Recombinant Human Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4)
-
货号:CSB-YP005065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP005065HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP005065HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cdk 4; cdk4; CDK4 protein; CDK4_HUMAN; Cell division kinase 4; Cell division protein kinase 4; CMM 3; CMM3; Crk3; Cyclin dependent kinase 4; Cyclin-dependent kinase 4; Melanoma cutaneous malignant 3; MGC14458; p34 cdk4; PSK J3; PSK-J3
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-303
-
氨基酸序列ATSRYEPVA EIGVGAYGTV YKARDPHSGH FVALKSVRVP NGGGGGGGLP ISTVREVALL RRLEAFEHPN VVRLMDVCAT SRTDREIKVT LVFEHVDQDL RTYLDKAPPP GLPAETIKDL MRQFLRGLDF LHANCIVHRD LKPENILVTS GGTVKLADFG LARIYSYQMA LTPVVVTLWY RAPEVLLQST YATPVDMWSV GCIFAEMFRR KPLFCGNSEA DQLGKIFDLI GLPPEDDWPR DVSLPRGAFP PRGPRPVQSV VPEMEESGAQ LLLEMLTFNP HKRISAFRAL QHSYLHKDEG NPE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also phosphorylates SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and represses its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data indicate that PAQR4 has a tumorigenic effect on human breast cancers, and such effect is associated with a modulatory activity of PAQR4 on protein degradation of CDK4 PMID: 29228296
- MiR-340 overexpression inhibited tumor growth by regulating CDK4 expression. miR-340 functions as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and may provide a potential target of NSCLC treatment. PMID: 29935356
- CDK4 and XPO1 are not altered in a rare undifferentiated sarcoma, making them therapeutic targets PMID: 27329820
- while mTOR inhibitors restore endocrine sensitivity, CDK4/6 inhibitors may favor the emergence of estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) mutations resulting in ligand-independent activity of the receptor PMID: 28685610
- Inhibition of CDK4/6 is potentially a highly effective strategy for the treatment of SHH and MYC-amplified group 3 medulloblastoma. PMID: 28637687
