Recombinant Human Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1)
-
货号:CSB-YP001940HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP001940HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP001940HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP001940HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP001940HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:APOL1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:APO L; Apo-L; ApoL; APOL I; ApoL-I; APOL1; APOL1_HUMAN; APOLI; Apolipoprotein L; Apolipoprotein L I; Apolipoprotein L-I; Apolipoprotein L1; FSGS4
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:28-398
-
氨基酸序列EEA GARVQQNVPS GTDTGDPQSK PLGDWAAGTM DPESSIFIED AIKYFKEKVS TQNLLLLLTD NEAWNGFVAA AELPRNEADE LRKALDNLAR QMIMKDKNWH DKGQQYRNWF LKEFPRLKSE LEDNIRRLRA LADGVQKVHK GTTIANVVSG SLSISSGILT LVGMGLAPFT EGGSLVLLEP GMELGITAAL TGITSSTMDY GKKWWTQAQA HDLVIKSLDK LKEVREFLGE NISNFLSLAG NTYQLTRGIG KDIRALRRAR ANLQSVPHAS ASRPRVTEPI SAESGEQVER VNEPSILEMS RGVKLTDVAP VSFFLVLDVV YLVYESKHLH EGAKSETAEE LKKVAQELEE KLNILNNNYK ILQADQEL
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
问答及客户评论
We are interested in this product (all expression systems), but we would like it without the tag. Can you provide this product without the tag?
Recombinant Human Apolipoprotein L1(APOL1)
CSB-YP001940HU >> Yeast
CSB-EP001940HU >> E.coli
CSB-BP001940HU >> Baculovirus
CSB-MP001940HU >> Mammalian cell
Expression Region: 28-398aa; Full length of the mature protein.
Tag information:EP, YP, BP, MP: Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The expected tag for each expression system is listed as follows:
YP: N-terminal 6xHis-tagged; EP, BP, MP: N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged.
Target Protein Sequence:
EEAGARVQQNVPSGTDTGDPQSKPLGDWAAGTMDPESSIFIEDAIKYFKEKVSTQNLLLLLTDNEAWNGFVAAAELPRNEADELRKALDNLARQMIMKDKNWHDKGQQYRNWFLKEFPRLKSELEDNIRRLRALADGVQKVHKGTTIANVVSGSLSISSGILTLVGMGLAPFTEGGSLVLLEPGMELGITAALTGITSSTMDYGKKWWTQAQAHDLVIKSLDKLKEVREFLGENISNFLSLAGNTYQLTRGIGKDIRALRRARANLQSVPHASASRPRVTEPISAESGEQVERVNEPSILEMSRGVKLTDVAPVSFFLVLDVVYLVYESKHLHEGAKSETAEELKKVAQELEEKLNILNNNYKILQADQEL
Please remark your requirement for tag removal if you need the untagged protein or tag removal when placing the order.
We can try enzyme digestion, we are sure the C-terminal tag can be removed, but we can't 100% guarantee N-terminal tag can be removed successfully.
The overall success rate of enzyme digestion data analysis is 75%-86%.
a. Not all protein tags can be removed as some proteins will be very unstable after tag removal.
b. If we succeed in removing the tag, we will charge for extra cost accordingly.
c. If we fail in removing the tag, we won’t charge for any extra cost and provide the fusion protein, and remark this information in datasheet as follows
“Note: The laboratory determined that the Tag on your protein could not be removed with standard laboratory procedures. Your protein is being supplied with the Tag intact.”
Generally, the delivery time will be extended for 3 working days.
