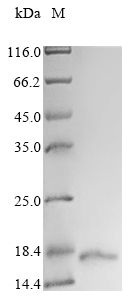
Recombinant Human Apolipoprotein B-100 (APOB), partial
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP001918HUb0
-
规格:¥1344
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Apo B 100; Apo B; Apo B-100; Apo B-48; Apo B100; Apo B48; ApoB 100 ; ApoB 48; APOB; APOB_HUMAN; Apolipoprotein B (including Ag(x) antigen); Apolipoprotein B 100; Apolipoprotein B 48; Apolipoprotein B; Apolipoprotein B-48; Apolipoprotein B100; Apolipoprotein B48; FLDB; LDLCQ4
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:14.7 kDa
-
表达区域:28-127aa
-
氨基酸序列EEEMLENVSLVCPKDATRFKHLRKYTYNYEAESSSGVPGTADSRSATRINCKVELEVPQLCSFILKTSQCTLKEVYGFNPEGKALLKKTKNSEEFAAAMS
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Apolipoprotein B is a major protein constituent of chylomicrons (apo B-48), LDL (apo B-100) and VLDL (apo B-100). Apo B-100 functions as a recognition signal for the cellular binding and internalization of LDL particles by the apoB/E receptor.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- s performed an analysis of public databases and literature for every variant published associated with FH, in the genes LDLR, APOB, and PCSK9. PMID: 29261184
- Targeted next generation DNA sequencing revealed several rare heterozygous missense variants in both MTTP and APOB genes known or predicted to be deleterious, in addition to a novel heterozygous missense variant in SAR1B, which encodes the gene causing chylomicron retention disease PMID: 29540175
- Single nucleotide polymorphisms rs693 and rs6725189 of the apoB gene are associated with calcific aortic stenosis in Chinese subjects, in Xinjiang, China. PMID: 29514644
- In conclusion, this study demonstrated that an APOB SNP, rs1042034, is closely associated with HCV infection through lipid metabolism alteration. PMID: 29382324
