26942411
- During oogenesis lgd loss of function causes ectopic activation of the Drosophila BMP signalling pathway. PMID: 25804739
- in the absence of Dpp spreading, wing disc patterning is lost; however, lateral cells still divide at normal rates PMID: 26550827
- Cullin-2 protein present in the somatic cells is involved in a non cell-autonomous regulation of the extent of Dpp signaling and thus controls the differentiation of GSCs to cystoblasts PMID: 26206612
- Dpp and Gbb are produced by enterocytes and act in conjunction to promote intestinal stem cell self-renewal by antagonizing Notch signaling. PMID: 24618900
- Mad linker phosphorylations control the intensity and range of the BMP-activity gradient in developing Drosophila tissues. PMID: 25377173
- Thickveins (Tkv; a type I receptor of Dpp) is highly expressed in stromal cells next to Dpp-producing cells and functions to remove excess Dpp outside the stem cell niche. PMID: 26008746
- s studied BMP-dependent gene regulation during Drosophila oogenesis by following the signal transmission from Dpp to its target broad (br), a gene with a crucial function in eggshell patterning and identified regulatory sequences that account for expression of both brk and br, and connect these to the transcription factors of the pathway. PMID: 25704512
- Dpp/Gbb signaling is required for normal intestinal regeneration during infection. PMID: 25553980
- Decapentaplegic (DPP) and JNK form a coherent feed-forward loop that controls the specification and differentiation of leading edge cells during Drosophila melanogaster dorsal closure. PMID: 25601405
- Dpp plays a dual role during dorsal closure. It cooperates with JNK in stimulating cell migration and also prevents JNK from inducing apoptosis. PMID: 25307481
- novel mechanisms by which Dpp affects the cellular differentiation of wing-veins. PMID: 24591046
