Recombinant Human Docking protein 1 (DOK1)
-
中文名称:人DOK1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP858723HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DOK1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP858723HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DOK1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP858723HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人DOK1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP858723HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:DOK1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Docking protein 1 62kD ; Docking protein 1; DOK 1; DOK1; DOK1_HUMAN; Downstream of tyrosine kinase 1; p62(dok); P62DOK; pp62
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-481
-
氨基酸序列MDGAVMEGPL FLQSQRFGTK RWRKTWAVLY PASPHGVARL EFFDHKGSSS GGGRGSSRRL DCKVIRLAEC VSVAPVTVET PPEPGATAFR LDTAQRSHLL AADAPSSAAW VQTLCRNAFP KGSWTLAPTD NPPKLSALEM LENSLYSPTW EGSQFWVTVQ RTEAAERCGL HGSYVLRVEA ERLTLLTVGA QSQILEPLLS WPYTLLRRYG RDKVMFSFEA GRRCPSGPGT FTFQTAQGND IFQAVETAIH RQKAQGKAGQ GHDVLRADSH EGEVAEGKLP SPPGPQELLD SPPALYAEPL DSLRIAPCPS QDSLYSDPLD STSAQAGEGV QRKKPLYWDL YEHAQQQLLK AKLTDPKEDP IYDEPEGLAP VPPQGLYDLP REPKDAWWCQ ARVKEEGYEL PYNPATDDYA VPPPRSTKPL LAPKPQGPAF PEPGTATGSG IKSHNSALYS QVQKSGASGS WDCGLSRVGT DKTGVKSEGS T
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:DOK proteins are enzymatically inert adaptor or scaffolding proteins. They provide a docking platform for the assembly of multimolecular signaling complexes. DOK1 appears to be a negative regulator of the insulin signaling pathway. Modulates integrin activation by competing with talin for the same binding site on ITGB3.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Taken together, these results indicate that ATRA-enhanced expression of DOK1 activates PPARgamma leading to inhibition of cell proliferation and enhancement of cell apoptosis in MCF-7 cell. PMID: 28396148
- DOK1 was identified as a prognostic factor for non-metastatic CRC, and, via its drugability by PPARgamma-agonist, may constitute a potential target for future cancer treatments. PMID: 27428427
- DOK3 expression was not altered much in HTLV-1-infected T cells. PMID: 27265473
- Results indicate that hypermethylation of tumor suppressor protein RASSF1A and docking protein 1 (DOK1) contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis and is associated to clinicopathological characteristics. PMID: 27078152
- Data show that residues Ser745 and Ser756 in the integrin beta2 tail, which are adjacent to the NxxF motif, are required for docking protein 1, docking protein 1, 62kDa (downstream of tyrosine kinase 1) (Dok1) interaction. PMID: 26108885
- results support a model in which Dok1 phosphorylation normally suppresses localized Ras pathway activity in Crk-transformed cells via recruitment and/or activation of RasGAP PMID: 25043303
- Data implicate existence of alternate conformational states around the ligand binding pocket of the PTB domain of phosphoprotien Dok1 either in the native or in the near native conditions. PMID: 24587391
- Deregulation of DOK1 gene expression by EBV and novel insights into the regulation of the DOK1 tumor suppressor in viral-related carcinogenesis. PMID: 24809689
- point mutations in DOK1 and DOK2 genes are detected with low frequency in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia but may have consequences for the function of the DOK2 PTB domain PMID: 25252871
- A crucial role for DOK1 in the regulation of PDGF-BB-mediated tumour cell motility through a p130Cas-Rap1 signalling pathway. PMID: 24762811
- Taken together, these results reveal that Dok1 and Dok2 proteins are involved in an intrinsic negative feedback loop downstream of natural killer-cell-activating receptors in mouse and human. PMID: 24963146
- BRK has a role in targeting Dok1 for ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation and in promoting cell proliferation and migration PMID: 24523872
- The unique N-terminal region of SRMS regulates enzymatic activity and phosphorylation of its novel substrate docking protein 1. PMID: 23822091
- DNA methylation of the DOK1 core promoter region found in head and neck cancer cell lines hampered the recruitment of E2F1 to the DOK1 promoter and compromised DOK1 expression. PMID: 23028047
