Recombinant Hepatitis C virus Genome polyprotein, partial
-
货号:CSB-YP333311HEY1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP333311HEY1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP333311HEY1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP333311HEY1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP333311HEY1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:N/A
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Genome polyprotein; Fragment
-
种属:Hepatitis C virus (isolate HC-J5) (HCV)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Packages viral RNA to form a viral nucleocapsid, and promotes virion budding (Probable). Participates in the viral particle production as a result of its interaction with the non-structural protein 5A. Binds RNA and may function as a RNA chaperone to induce the RNA structural rearrangements taking place during virus replication. Modulates viral translation initiation by interacting with viral IRES and 40S ribosomal subunit. Affects various cell signaling pathways, host immunity and lipid metabolism (Probable). Prevents the establishment of cellular antiviral state by blocking the interferon-alpha/beta (IFN-alpha/beta) and IFN-gamma signaling pathways and by blocking the formation of phosphorylated STAT1 and promoting ubiquitin-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation of STAT1. Activates STAT3 leading to cellular transformation. Regulates the activity of cellular genes, including c-myc and c-fos. May repress the promoter of p53, and sequester CREB3 and SP110 isoform 3/Sp110b in the cytoplasm. Represses cell cycle negative regulating factor CDKN1A, thereby interrupting an important check point of normal cell cycle regulation. Targets transcription factors involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and in the immune response: suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappa-B activation, and activates AP-1. Binds to dendritic cells (DCs) via C1QR1, resulting in down-regulation of T-lymphocytes proliferation. Alters lipid metabolism by interacting with hepatocellular proteins involved in lipid accumulation and storage. Induces up-regulation of FAS promoter activity, and thereby contributes to the increased triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes (steatosis).; Forms a heterodimer with envelope glycoprotein E2, which mediates virus attachment to the host cell, virion internalization through clathrin-dependent endocytosis and fusion with host membrane. Fusion with the host cell is most likely mediated by both E1 and E2, through conformational rearrangements of the heterodimer required for fusion rather than a classical class II fusion mechanism. E1/E2 heterodimer binds host apolipoproteins such as APOB and ApoE thereby forming a lipo-viro-particle (LVP). APOE associated to the LVP allows the initial virus attachment to cell surface receptors such as the heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), syndecan-1 (SDC1), syndecan-1 (SDC2), the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and scavenger receptor class B type I (SCARB1). The cholesterol transfer activity of SCARB1 allows E2 exposure and binding of E2 to SCARB1 and the tetraspanin CD81. E1/E2 heterodimer binding on CD81 activates the epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway. Diffusion of the complex E1-E2-EGFR-SCARB1-CD81 to the cell lateral membrane allows further interaction with Claudin 1 (CLDN1) and occludin (OCLN) to finally trigger HCV entry.; Forms a heterodimer with envelope glycoprotein E1, which mediates virus attachment to the host cell, virion internalization through clathrin-dependent endocytosis and fusion with host membrane. Fusion with the host cell is most likely mediated by both E1 and E2, through conformational rearrangements of the heterodimer required for fusion rather than a classical class II fusion mechanism. The interaction between envelope glycoprotein E2 and host apolipoprotein E/APOE allows the proper assembly, maturation and infectivity of the viral particles. This interaction is probably promoted via the up-regulation of cellular autophagy by the virus. E1/E2 heterodimer binds host apolipoproteins such as APOB and APOE thereby forming a lipo-viro-particle (LVP). APOE associated to the LVP allows the initial virus attachment to cell surface receptors such as the heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), syndecan-1 (SDC1), syndecan-1 (SDC2), the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and scavenger receptor class B type I (SCARB1). The cholesterol transfer activity of SCARB1 allows E2 exposure and binding of E2 to SCARB1 and the tetraspanin CD81. E1/E2 heterodimer binding on CD81 activates the epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway. Diffusion of the complex E1-E2-EGFR-SCARB1-CD81 to the cell lateral membrane allows further interaction with Claudin 1 (CLDN1) and occludin (OCLN) to finally trigger HCV entry. Inhibits host EIF2AK2/PKR activation, preventing the establishment of an antiviral state. Viral ligand for CD209/DC-SIGN and CLEC4M/DC-SIGNR, which are respectively found on dendritic cells (DCs), and on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and macrophage-like cells of lymph node sinuses. These interactions allow the capture of circulating HCV particles by these cells and subsequent facilitated transmission to permissive cells such as hepatocytes and lymphocyte subpopulations.