- Loss of Bar from the undifferentiated retinal precursor cells leads to ectopic expression of Prospero and dPax2, two transcription factors essential for cone cell specification, resulting in excess cone cell differentiation. PMID: 24505414
- The signaling dynamics of the morphogen Dpp, one of several Drosophila factors controlling morphogenetic growth, was measured in the developing eye. PMID: 24757005
- These data reveal novel mechanisms by which post-translational regulation of Scw can modulate Dpp signaling activity. PMID: 24560644
- We propose that developmental BMP signaling potentiates NMJs for rapid activity-dependent structural plasticity that is achieved by muscle release of retrograde signals that regulate local presynaptic actin cytoskeletal dynamics. PMID: 24647957
- Genetic loss-of-function conditions for diaphanous, shibire, neuroglian, and capricious perturbed cytonemes by reducing their number or only the synapses they make with cells they target, and reduced cytoneme-mediated transport of Dpp and Dpp signaling. PMID: 24385607
- Drosophila piwi mutants exhibit germline stem cell tumors that are sustained by elevated Dpp signaling. PMID: 23891114
- Dpp signaling is required for copper cell regeneration and gut compartmentalization. PMID: 23810561
- optix functions together with hh to regulate dpp in the morphogenetic furrow, serving as a link between the RD network and the patterning pathways controlling normal retinal development PMID: 23792115
- spatial distribution of Dpp is tightly regulated at the extracellular level allowing diffusible ligands to form elaborate wing vein patterns PMID: 22542596
- Dpp-induced Egfr signaling triggers postembryonic wing development in Drosophila. PMID: 23479629
- data demonstrate Dpp signaling is primarily activated in enterocytes and Dpp is expressed specifically in tracheal cells that reach the intestinal cells through the visceral muscles PMID: 23369712