- APOB rs11279109 is associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease in Kuwaiti population. PMID: 29362515
- The simultaneous retention of fibrinogen and APOB-lipoproteins in FSD can be detected in routinely stained histological sections. The analysis of protein structures unraveled the pathomorphogenesis of this unexpected phenomenon. Fibrinogen gamma chain mutations provoke conformational changes in the region of the globular domain involved in the "end-to-end" interaction, thus impairing the D-dimer formation PMID: 29244742
- APOB polymorphism rs679899 is associated with type 2 diabetes and glutamyl transpeptidase levels, while the LIPC polymorphism rs6083 may influence plasma lipid levels in Chinese Han population. PMID: 29883758
- We present a case of homozygous familial defective apolipoprotein B-100 due to APOB R3500Q (rs5742904) treated with evolocumab ..Identification of a patient homozygous for familial defective apolipoprotein B-100(FDB) and successful treatment with PCSK9 inhibition PMID: 28988723
- Increased LDL levels were observed over time in patients with the -7673G>A polymorphism of the ApoB gene. PMID: 29846435
- Review/Meta-analysis: significant association of APOB rs1801701 GA, and APOB rs1042031 GA with increased risk of ischemic stroke. PMID: 28865324
- Serum apoB/A-I ratio appears to have value for predicting SAP in patients with AP. PMID: 28677336
- Apolipoprotein B is associated with carotid atherosclerosis progression PMID: 28826575
- Results show differences in the apoB100 secondary structure content among lipoproteins incubated at pH 7.4 or at pH 5.0 that could resemble those occurring in the early or late endosomes, respectively. PMID: 27824107