-
亚细胞定位:[Core protein precursor]: Host endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein. Host mitochondrion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Envelope glycoprotein E1]: Virion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [Envelope glycoprotein E2]: Virion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host lipid droplet.
-
蛋白家族:Hepacivirus polyprotein family
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
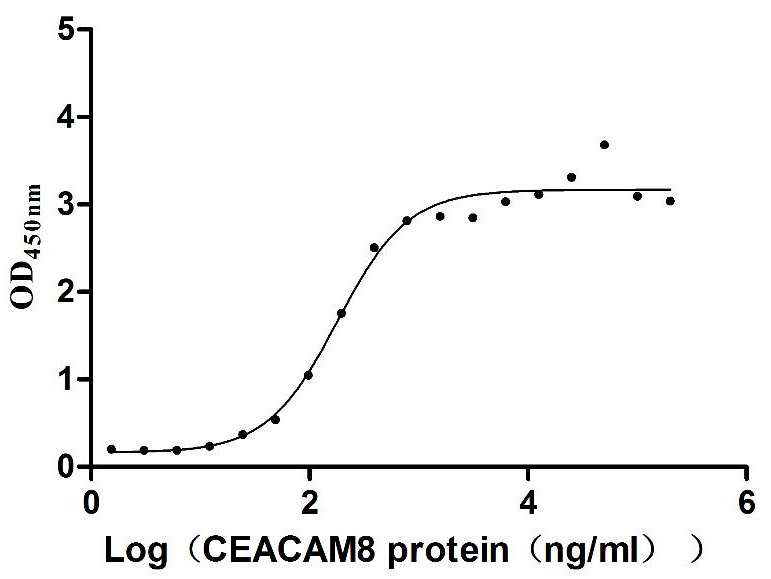
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
