Recombinant Human Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
-
货号:CSB-YP361848HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP361848HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP361848HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP361848HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cdc 2; Cdc2; CDC28A; CDK 1; CDK1; CDK1_HUMAN; CDKN1; CELL CYCLE CONTROLLER CDC2; Cell division control protein 2; Cell division control protein 2 homolog; Cell division cycle 2 G1 to S and G2 to M; Cell division protein kinase 1; Cell Divsion Cycle 2 Protein; Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1; Cyclin-dependent kinase 1; DKFZp686L20222; MGC111195; p34 Cdk1; p34 protein kinase; P34CDC2
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-297
-
氨基酸序列MEDYTKIEKI GEGTYGVVYK GRHKTTGQVV AMKKIRLESE EEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELRH PNIVSLQDVL MQDSRLYLIF EFLSMDLKKY LDSIPPGQYM DSSLVKSYLY QILQGIVFCH SRRVLHRDLK PQNLLIDDKG TIKLADFGLA RAFGIPIRVY THEVVTLWYR SPEVLLGSAR YSTPVDIWSI GTIFAELATK KPLFHGDSEI DQLFRIFRAL GTPNNEVWPE VESLQDYKNT FPKWKPGSLA SHVKNLDENG LDLLSKMLIY DPAKRISGKM ALNHPYFNDL DNQIKKM
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays a key role in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle by modulating the centrosome cycle as well as mitotic onset; promotes G2-M transition, and regulates G1 progress and G1-S transition via association with multiple interphase cyclins. Required in higher cells for entry into S-phase and mitosis. Phosphorylates PARVA/actopaxin, APC, AMPH, APC, BARD1, Bcl-xL/BCL2L1, BRCA2, CALD1, CASP8, CDC7, CDC20, CDC25A, CDC25C, CC2D1A, CENPA, CSNK2 proteins/CKII, FZR1/CDH1, CDK7, CEBPB, CHAMP1, DMD/dystrophin, EEF1 proteins/EF-1, EZH2, KIF11/EG5, EGFR, FANCG, FOS, GFAP, GOLGA2/GM130, GRASP1, UBE2A/hHR6A, HIST1H1 proteins/histone H1, HMGA1, HIVEP3/KRC, LMNA, LMNB, LMNC, LBR, LATS1, MAP1B, MAP4, MARCKS, MCM2, MCM4, MKLP1, MYB, NEFH, NFIC, NPC/nuclear pore complex, PITPNM1/NIR2, NPM1, NCL, NUCKS1, NPM1/numatrin, ORC1, PRKAR2A, EEF1E1/p18, EIF3F/p47, p53/TP53, NONO/p54NRB, PAPOLA, PLEC/plectin, RB1, TPPP, UL40/R2, RAB4A, RAP1GAP, RCC1, RPS6KB1/S6K1, KHDRBS1/SAM68, ESPL1, SKI, BIRC5/survivin, STIP1, TEX14, beta-tubulins, MAPT/TAU, NEDD1, VIM/vimentin, TK1, FOXO1, RUNX1/AML1, SAMHD1, SIRT2 and RUNX2. CDK1/CDC2-cyclin-B controls pronuclear union in interphase fertilized eggs. Essential for early stages of embryonic development. During G2 and early mitosis, CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation activates CDK1/cyclin complexes which phosphorylate several substrates that trigger at least centrosome separation, Golgi dynamics, nuclear envelope breakdown and chromosome condensation. Once chromosomes are condensed and aligned at the metaphase plate, CDK1 activity is switched off by WEE1- and PKMYT1-mediated phosphorylation to allow sister chromatid separation, chromosome decondensation, reformation of the nuclear envelope and cytokinesis. Inactivated by PKR/EIF2AK2- and WEE1-mediated phosphorylation upon DNA damage to stop cell cycle and genome replication at the G2 checkpoint thus facilitating DNA repair. Reactivated after successful DNA repair through WIP1-dependent signaling leading to CDC25A/B/C-mediated dephosphorylation and restoring cell cycle progression. In proliferating cells, CDK1-mediated FOXO1 phosphorylation at the G2-M phase represses FOXO1 interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and thereby promotes FOXO1 nuclear accumulation and transcription factor activity, leading to cell death of postmitotic neurons. The phosphorylation of beta-tubulins regulates microtubule dynamics during mitosis. NEDD1 phosphorylation promotes PLK1-mediated NEDD1 phosphorylation and subsequent targeting of the gamma-tubulin ring complex (gTuRC) to the centrosome, an important step for spindle formation. In addition, CC2D1A phosphorylation regulates CC2D1A spindle pole localization and association with SCC1/RAD21 and