- Elevated serum apoB levels independently predict an increased risk for incident non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PMID: 28106941
- This study shows that the ApoB-516C/T promoter gene polymorphism has no impact on the risk of hepatitis C virus infection. However, the C/T genotype may be a protective factor for females. PMID: 28370191
- association of TM6SF2 rs58542926 genotype with increased serum tyrosine levels and decreased apoB-100 particles in Finns PMID: 28539357
- that apos involved in TG metabolism such as apoC2, C3, E, and A4 (micromolar concentration), and apoB48 and apoA5 (single-digit nanomolar concentration) can be quantified from a single digestion mixture. PMID: 24694356
- These findings indicate that maternal apo B levels are significantly associated with apo B levels in their pre-school age children, adjusted for confounding variables. Furthermore, the mother-child correlations in apo B levels were independent of mother-child adiposity. Measurement of apo B levels in mothers may identify both high-risk children and mothers who may benefit from intervention. PMID: 28799493
- Individuals with apoB higher than predicted by non-HDL-C had significantly higher levels of PAI-1, which may contribute to the increased risk of future atherothrombotic events PMID: 28502501
- analysis of five likely pathogenic heterozygous rare variants that include four novel nonsense mutations in APOB (p.Gln845*, p.Gln2571*, p.Cys2933* and p.Ser3718*) and a rare variant in PCSK9 (Minor Allele Frequency <0.1%). PMID: 27179706
- In this sample of older adults with mild cognitive impairment, the presence of at least one copy of ApoE4 was associated with the development of both increased gait variability and cognitive decline during 1 year of follow-up PMID: 28482102