- We propose that the double role of KAY-alpha in the two transcriptional loops controlling Drosophila circadian behavior brings precision and stability to their oscillations PMID: 23175847
- Dpp transport occurs by simple, rapid diffusion in the extracellular space. PMID: 22445299
- dpp controls morphogenesis of the ventral adult head through expression in the eye-antennal disc by a 3.5 kb enhancer in the 5' end of the gene. We recovered a 15 bp deletion mutation within this enhancer that identified a homeotic response element. PMID: 22824425
- collagen IV functions to immobilize free Dpp in the Drosophila embryo PMID: 22733779
- Fat facets deubiquitylation of Medea/Smad4 modulates interpretation of a Dpp morphogen gradient PMID: 22745309
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted. Note=Is internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
-
蛋白家族:TGF-beta family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in the dorsal region of the embryo, and becomes enriched in a dorsal midline stripe just prior to gastrulation. Expressed in midgut mesoderm and in two overlapping regions of the embryonic large intestine. Expressed in a long-range concentration
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: dme:Dmel_CG9885
STRING: 7227.FBpp0077451
UniGene: Dm.4767
Most popular with customers
-
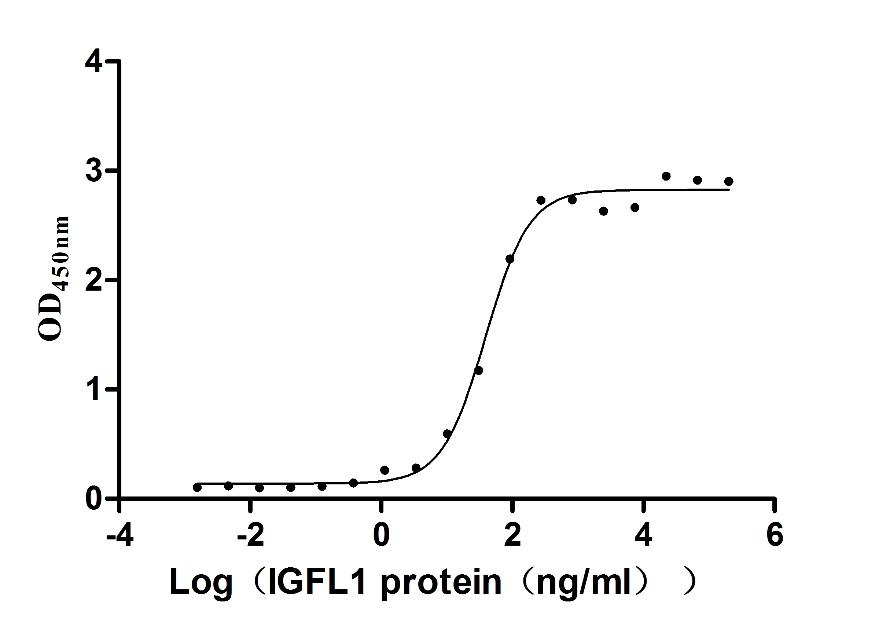
Recombinant Human Insulin growth factor-like family member 1 (IGFL1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
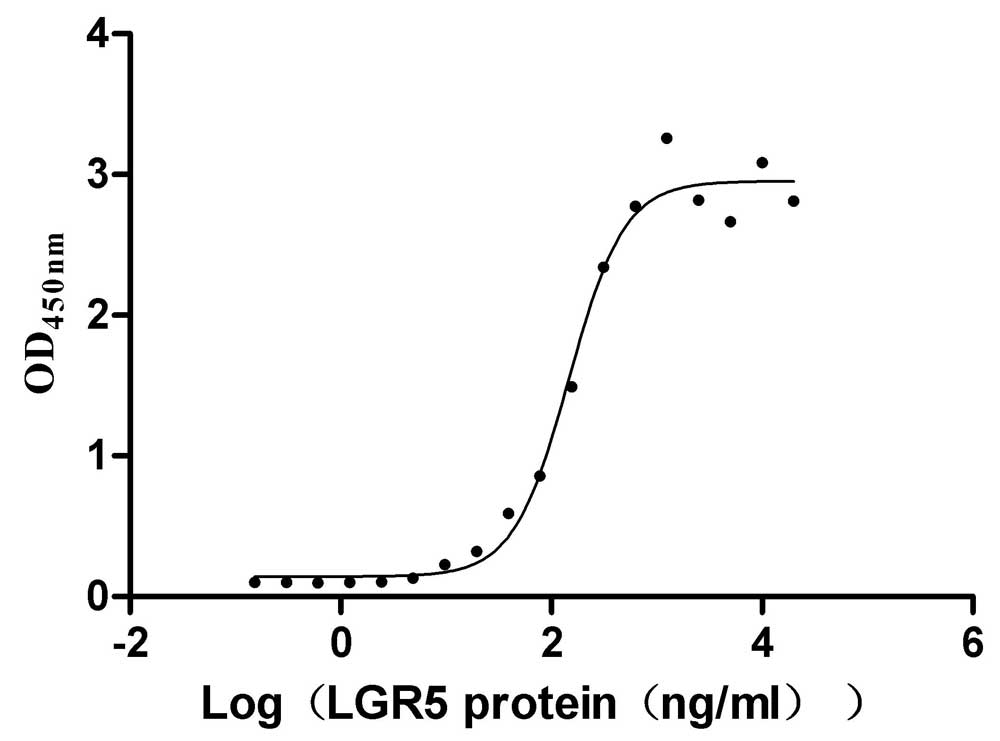
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
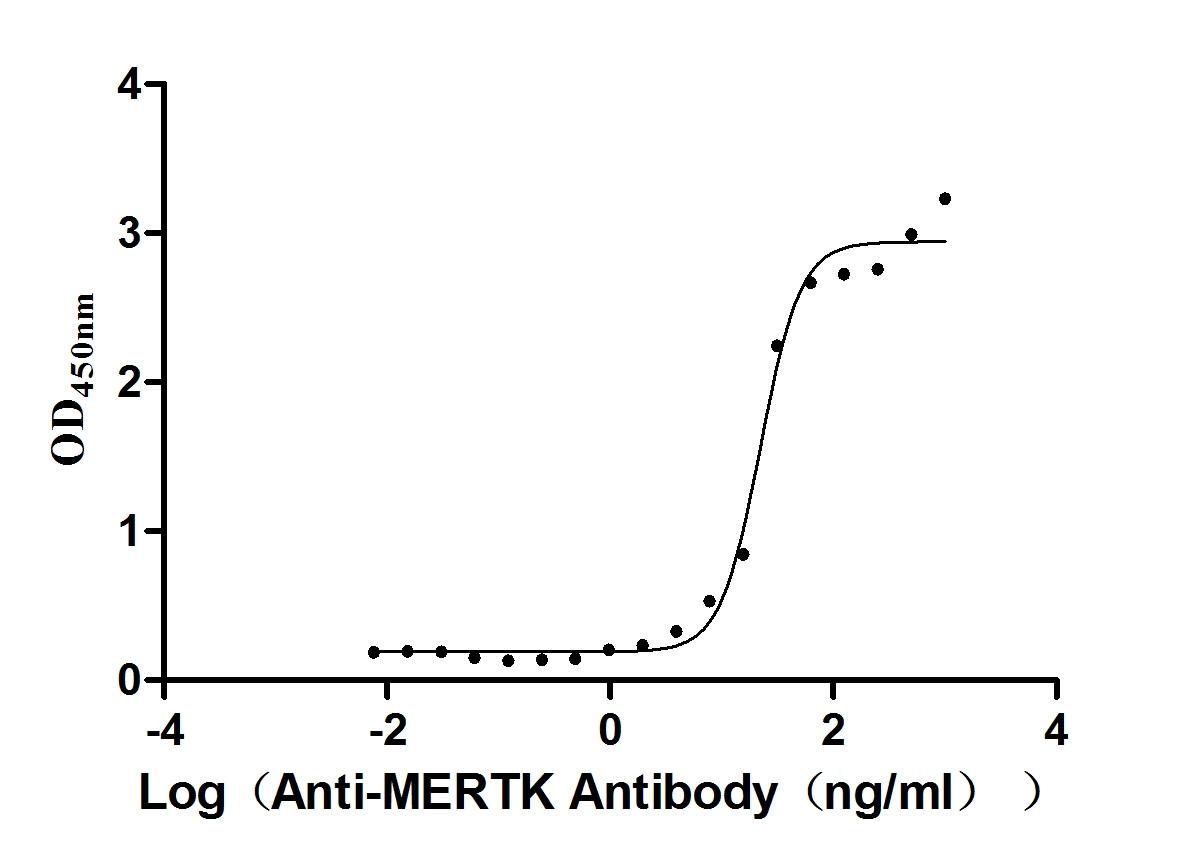
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
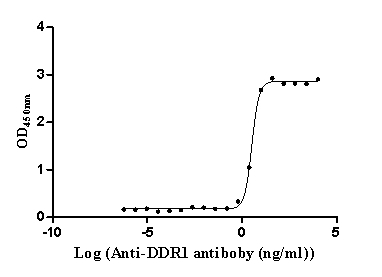
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)