centriole cohesion during mitosis. The phosphorylation of Bcl-xL/BCL2L1 after prolongated G2 arrest upon DNA damage triggers apoptosis. In contrast, CASP8 phosphorylation during mitosis prevents its activation by proteolysis and subsequent apoptosis. This phosphorylation occurs in cancer cell lines, as well as in primary breast tissues and lymphocytes. EZH2 phosphorylation promotes H3K27me3 maintenance and epigenetic gene silencing. CALD1 phosphorylation promotes Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration. CDK1-cyclin-B complex phosphorylates NCKAP5L and mediates its dissociation from centrosomes during mitosis. Regulates the amplitude of the cyclic expression of the core clock gene ARNTL/BMAL1 by phosphorylating its transcriptional repressor NR1D1, and this phosphorylation is necessary for SCF(FBXW7)-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NR1D1. Phosphorylates EML3 at 'Thr-881' which is essential for its interaction with HAUS augmin-like complex and TUBG1.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes and facilitates its cell entry.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our results indicate that MCM7 may exert certain functions on spindle formation to prevent cytokinesis during early mitosis by regulating CDK1 activity. PMID: 28588300
- Results demonstrated that CDK1 was increased in human breast cancer and promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle in breast cancer cell lines. PMID: 30272324
- A CDK1-dependent regulation of the WRN-DNA2-mediated resection and identify a new function of WRN as a DSB repair pathway switch are reported. PMID: 27634057
- High CDK1 expression is associated with HIV-1 infection. PMID: 29084722
- the miR-181a was down-regulated in NSCLC and miR-181a inhibited the cell proliferation by regulating CDK1 expression. PMID: 28946554
- Thus, Cyclin A/Cdk1 phosphorylation primes MYPT1 for Plk1 binding. These data demonstrate cross-regulation between Cyclin A/Cdk1-dependent and Plk1-dependent phosphorylation of substrates during mitosis to ensure efficient correction of kinetochore microtubule attachment errors necessary for high mitotic fidelity. PMID: 29154753
- It has been suggested that through interaction with miR-490-3p DLEU1 may influence the expression of CDK1, CCND1 and SMARCD1 protein, subsequently promoting the development and progression of ovarian carcinoma. PMID: 28598010
- The present study suggested that abnormal activation of CDK1 was implicated in the proliferation and apoptosis regulation of ovarian cancer cells, which might due to the aberrant regulations of the upstream Chk1-CDC25C and P53-P21WAF1 signaling pathway. PMID: 28899430
- CDK1-mediated mitotic phosphorylation of PDZ-binding kinase is involved in cytokinesis and inhibits its oncogenic activity. PMID: 28780319
- DNM2 is a substrate for CDK1-dependent phosphorylation, which plays an important role in the regulation of human sperm acrosomal exocytosis. PMID: 29044420
- These findings suggest that Cdc2 is positively associatd with the development of taxol resistance. The Cdc2 inhibitor, purvalanol A, enhanced the cytotoxic effects of taxol through Op18/stathmin. PMID: 28534969
- With tissue microarrays of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, we determined the prognostic values of the core genes in the network and found that RAD21, CDK1, and HDAC2 expression levels were negatively associated with overall survival for HCC patients. The multivariate Cox regression analyses suggested that CDK1 was an independent prognostic factor, which was validated in an independent case cohort. PMID: 28434945
- this study shows that CDK1 is a prognostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma PMID: 27835911
- cytoplasmic Cdk1 expression is elevated in ovarian cancer and predicts a poor overall survival PMID: 27385216
- findings demonstrate the involvement of consensus Cdk1 phosphorylation sites on Mis18 complex assembly and thus provide a rationale for cell cycle-regulated timing of Mis18 assembly and CENP-A deposition PMID: 28377371