靶点详情
-
功能:May play a role in lipid exchange and transport throughout the body. May participate in reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral cells to the liver.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Plasma concentrations of TNFR1, TNFR2, and KIM1 are independently associated with renal outcome and improve discrimination or reclassification of African ancestry individuals with a high-risk APOL1 genotype and preserve renal function. PMID: 29685497
- APOL1 risk variants did not associate with subclinical markers of atherosclerosis or left ventricular hypertrophy in middle-aged black adults with preserved kidney function. PMID: 29042080
- Review of the role of APOL1 in kidney disease in children and young adults of African ancestry. APOL1 explains almost 70% of the excess risk of kidney disease in those of African descent, and is common in children with glomerular disease. PMID: 29406442
- Association of chronic kidney disease with APOL1 risk alleles was not identified in Aboriginal people in remote areas of Australia. PMID: 28314584
- APOL1 Risk Variant is associated with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. PMID: 29531077
- APOL1, alpha-thalassemia, and BCL11A variants as a genetic risk profile for progression of chronic kidney disease in sickle cell anemia. PMID: 27658436
- Among blacks with established moderate CKD, the APOL1 high-risk variants are associated with greater risk of incident proteinuria. After proteinuria onset, kidney function declines more rapidly but does not differ by APOL1 risk status. PMID: 29051146
- In individuals at risk for nondiabetic kidney disease based on African ancestry, the majority of that risk can be explained by two variants in the APOL1 gene. PMID: 29110756
- Considering APOL1 evolution also may help us understand how APOL1 risk variants cause kidney disease in modern humans. PMID: 29110757
- APOL1 variants are associated with HIV-associated nephropathy(HIVAN), a podocyte disease,but not with HIV-immune complex disease, primarily a disease of the mesangium. PMID: 29110758
- the associations of the APOL1 risk variants with microalbuminuria, incident CKD, and subsequent kidney function decline implicate a potential role in both the development and progression of CKD. Unlike the consistent association with CKD, the association of the APOL1 risk variants with cardiovascular disease is less clear. PMID: 29110759
- The presence of two APOL1 renal risk variants in deceased donors shortens survival of their renal allografts. No study has examined the potential interaction of APOL1 genotype of the donors, deceased or living, and recipients. PMID: 29110760
- expression of G1 or G2 APOL1 results in significantly more cell death compared with wild-type APOL1 (G0) in various human cells in culture PMID: 29110762
- Genetic variant in apolipoprotein L1 is not associated with preterm birth in African American population. PMID: 27638911
- This is the first report of a specific association of APOL1 with small vessel disease (SVD) ischemic stroke. PMID: 28975602
- study found strong evidence for no association with Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense Human African trypanosomiasis and APOL1 G2 in two Ugandan populations PMID: 29470556
- APOL1 variants are not associated with longitudinal blood pressure in blacks. PMID: 28545715
- Letter: no APOL1 risk allele variants in Indian patients with chronic kidney disease. PMID: 27633872