- SOX12 can increase the expression of CDK4 and IGF2BP1, which confer malignant phenotypes to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PMID: 28975985
- Study showed that CDK4 and BCAS2 may be target genes of miR-486 and levels of CDK4 and BCAS2 were both significantly higher in the esophageal cancer tissues and cell lines than levels in the normal tissues and cells. PMID: 29115564
- blocking CDK4 activity efficiently eliminated both normal and chemotherapy-resistant cancer cells in triple negative breast cancers, highlighting CDK4 as a promising novel therapeutic target for these aggressive breast tumors. PMID: 27759034
- Amplification of gene CDK4 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. PMID: 28381877
- Ongoing trials of doublet and triplet targeted therapies containing ribociclib seek to identify optimal CDK4/6-based targeted combination regimens for various tumor types and advance the field of precision therapeutics in oncology PMID: 28351928
- Palbociclib induces activation of AMPK and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in a CDK4/6-independent manner PMID: 28453226
- The combination of ribociclib, a dual inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4 and 6, and the ALK inhibitor ceritinib demonstrated higher cytotoxicity and synergy scores (P = 0.006) in cell lines with ALK mutations as compared with cell lines lacking mutations or alterations in ALK . PMID: 27986745
- Results showed that CDK4 expression was up-regulated in colorectal carcinoma and suggested that cdc37 increased the stability of CDK4 to activate RB1 which ultimately promotes G1-S transition. PMID: 29288563
- Data show that sulfatase 1 (hSulf-1) overexpression in melanoma cells can inhibit cell proliferation and induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by decreasing the protein kinase B (AKT) phosphorylation and limiting cyclin dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) nuclear import. PMID: 27806323