- S130 of p21 is phosphorylated by Cdk1/cyclin B1 during mitosis, which reduces p21's stability and binding affinity to Cdk1/cyclin B1 PMID: 27384476
- Findings suggest that mitotic CDK1-directed phosphorylation of delta-4E-BP1 may yield a gain of function, distinct from translation regulation, that may be important in tumorigenesis and mitotic centrosome function. PMID: 27402756
- The s demonstrate that CDK1 controls Mis18 complex recruitment to centromeres by regulating oligomerization of M18BP1 through the Mis18alpha:Mis18beta scaffold. PMID: 28059702
- These data show that complementary mechanisms, such as mother-daughter centriole proximity and CDK1-CyclinB interaction with centriolar components, ensure that centriole biogenesis occurs once and only once per cell cycle, raising parallels to the cell-cycle regulation of DNA replication and centromere formation. PMID: 27112295
- Residual Cdk1/Cdk2 activity after DNA damage promotes cell senescence. PMID: 28345297
- evidence that CDK1/2 participate in the regulation of constitutive pre-mRNA splicing by EGF stimulation in MDA-MB-468 cells. PMID: 27109354
- our study demonstrate that KCTD12 binds to CDC25B and activates CDK1 and Aurora A to facilitate the G2/M transition and promote tumorigenesis and that Aurora A phosphorylates KCTD12 at serine 243 to trigger a positive feedback loop, thereby potentiating the effects of KCTD12. Thus, the KCTD12-CDC25B-CDK1-Aurora A axis has important implications for cancer diagnoses and prognoses. PMID: 28869606
- FOXM1 may play a central role in the skp2-cdk1 loop driving tumor progression. PMID: 27684411
- TRAP1 is relevant in the control of key cell cycle regulators in tumor cells. TRAP1/TBP7 quality control of CDK1 and MAD2 contributes mechanistically to the regulation of mitotic entry and transit. PMID: 28678347
- The Vgll4 is phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) during antimitotic drug-induced mitotic arrest and also in normal mitosis. PMID: 28739871
- Results suggest that the cyclin-dependent kinase I (CDK1) phosphotyrosine (pTyr15) protein is a potential indicator of the progression of colorectal cancer. PMID: 27383761
- These results suggest that inhibition of CDK-1 in G2 causes unpredicted effects in mitosis, even after CDK-1 inhibition is relieved. PMID: 27281342
- Date show that when Wee1 alone is inhibited, Chk1 suppresses CDC45 loading and thereby limits the extent of unscheduled replication initiation and subsequent S-phase DNA damage, despite very high CDK-activity. PMID: 28030798
- CDK1 is a positive regulator of the IFN signaling pathway. The overexpression of CDK1 might contribute to the abnormally amplified type I IFN signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus. PMID: 26663909
- the mechanism of Plk1 activation and the potential role of Bora phosphorylation by Cdk1, is reported. PMID: 27831827
- The data presented here suggest that the temporal separation of pro- and anti-apoptotic pathways by selective inhibition of CDK2 disrupts coherent signaling modules and may synergize with anti-proliferative drugs, averting toxic side effects from CDK1 inhibition. PMID: 27831832
- Study greatly increases the known substrate space of Cdk1 and adds to the understanding of how mitotic progression is regulated by Cdk1-dependent phosphorylation pathways. PMID: 27134283
- periodic phosphorylation of Ku70 by cyclin-cyclin dependent kinases prevents the interaction of Ku with replication origin after initiation events in S-phase. PMID: 27402161
- inhibition of sumoylation increases the activity of CDK1. PMID: 27520372
- Cdk1-induced desmin phosphorylation is required for efficient separation of desmin-IFs and generally detected in muscular mitotic cells in vivo. PMID: 27565725