- APOL1 copy number variations may be not associated with susceptibility to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in Chinese population. PMID: 28494221
- APOL1 Genetic Variations are associated with acute rejection. PMID: 27862962
- These results implicate both forms of human African trypanosomiasis in the selection and persistence of otherwise detrimental APOL1 kidney disease variants. PMID: 28537557
- APOL1 variant is associated with End-Stage Renal Disease. PMID: 27588375
- The enhanced expression of GRP78 by podocytes expressing APOL1 variants would indicate endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. PMID: 28385815
- Among patients with CKD attributed to hypertension, those with the APOL1 high-risk genotype were more likely to experience a steady decline trajectory in eGFR than those without the APOL1 high-risk genotype. These findings suggest a persistent underlying pathophysiologic process in those patients with the APOL1 high-risk genotype. PMID: 27230965
- APOL1 Gene variation is associated with end-stage renal disease. PMID: 27997071
- Apolipoprotein L1 and apolipoprotein A-IV and their association with kidney function PMID: 27870653
- Data suggest that APOL1 confers chloride-selective permeability to preformed phospholipid vesicles; this selectivity is strongly pH-sensitive, with maximal activity at pH 5 and little activity above pH 7; APOL1 permease activity requires calcium ions; APOL1 stably associates with phospholipid vesicles, requiring low pH and presence of negatively charged phospholipids for maximal binding. PMID: 28918394
- Strict blood pressure control during chronic kidney disease associates with a lower risk of death in blacks with the high-risk CKD APOL1 genotype. PMID: 27927600
- Divergent intracellular biological pathways of ancestral and variant APOL1 may explain a worsened prognosis as demonstrated in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. PMID: 28265848
- Roles of APOL1 G1 and G2 variants in sickle cell disease patients: kidney is the main target. PMID: 28699644
- Two APOL1 renal-risk variants are associated with longer dialysis survival in African Americans with non-diabetic end-stage renal disease. PMID: 27157696
- The frequency of APOL1 risk variants ranged from 7.0% to 11.0%. PMID: 28732083
- The synergy of circulating factor suPAR and APOL1 G1 or G2 on alphavbeta3 integrin activation is a mechanism for CKD. PMID: 28650456
- Among African Americans with hypertension-attributed chronic kidney disease, APOL1 risk variants were not associated with an overall risk for cardiovascular disease although some signals for cardiovascular mortality were noted. PMID: 28572159
- The proteomic profile of apoL1 is modified in HDLs of high cardiovascular risk patients, and apoL1 plasma levels are significantly lower in serum and in HDL3 of patients that will suffer an adverse cardiac event within 3 years. PMID: 27112635
- Relationships between APOL1 kidney risk variants and cardiovascular disease (CVD) susceptibility and CVD-related death remain controversial. Some studies detected an increased risk for CVD, whereas others support protection from death and subclinical CVD and cerebrovascular disease PMID: 28143671