- The impact of smoking on the levels of apolipoprotein B (APOB) was evaluated by analyzing data from NHANES for the years 2007-2012 for US adolescents aged 12-19 years and adults aged greater than or eqult to 20 years. The study found that smoking did not influence the observed levels of APOB for either adolescents or adults. PMID: 28672200
- Identify LDLR, APOB and PCSK9 novel mutations causing familial hypercholesterolemia in the central south region of China. PMID: 28235710
- Rare variants of APOB or PCSK9 were identified in nine of the 22 study patients with extremely low LDL-C levels PMID: 29036232
- Eicosapentaenoic acid has direct antioxidant benefits in various apoB-containing subfractions. PMID: 26945158
- Association of plasma apoB with IR in obese subjects is dependent on gynoid WAT dysfunction PMID: 28391908
- Serum ApoB was not significantly different between term SGA newborns and control term newborns. PMID: 28304324
- APOB associated with Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Polygenic Hypercholesterolemia in patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome , age /=160 mg/dl. PMID: 28958330
- we identified common intronic SNPs (rs676210 and rs1042034) in the APOB gene and found five SNPs that were collectively associated with hyperlipidemia in the adult Chinese Yugur population. Importantly, we demonstrated that the G allele of rs676210 may confer an increased risk of hyperlipidemia. PMID: 28902930
- APOB missense variants, A224T and V925L, in a black South African woman with marked hypocholesterolemia PMID: 27206948
- male gender, ageing in women and menopause were associated with increased apoB concentrations. PMID: 27086565