- Studies demonstrate DOK-1 regulates allergen-induced Th2 immune responses by selective stimulation and inhibition of STAT-4 and STAT-6 signaling pathways, respectively. PMID: 22514638
- hypermethylation of DOK1 is a potentially critical event in human carcinogenesis. PMID: 21796618
- These findings are suggestive for a possible tumor suppressor role of DOK1 in epithelial ovarian cancer. PMID: 21856257
- Cav1 cooperated with the endogenous Ras/MAPK inhibitor docking protein 1 (Dok1) to promote the ligand-dependent transcriptional activity of PPARgamma and to inhibit cell proliferation PMID: 21690289
- these data support a model in which proteasome- mediated degradation of Dok-1 is an important contributive step toward tumor development and/or progression driven by OTKs PMID: 21536658
- Dok1 negatively regulates Dok2-mediated CD200R signaling through the recruitment of CrkL. PMID: 21078907
- Identification of DOK genes as lung tumor suppressors. PMID: 20139980
- The novel platelet adapter Dok-1 is tyrosine phosphorylated in an Src kinase-independent manner downstream of alphaIIbbeta3 in human platelets, leading to an interaction with Grb2 and SHIP-1. PMID: 19682241
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Src family kinases are required for phosphorylation and membrane recruitment of Dok-1 in c-Kit signaling. PMID: 11825908
- Dok-1 acts as an adaptor protein that links the activin receptors with the Smads, suggesting a novel function for Dok-1 in activin signaling leading to B-cell apoptosis. PMID: 11927552
- DOK1 and DOK2 interact with the Tec protein tyrosine kinase. PMID: 14647425
- Dok-1 plays an important role in SDF-1alpha/CXCL12-induced chemotaxis in T cells. PMID: 15345598
- This result indicates that germline mutations in Dok1 are unlikely to cause an inherited predisposition to CLL. PMID: 15541476
- DOK1 mediates SHP-2/beta3 association in response to IGF-I thereby mediating the effect of integrin ligand occupancy on IGF-IR-linked signaling in smooth muscle cells. PMID: 15546884
- IKKbeta phosphorylates Dok1 S(439)S(443) and S(446)S(450) after TNF-alpha, IL-1, or gamma-radiation and implicate the critical Dok1 serines in Dok1 effects after tyrosine kinase activation PMID: 15574499
- Phosphotyrosine-binding mediated oligomerization of Dok-1 and Dok-2 represents an essential step for Dok phosphorylation and function. PMID: 16177091
- Data show that Dok1 expression and structure are affected in a subset of Burkitt's lymphoma samples, suggesting its possible role in this type of cancer. PMID: 16338067
- These data suggest a mechanistic basis for the inhibitory effect of Dok-1 on growth factor-induced mitogenesis and its role as a tumor suppressor. PMID: 16537894
- The data provide evidence that DOK1 protein has a role in regulating cell proliferation and differentiation and is positive regulators of the MAPK signaling pathway in this context. PMID: 16823827
- results demonstrate differential modes of regulation of Dok1 and Dok2 in platelets, and raise the possibility that Dok2 plays an important role in integrin outside-in signaling through a physical and functional interaction with integrin alphaIIbbeta3 PMID: 17092301
- Upon phosphorylation of Tyr 747 in the beta3 integrin tail, however, Dok1 then binds much more strongly than talin. PMID: 18156175
- These results suggest that engagement of different adaptor proteins by Ret results in very different downstream signaling and functions within neurons and that Dok recruitment leads to a rapid receptor relocation and formation of microspikes. PMID: 18353552
- Dok-1/Dok-2 pleckstrin homology domains bind in vitro to the rare phosphoinositide species, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate PMID: 19299694
- CD45 recruits adaptor DOK-1 to the proximal plasma membrane to serve as a downstream effector, resulting in negative regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. PMID: 19481264
- Results identified an N-terminally truncated isoform of human Dok-1 with N-terminal acetylation as seen in the wild-type. PMID: 19481542
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus.; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm, perinuclear region.