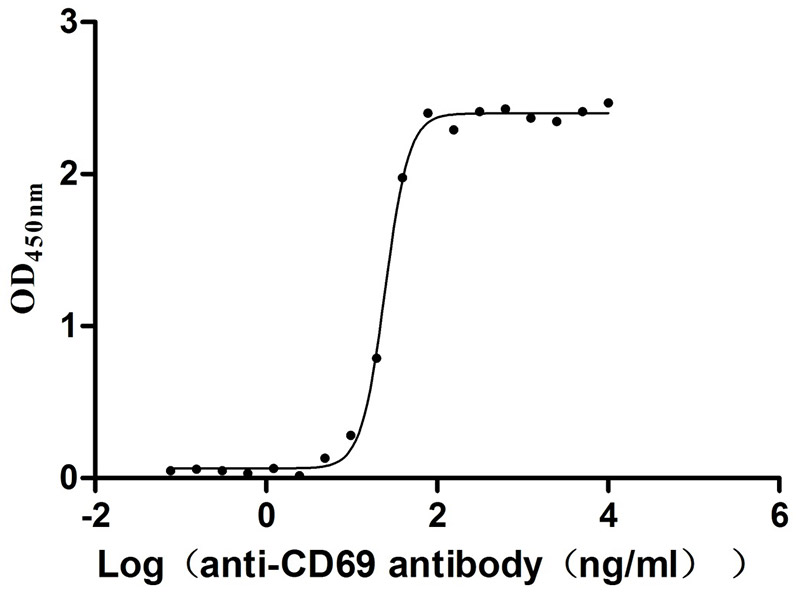
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
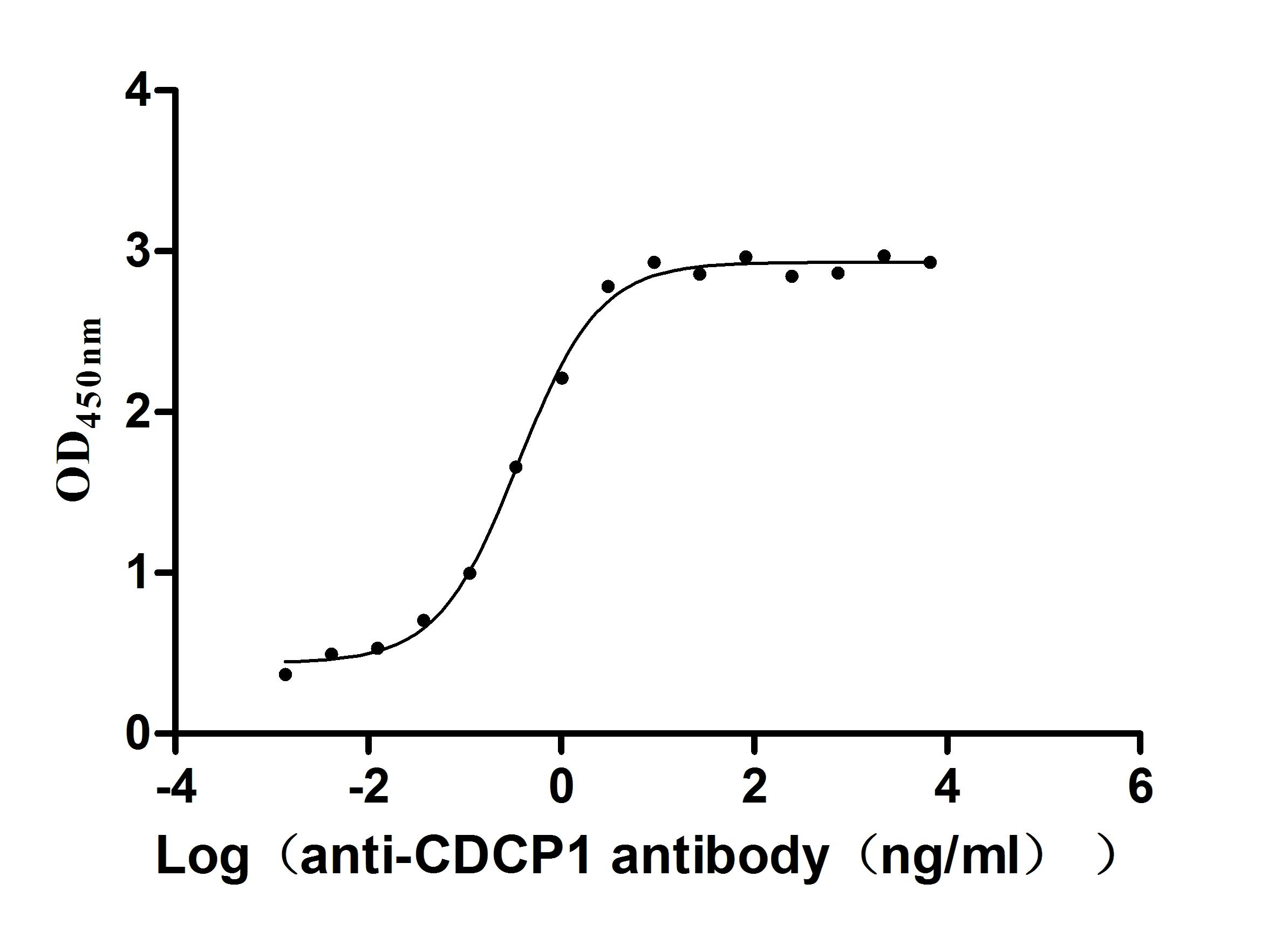
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
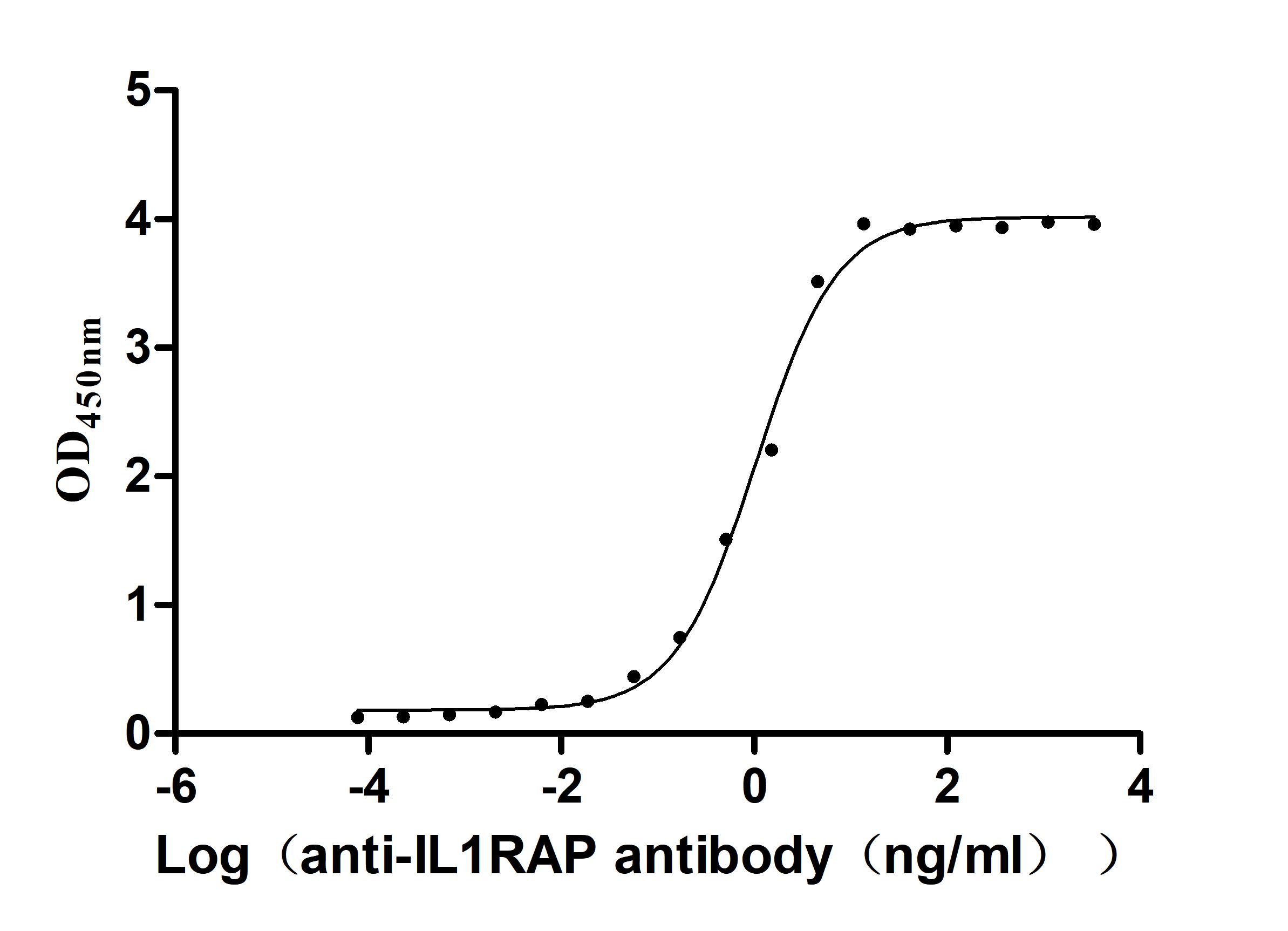
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)