- Data provide no evidence supporting an association between the APOB R3527Q variant and type 2 diabetes or glycemia. PMID: 28428224
- Levels of lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)], a complex between an LDL-like lipid moiety containing one copy of apoB, and apo(a), a plasminogen-derived carbohydrate-rich hydrophilic protein, are primarily genetically rIncreasing evidence suggests that age, sex, and hormonal impact may have a modest modulatory influence on Lp(a) levels. Among clinical conditions, Lp(a) levels are reported to be affected by kidney and liver diseases. PMID: 26637279
- Data suggest that amphipathic beta-strands in 200 N-terminal residues of beta1 domain of APOB are required for secretion of lipid-rich or lipid-poor particles; residues 300-700 or 1050-1500 of beta1 domain appear to be required for secretion of lipid-rich particles; MTTP is required for secretion of intact APOB but not of truncated APOB. (APOB = apolipoprotein B; MTTP = microsomal triglyceride transfer protein) PMID: 28702990
- Basal apoB secretion by BeWo cells supports the concept of basal lipoprotein particle secretion by placental syncytiotrophoblast. PMID: 28487135
- ApoB EcoRI confers a moderate risk for coronary heart disease and the E(-) allele at this locus might be a susceptibility allele for the development of disease (Meta-Analysis) PMID: 27637205
- APOB single nucleotide polymorphism and it's association with LDL cholesterol level and risk of coronary heart disease in Pakistani population PMID: 27112212
- High apoB48 concentration is associated with Atherosclerotic Lesion Progression. PMID: 27487947