- the level of Cdc6 phosphorylation at serine 54 (S54P) was increased in E7-expressing cells. S54P was associated with an increase in the total amount of Cdc6 and chromatin-bound Cdc6. DNA damage-enhanced upregulation and chromatin binding of Cdc6 appeared to be due to downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) as Cdk1 knockdown increased Cdc6 levels PMID: 27207654
- The data support a model where Cdc7 (de)phosphorylation is the molecular switch for the activation and inactivation of DNA replication in mitosis, directly connecting Cdc7 and PP1a/Cdk1 to the regulation of once-per-cell cycle DNA replication in mammalian cells. PMID: 27105124
- The Hippo signaling pathway was significantly associated with ER-negative breast cancer (pathway level P = 0.02). Gene-based analyses revealed that CDH1 was responsible for the pathway association (P < 0.01),corrected P = 0.02). rs142697907 in PTPN14 was associated with ER-positive breast cancer and rs2456773 in CDK1 with ER-negativity in case-only analysis after gene-level correction PMID: 27485598
- colon cancer-associated transcript 1/miR-490-3p/cyclin-dependent kinase 1 regulatory pathway promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 28381168
- our results suggest that alteration of CDK1 expression on both mRNA and protein level probably appears on the very early step of carcinogenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 26912061
- Ajuba is phosphorylated in vitro and in vivo by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) at Ser(119) and Ser(175) during the G2/M phase of the cell cycle PMID: 27226586
- These results reveal a crucial and conserved role of phosphorylation of the N terminus of Bora for Plk1 activation and mitotic entry. PMID: 27068477
- Aurora B may prefer Cdk1-phosphorylated Sororin as a substrate. PMID: 26177583
- we discovered a novel mechanism mediated by Smad4 to trigger 5-FU chemosensitivity through cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/CDC2/survivin cascade. PMID: 26647806
- These findings indicate that NSun2-mediated mRNA methylation regulates p27 and CDK1 levels during replicative senescence. PMID: 26687548
- FGFR1 contributes to cell proliferation in osteosarcoma MG63 cells, and FGFR1 mediated cell proliferation may be attributed to the regulation of the cell cycle regulator, CDK1. PMID: 26648125
- that leukemia-associated Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor can be directly phosphorylated by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 PMID: 26483157
- These results demonstrate a mechanism...by which CDK1 boosts mitochondrial bioenergetics to meet the increased cellular fuel demand for DNA repair and cell survival under genotoxic stress conditions PMID: 26670043
- CDK1 plays a comprehensive role in mediating genetic networks implicated in the progression of cervical cancer. PMID: 25786624
- Aurora B and CDK1 temporally regulate the binding affinity of EB2 for microtubules, thereby ensuring kinetochore microtubule dynamics, proper mitotic progression and genome stability. PMID: 27030108
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Mitochondrion. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Note=Cytoplasmic during the interphase. Colocalizes with SIRT2 on centrosome during prophase and on splindle fibers during metaphase of the mitotic cell cycle. Reversibly translocated from cytoplasm to nucleus when phosphorylated before G2-M transition when associated with cyclin-B1. Accumulates in mitochondria in G2-arrested cells upon DNA-damage.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily
-
组织特异性:Isoform 2 is found in breast cancer tissues.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1722
OMIM: 116940
KEGG: hsa:983
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000378699
UniGene: Hs.732435
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
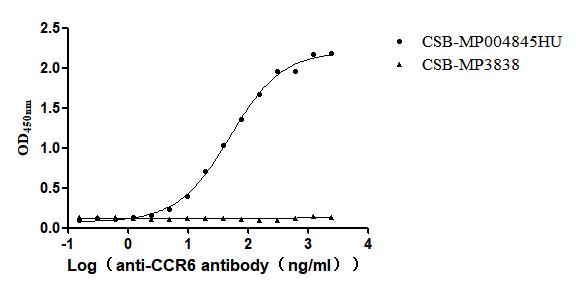
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
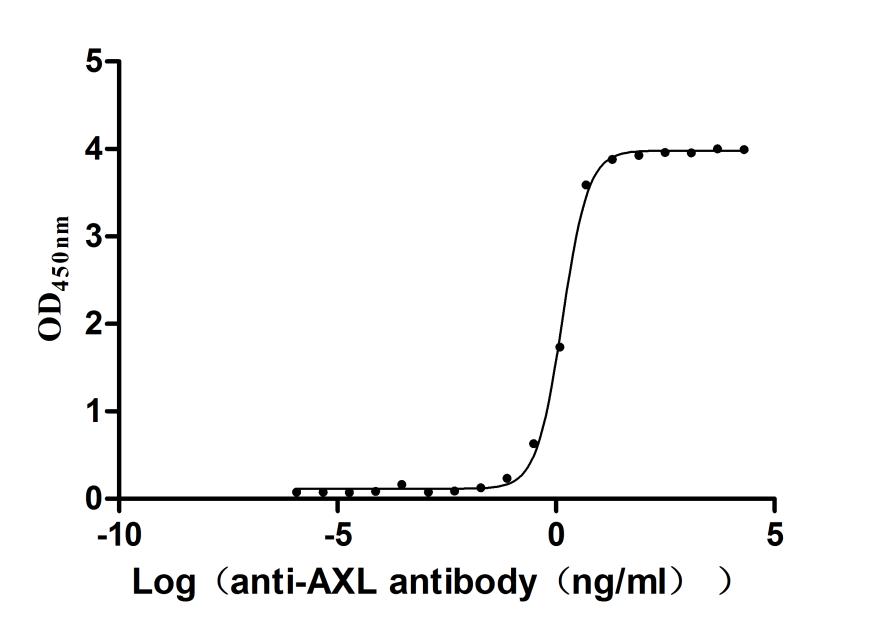
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO(AXL),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)