- mice with podocyte-specific expression of either APOL1 risk allele (G1 or G2), but not of the G0 allele, develop functional (albuminuria and azotemia), structural (foot-process effacement and glomerulosclerosis) and molecular (gene-expression) changes that closely resemble human kidney disease. Expression of the risk-variant APOL1 alleles interferes with endosomal trafficking and blocks autophagic flux. PMID: 28218918
- APOL1 single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with nephropathy. PMID: 26152403
- risk alleles are associated with higher systolic blood pressure and earlier hypertension diagnoses in young African Americans PMID: 28335839
- We report an unadjusted incidence of 1.2 CKD cases/100 person-years (95% CI: 0.5 to 2.5) in PHIV youth carrying APOL1 high-risk genotypes, with important implications for sub-Saharan Africa PMID: 27035887
- Overall, our results suggest podocyte depletion could predispose individuals with APOL1 risk genotypes to kidney disease in response to a second stressor, and add to other published evidence associating APOL1 expression with preeclampsia PMID: 27026370
- This new Drosophila model uncovers a novel mechanism by which upregulated expression of APOL1-G1 could precipitate renal disease in humans. PMID: 27864430
- Results suggest a pivotal role for mitochondrial dysfunction in APOL1-associated kidney disease PMID: 27821631
- Among blacks, the APOL1 high-risk genotype associated only with higher risk of end-stage renal disease in a fully adjusted analysis. Black race and APOL1 high-risk status were associated with faster eGFR decline PMID: 26966015
- GSTM1 null and APOL1 high-risk alleles deleteriously affect chronic kidney disease progression among blacks with hypertension, and subjects with both GSTM1 null and APOL1 high-risk genotypes had highest risk of adverse renal outcomes PMID: 26940095
- Our findings indicate that the presence of risk disease risk variants of APOL1 is permissive of HIV-1 persistence in human podocytes in synergy with IL-1beta, a cytokine that characterizes the inflammatory milieu of acute and chronic phases of HIV-1 infection. PMID: 27599995
- We show that the levels of one member of the family, apolipoprotein L1 (apoL1) is higher in papillary thyroid carcinoma compared to normal tissue. PMID: 27157405
- APOL1 genotype may provide additional diagnostic information to traditional clinical variables in predicting underlying FSGS spectrum lesions in blacks who are HIV positive. PMID: 26668025
- The homozygous N264K ApoL1 variant may be at increased risk of contracting human African trypanosomiasis. PMID: 27073096
- We examined whether APOL1 G1 and G2 renal-risk variant serum concentrations or lipoprotein distributions differed from nonrisk G0 APOL1 in African Americans without nephropathy. PMID: 26586272
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis 4 (FSGS4)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Apolipoprotein L family
-
组织特异性:Plasma. Found on APOA-I-containing high density lipoprotein (HDL3). Expressed in pancreas, lung, prostate, liver, placenta and spleen.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 618
OMIM: 603743
KEGG: hsa:8542
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000317674
UniGene: Hs.114309
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
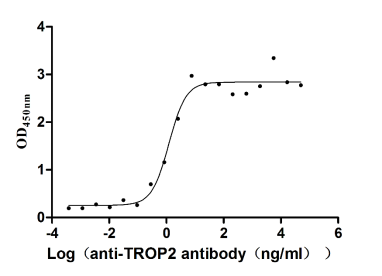
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
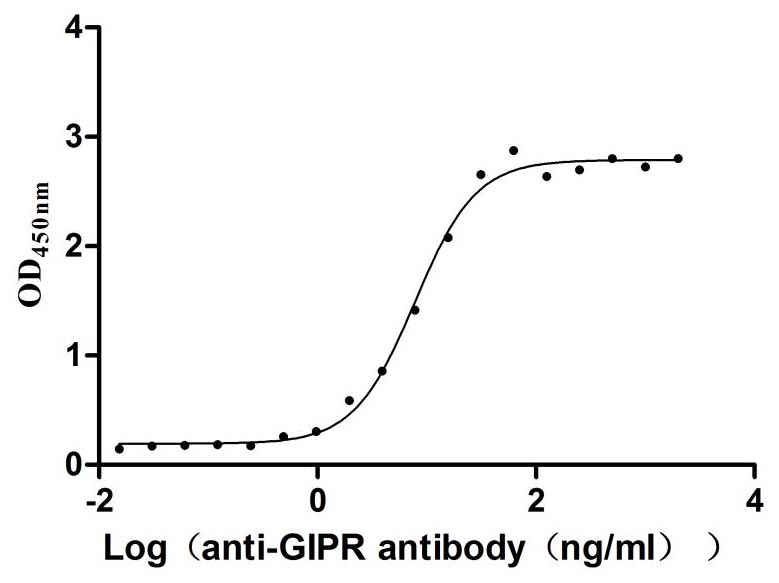
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
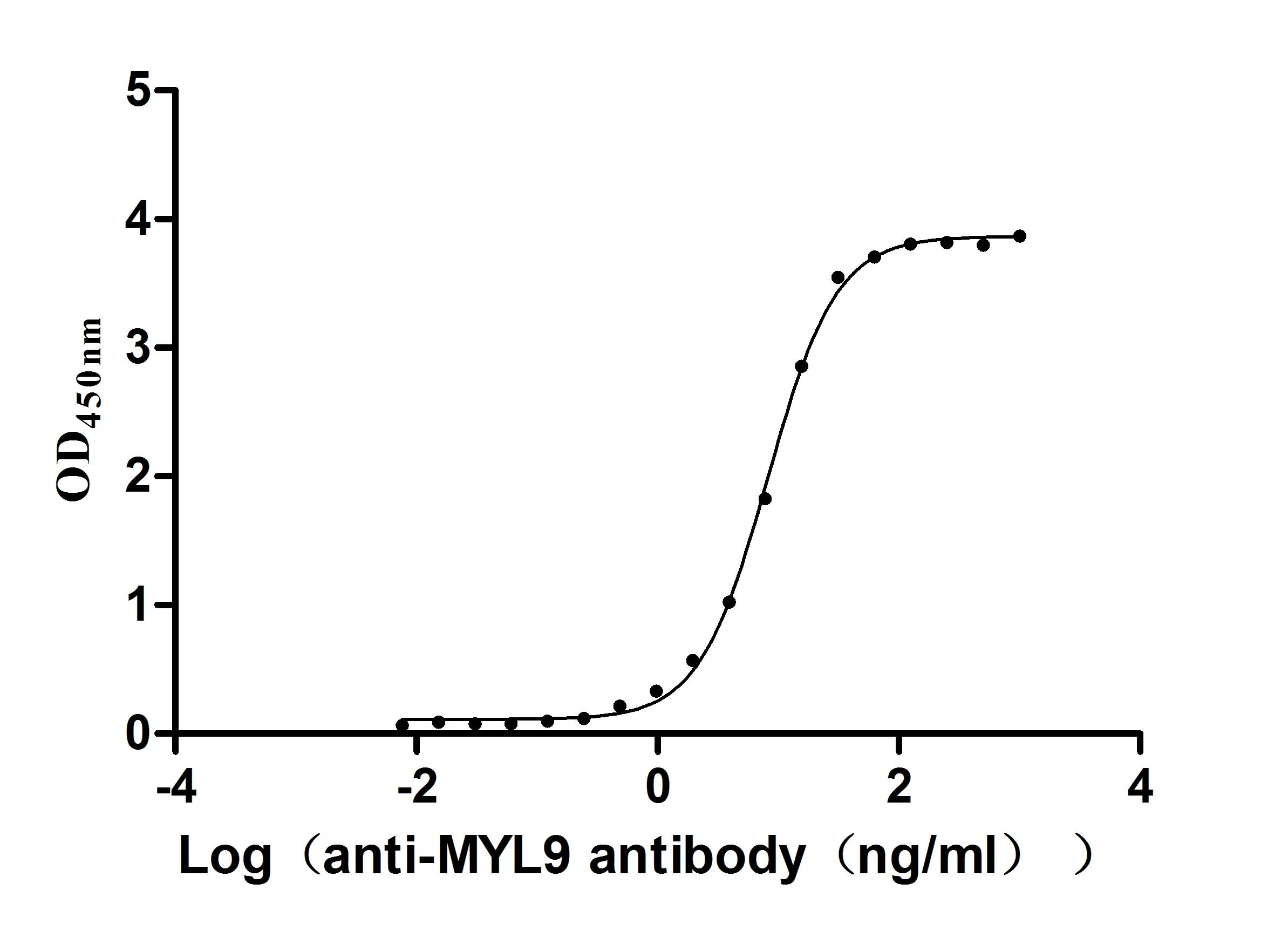
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)