- Autoantibodies to oxidized lipoproteins and immune complexes with apoB-100 lipoproteins vary significantly by sex, age, and ethnicity. Higher baseline IgG MDA-LDL titers independently associate with new major adverse cardiovascular events. PMID: 28473443
- miR-548p regulates apoB secretion by targeting its mRNA degradation. PMID: 28336556
- Adolescent girls with obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome have elevated fasting and postprandial plasma triglycerides and ApoB-lipoprotein remnants. PMID: 27997268
- the associations of rs693 and rs562338 polymorphisms representing the Apolipoprotein B locus with endophenotypes (total cholesterol [TC] and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) and phenotypes, were examined. PMID: 27683205
- ApoB100 is indispensable for HCV infection. ApoB is required for the generation of fully infectious HCV virions. PMID: 28018102
- a higher inflammatory status is associated with decreased triglyceride-rich-rich lipoprotein apoB-48 secretion among insulin resistant subjects PMID: 28183448
- Several protein markers were also deregulated in extracellular vesicless from bladder tumour patients, and our data suggest that the presence of ApoB in the 100,000 pellet is a clear marker for malignancy. PMID: 27751843
- 10 association studies for Han Chinese, with 1195 CHD patients and 1178 healthy subjects, we found that XbaI (rs693) polymorphisms in APOB were statistically significantly associated with Coronary Heart Disease in Han Chinese population PMID: 27172140
- We observed a significant interaction between Ins/Del ApoB genotype and dietary omega-3 PUFA intake with respect to BMI, WC, and obesity risk in both unadjusted (P = 0.007, P = 0.001, and P = 0.021, respectively) and adjusted (P = 0.007, P = 0.04, and P = 0.002, respectively) samples in NIDDM patients. PMID: 27210509