- we here show that subgroups of SDCs display genomic amplifications of MDM2 and/or CDK4, partly in association with TP53 mutations and rearrangement/amplification of HMGA2. PMID: 27662657
- CDK4/6 inhibition suppressed cell cycle progression of ER+/HER2- brreast cancer models. PMID: 27564114
- Proliferating tumor stem cells with high telomerase expression are suitable targets for CDK4/6 inhibitor, palbociclib. PMID: 28039467
- PRMT5 inhibited the interaction between CDK4 and CDKN2A and then activated the CDK4-RB-E2F pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells under glucose induction. PMID: 27708221
- This is the first clinical study exploring the use of a CDK4/6 inhibitor in a pediatric population. In this phase I study, we established the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of single-agent ribociclib in pediatric patients with neuroblastoma, MRTs, or other cancers with documented cyclin D-CDK4/6-INK4-retinoblastoma pathway aberrations PMID: 28432176
- Ribociclib (an oral, highly specific cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor) inhibits tumor growth. PMID: 27542767
- network-based rigidity analysis and emulation of thermal unfolding of the Cdk4-cyclin D complex and Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex revealed weak spots of kinase instability that are present in the native Cdk4 structure and are targeted by the chaperone during client recruitment PMID: 29267381
- The study of 140 cases confirms that the incidence of MDM2/CDK4 amplification is low (5%) in large and/or deep-seated (subfascial) lipomatous neoplasms with histological features of a lipoma (or lipoma variant). PMID: 27020493
- miR-486-5p inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by down-regulating the expression of CDK4. PMID: 27049724
- Combined PI3Kalpha and CDK4/6 inhibition significantly improved disease control in human xenograft models compared with either monotherapy. PMID: 28947417
- High amplification levels of CDK4 is associated with dedifferentiated liposarcoma. PMID: 29153098
- Activation of cdk4 triggers NAFLD. PMID: 27373160
- Our results show that combined exogenous expression of hTERT and mutant CDK4 is an effective method to generate single-cell-derived Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) clones. This provides an innovative and suitable approach to investigate the heterogeneous function and phenotype of CAFs PMID: 28364361
- these findings support that PIKE amplification or overexpression coordinately acts with CDK4 to drive glioblastoma tumorigenesis. PMID: 28368413
- Specific E2Fs also have prognostic value in breast cancer, independent of clinical parameters. We discuss here recent advances in understanding of the RB-E2F pathway in breast cancer. We also discuss the application of genome-wide genetic screening efforts to gain insight into synthetic lethal interactions of CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer for the development of more effective combination therapies. PMID: 26923330
- p16 in combination with MDM2 and CDK4 immunohistochemistry may help in the differential diagnosis of atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. PMID: 27597521
- conclude that p16 is highly sensitive for retroperitoneal DDL. However, the lack of specificity limits the diagnostic utility compared with the more established markers MDM2 and CDK4 PMID: 26509911
- CDK4 overexpression is associated with cancer. PMID: 27206849
- High CDK4 expression is associated with Melanoma. PMID: 26988987
- Staining for MDM2 and CDK4 was noted in 25/56 and 23/56 atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma (ALT/WDL), respectively, giving a sensitivity of 45% and 41% and a specificity of 98% and 92%. Staining was noted exclusively in the nuclei of atypical cells and not in the nuclei of adipocytes. Staining for MDM2 and CDK4 occurred in 2/125 and 10/117 benign lipomatous lesions, respectively. PMID: 27508976