- Multiple novel LDLR and ApoB mutations have been identified in a-United Kingdom-based cohort with familial hypercholesterolemia. PMID: 26748104
- Data suggest that LDL-C/apoB ratio (ratio of plasma level of total cholesterol to plasma level of apolipoprotein B) is an important biomarker in overall evaluation of atherogenicity in obese, overweight, and normal-weight men; this study of qualitative changes in lipid/lipoprotein profile for early diagnosis of dyslipidemias leading to atherosclerosis was conducted in Russia. PMID: 27347637
- Mutations in APOB is associated with hypobetalipoproteinemia. PMID: 26916057
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Hypobetalipoproteinemia, familial, 1 (FHBL1); Familial ligand-defective apolipoprotein B-100 (FDB)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Secreted. Lipid droplet.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 603
OMIM: 107730
KEGG: hsa:338
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000233242
UniGene: Hs.120759
Most popular with customers
-
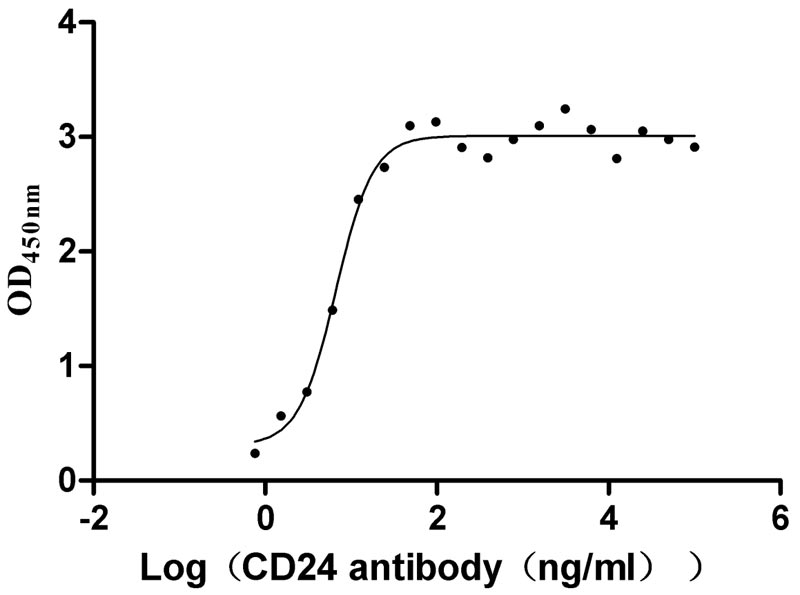
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
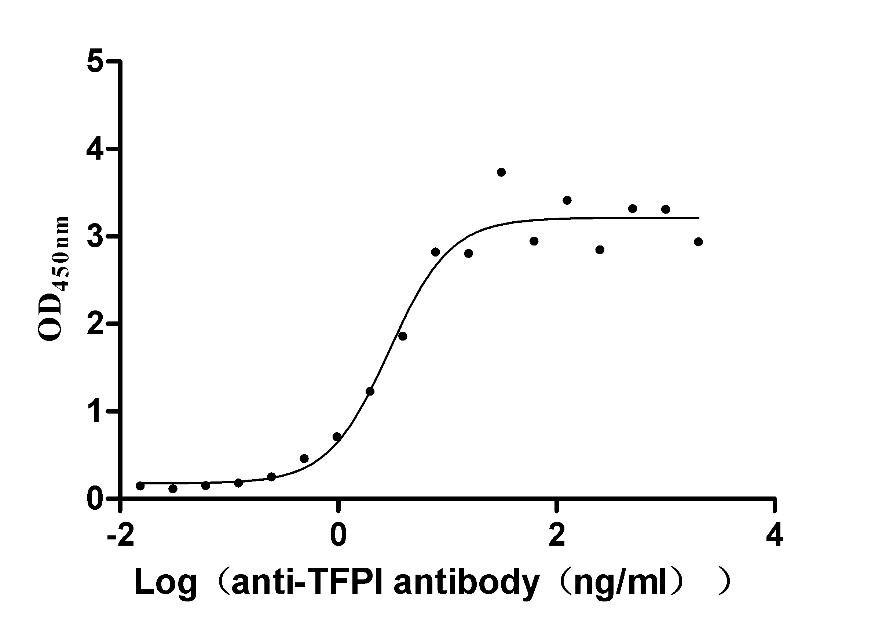
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
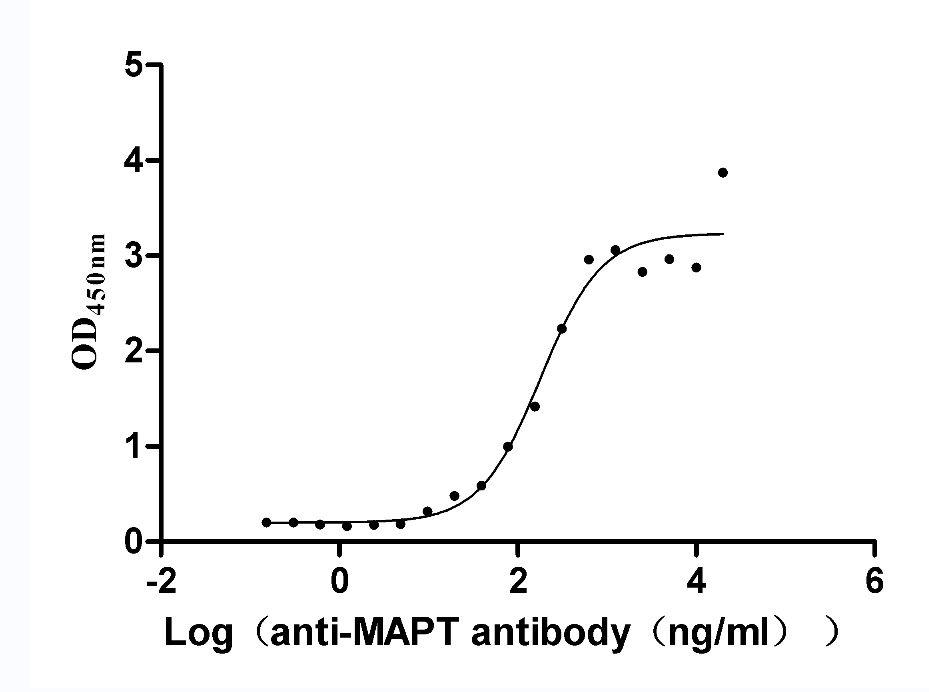
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
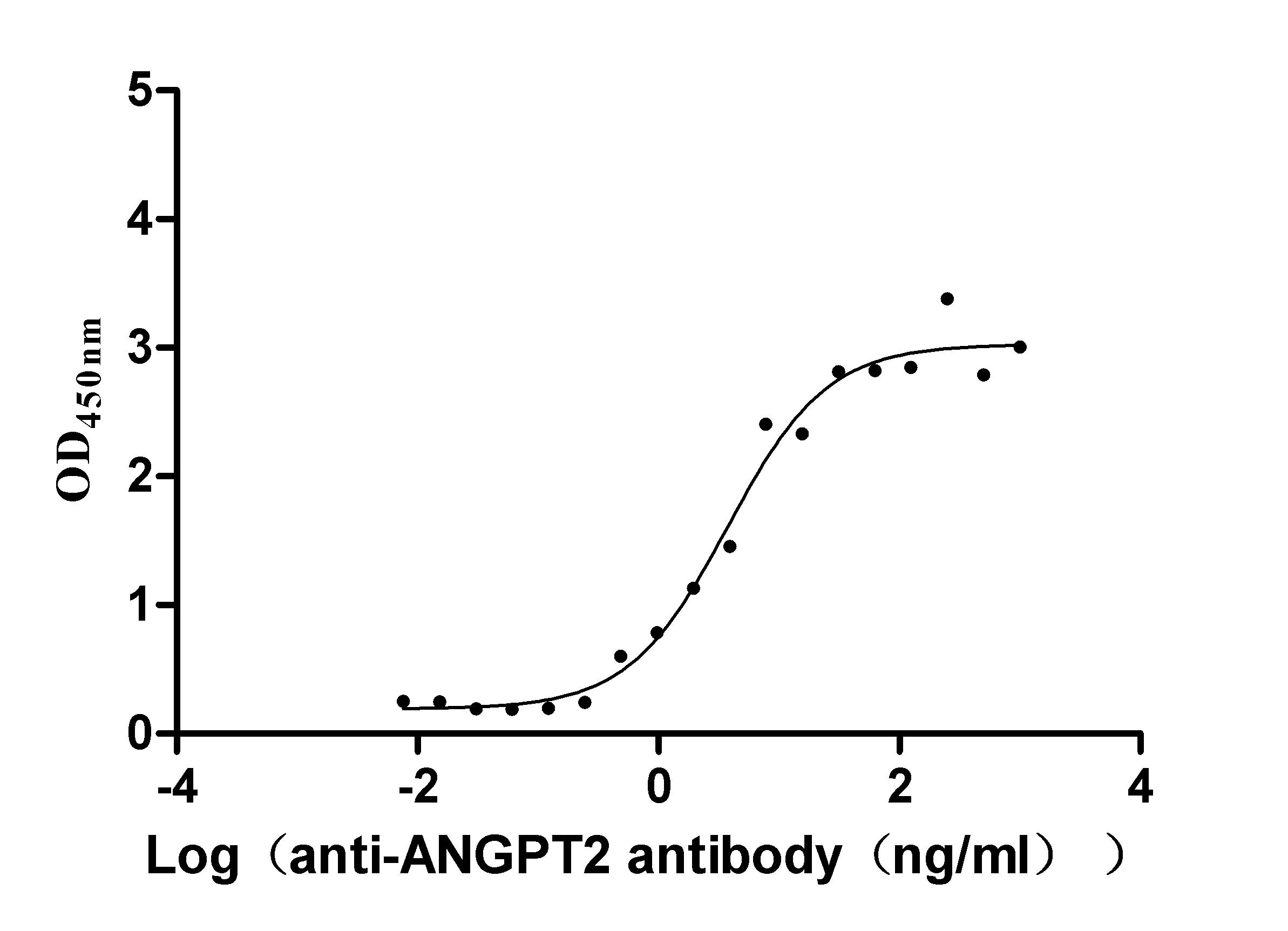
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
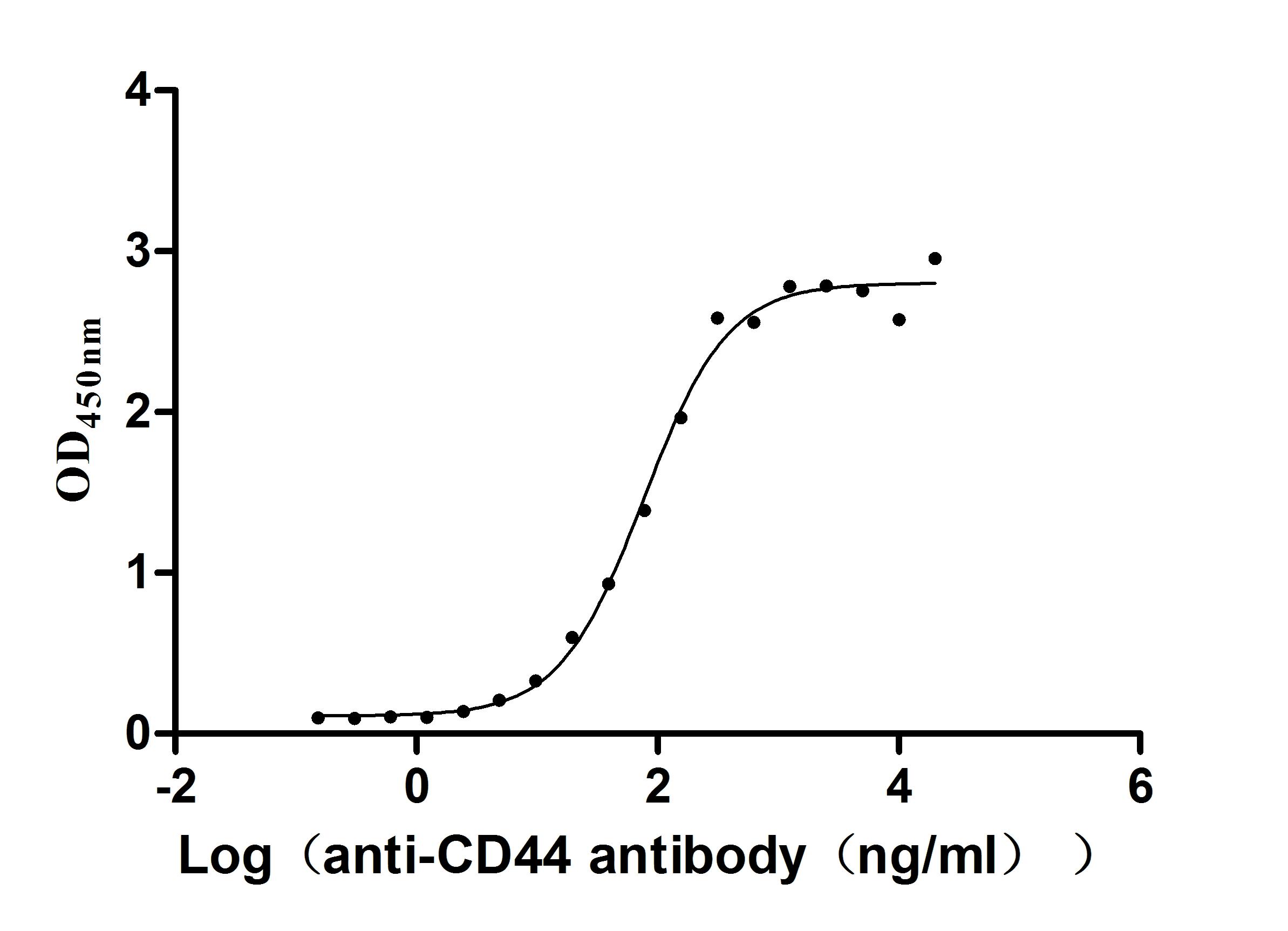
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
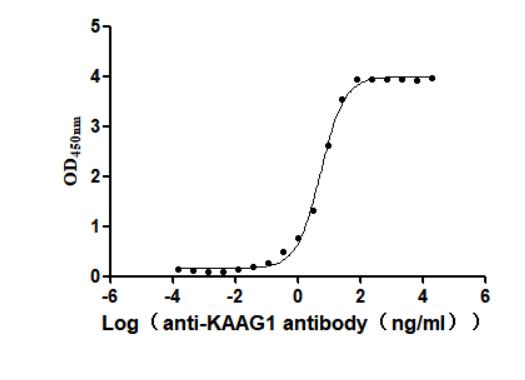
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
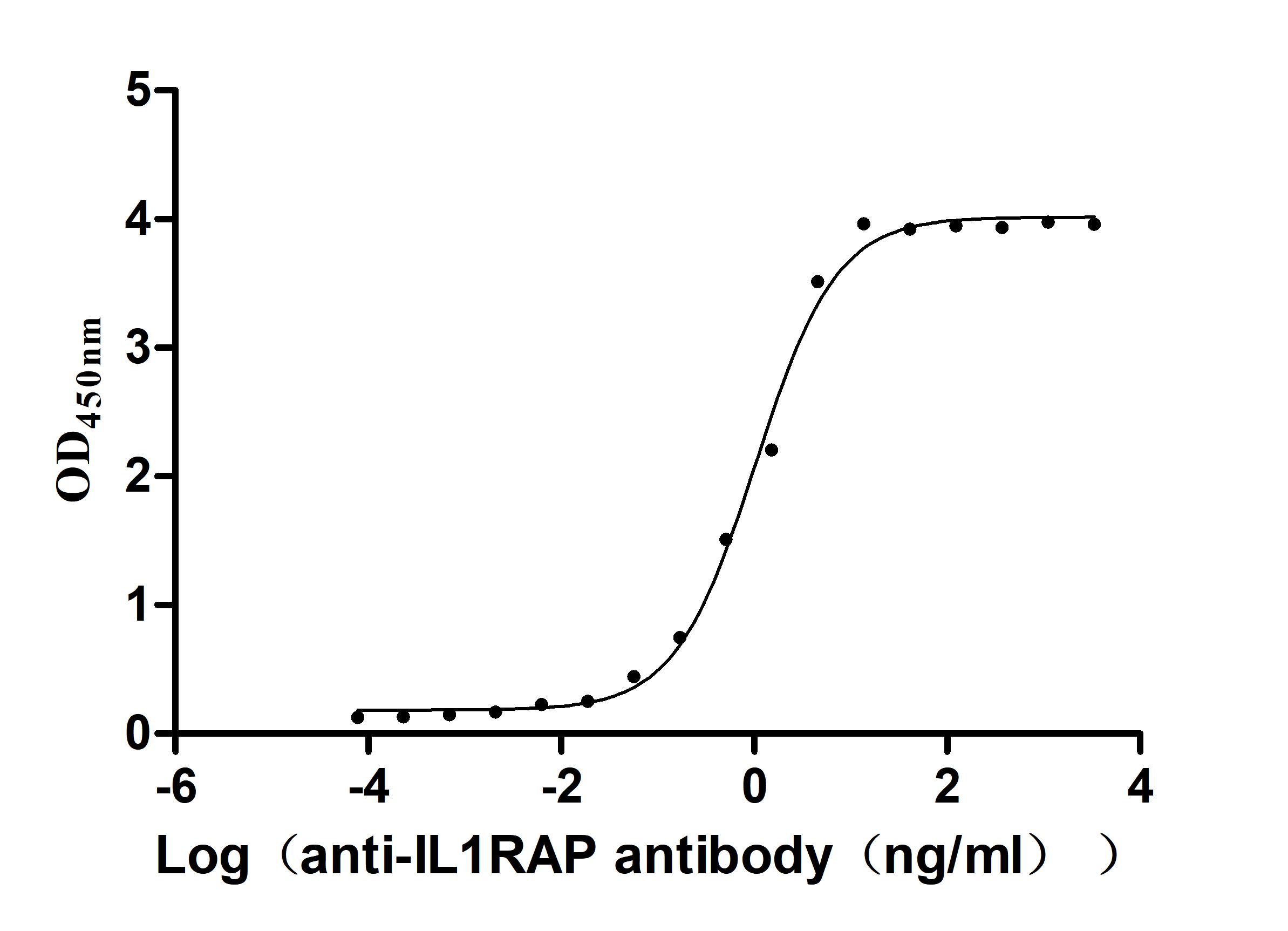
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)