- Cdk4 inhibition leads to directing human mesenchymal stem cells to a multipotent neurogenic fate by inactivating Smads-STAT3 signaling. PMID: 27192561
- Reduced SIRT2 expression during tumorigenesis failed to repress cyclindependent kinase 4 expression, which eventually led to accelerated cell proliferation. PMID: 28259910
- older patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung cancer have raised serums CDK4 levels, which has the potential to emerge as a biomarker in clinical practice PMID: 27815686
- we illustrate that the miR-124/CDK4 axis plays an important role in radiation sensitivity of human esophageal cancer cells by targeting CDK4. PMID: 27323123
- MiR-16 upregulation could reduce CDK4 expression. PMID: 26383521
- both miR-613 mimics and inhibitors could decrease and increase CDK4 protein levels in non-small cell lung cancer-derived cells, respectively. PMID: 26744345
- Upregulation of CDK4 expression is associated with gastric cancer. PMID: 26735582
- Our studies demonstrate that CDK4 and miR-15a comprise an abnormal automodulatory feedback loop stimulating the pathogenesis and inducing chemotherapy resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma . PMID: 26993269
- miR-539 plays an important role in the initiation and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting CDK4. PMID: 26559153
- The concept that cotargeting MEK and CDK4/6 would prove efficacious in KRAS-mutant (KRAS(mt)) colorectal cancers. PMID: 26369631
- This review highlights our current understanding of CDK signaling in both normal and malignant breast tissues, with special attention placed on recent clinical advances in inhibition of CDK4/6 in ER+ disease PMID: 26857361
- concurrent inhibition of ESR1 and the cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) significantly increased progression-free survival in advanced patients PMID: 25991817
- amplification of HMGA2 was associated with the atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma histological type and a good prognosis, whereas CDK4 and JUN amplifications were associated with dedifferentiated liposarcoma histology PMID: 26336885
- CDK4 Amplification Reduces Sensitivity to CDK4/6 Inhibition in Fusion-Positive Rhabdomyosarcoma PMID: 25810375
- Observations disclose the presence of CDK4 protein in human erythrocytes and its involvement in suicidal erythrocyte death. PMID: 26418250
- Data show that the p16/CDKN2A-cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4)-RB1 protein pathway is frequently disrupted in fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (FS-DFSP). PMID: 25852058
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Melanoma, cutaneous malignant 3 (CMM3)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus membrane.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, CDC2/CDKX subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 1773
OMIM: 123829
KEGG: hsa:1019
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000257904
UniGene: Hs.95577
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
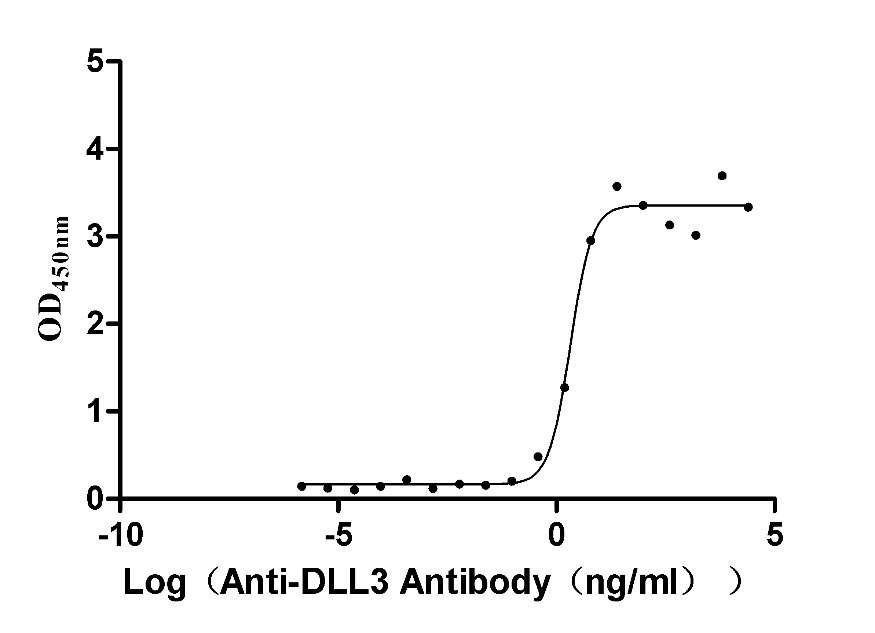
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
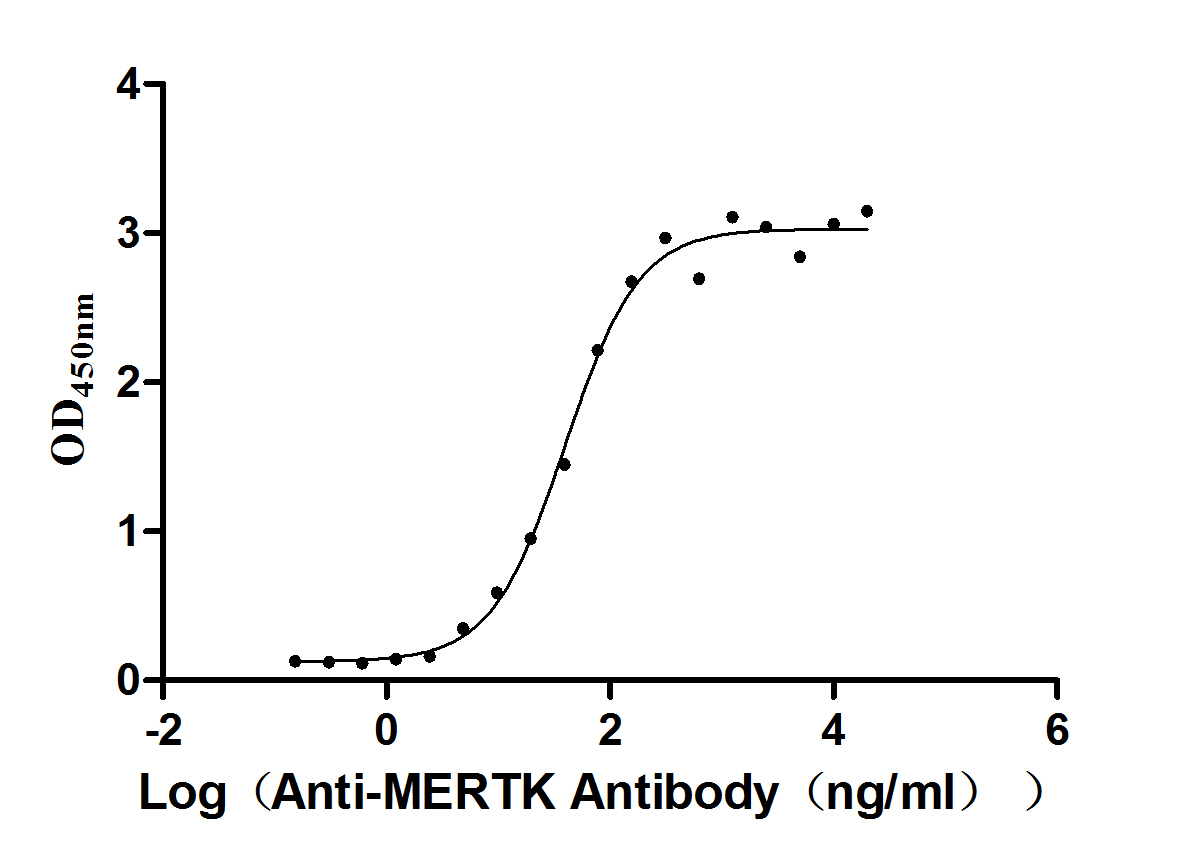
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
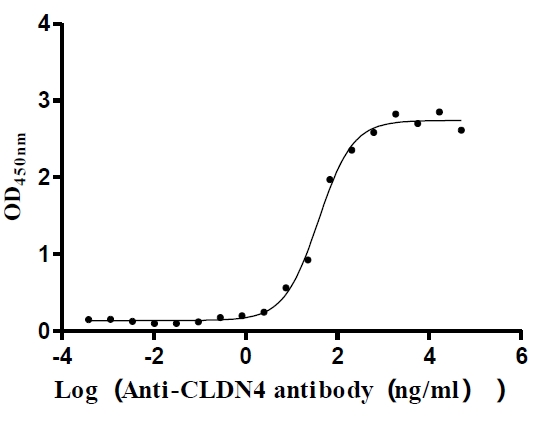
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
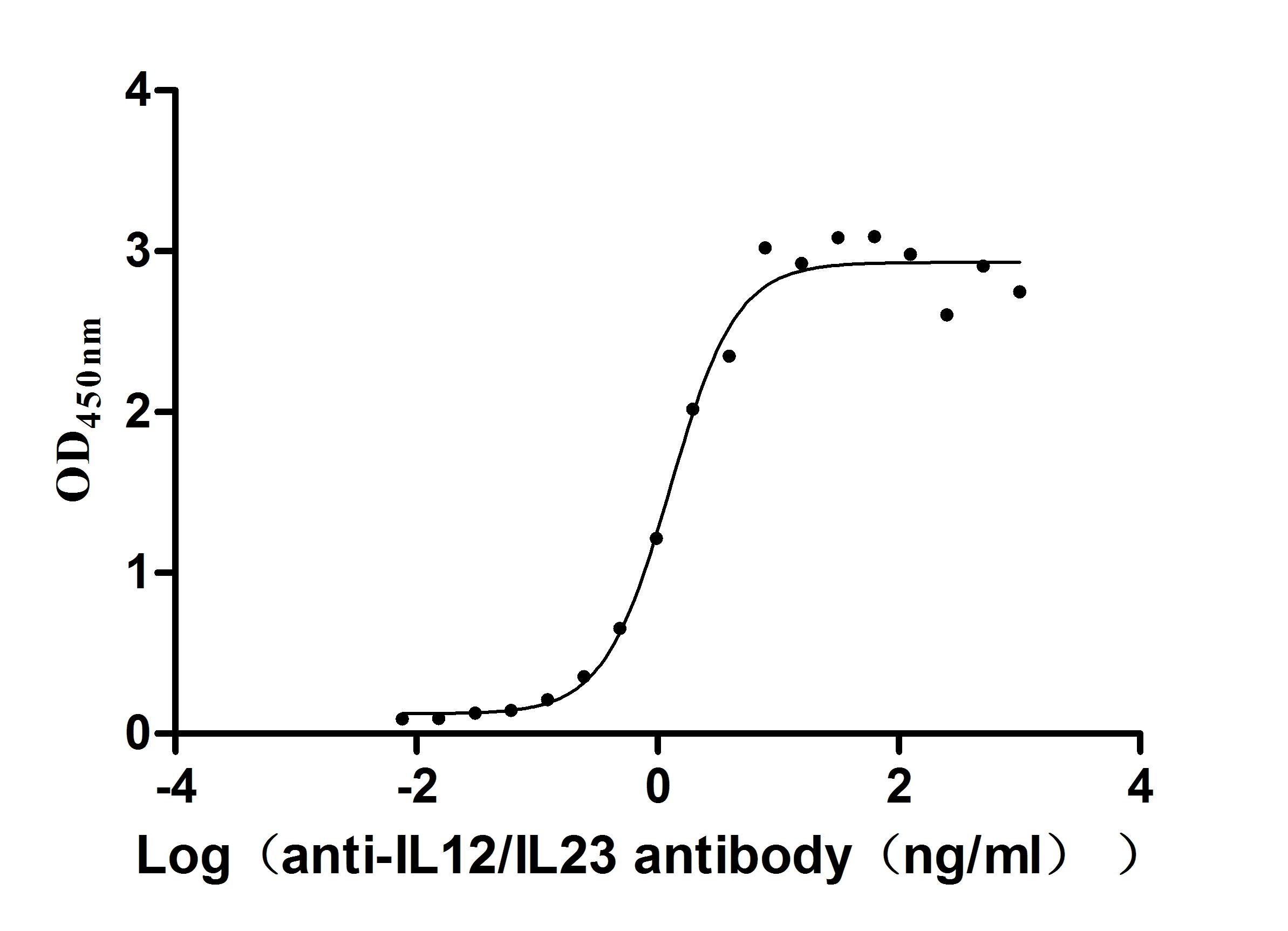
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
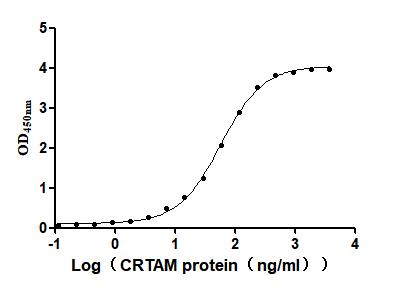
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
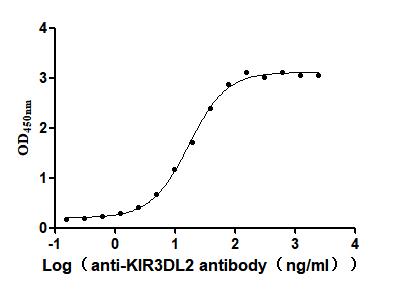
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
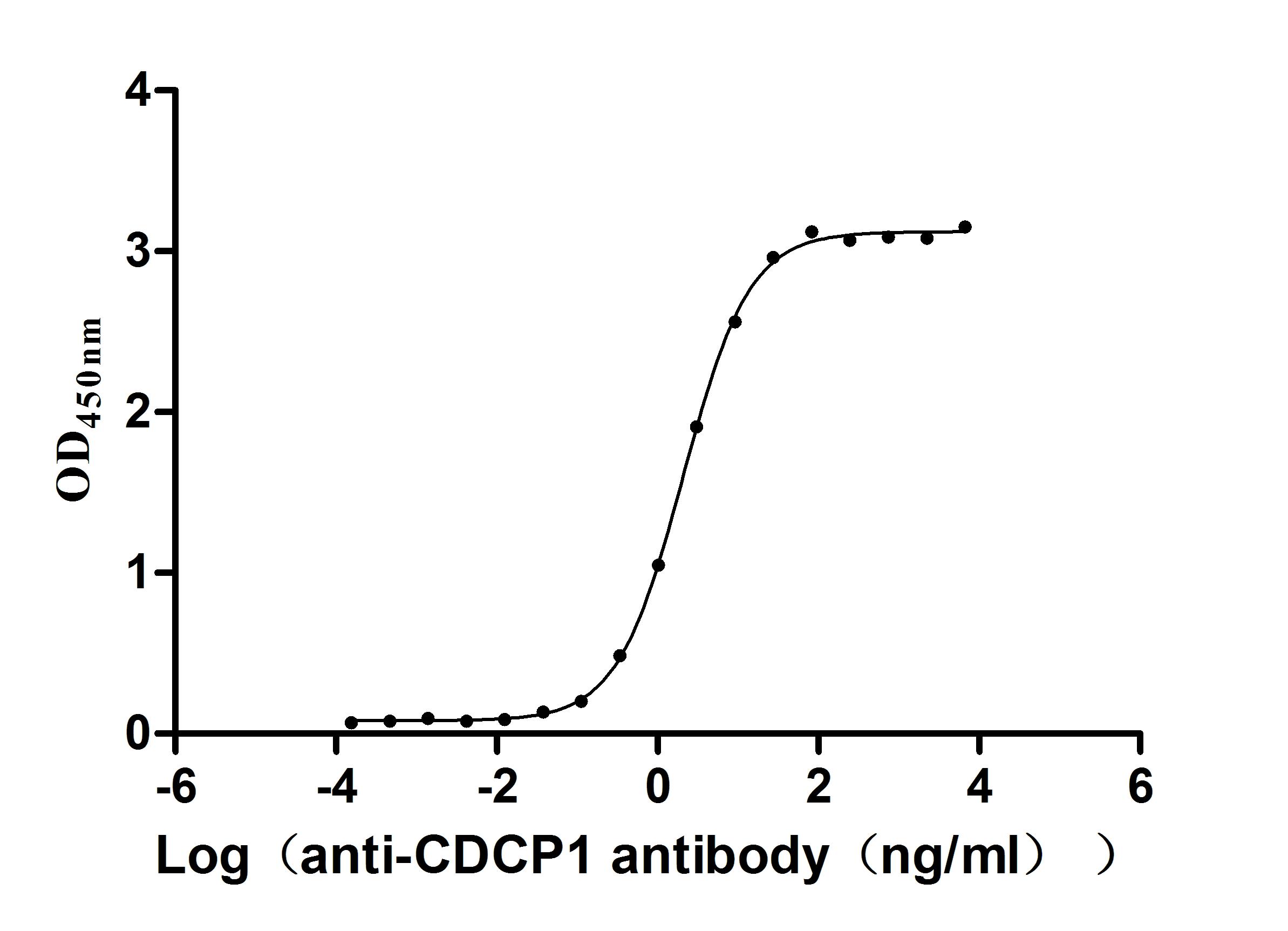
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)