-
蛋白家族:DOK family, Type A subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in pancreas, heart, leukocyte and spleen. Expressed in both resting and activated peripheral blood T-cells. Expressed in breast cancer.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2990
OMIM: 602919
KEGG: hsa:1796
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000233668
UniGene: Hs.103854
Most popular with customers
-
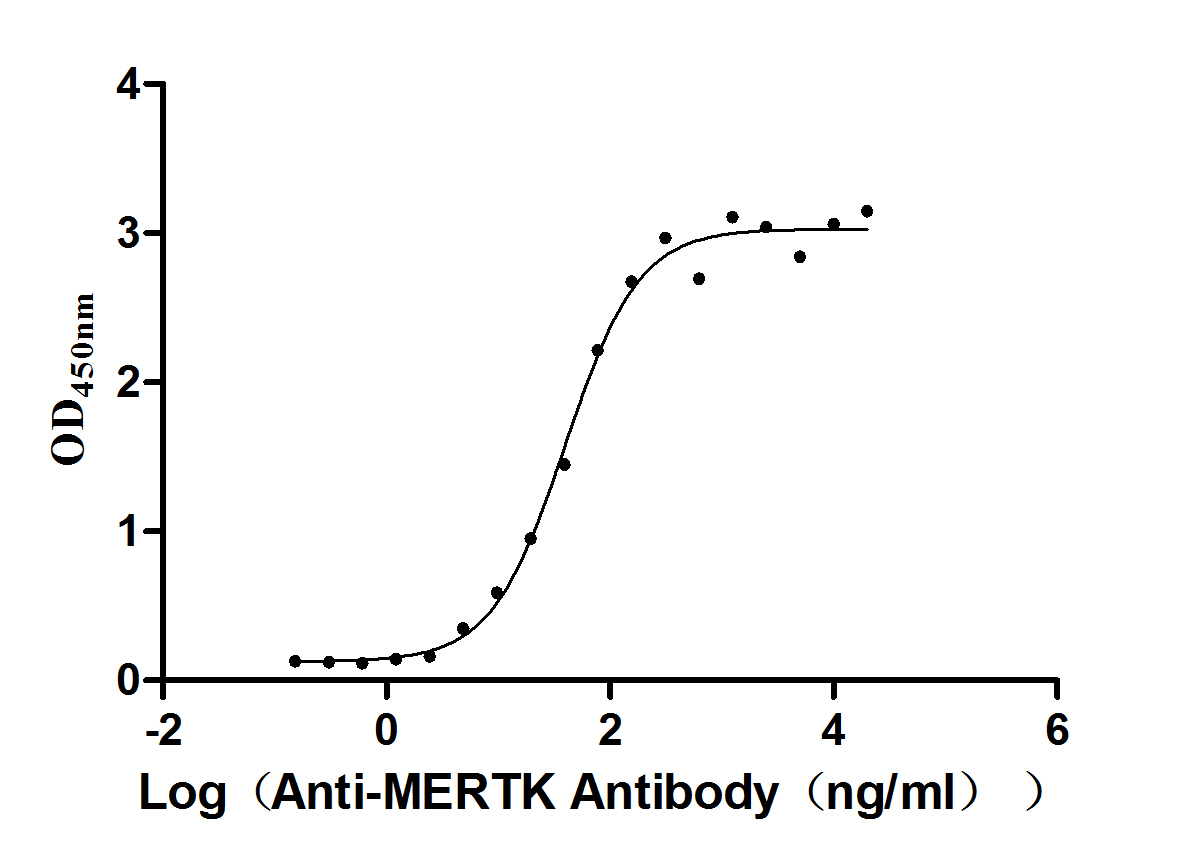
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
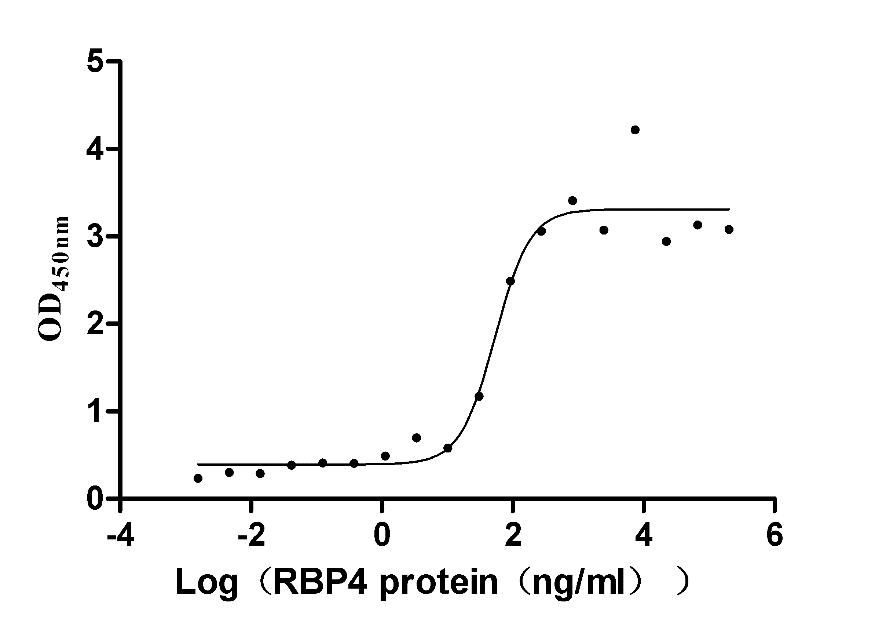
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
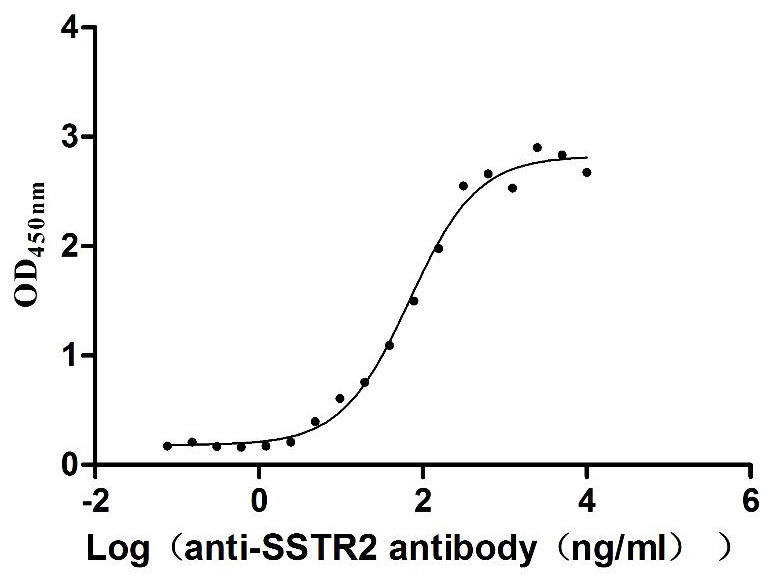
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
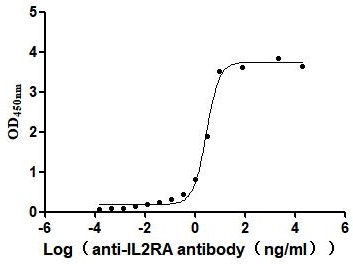
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
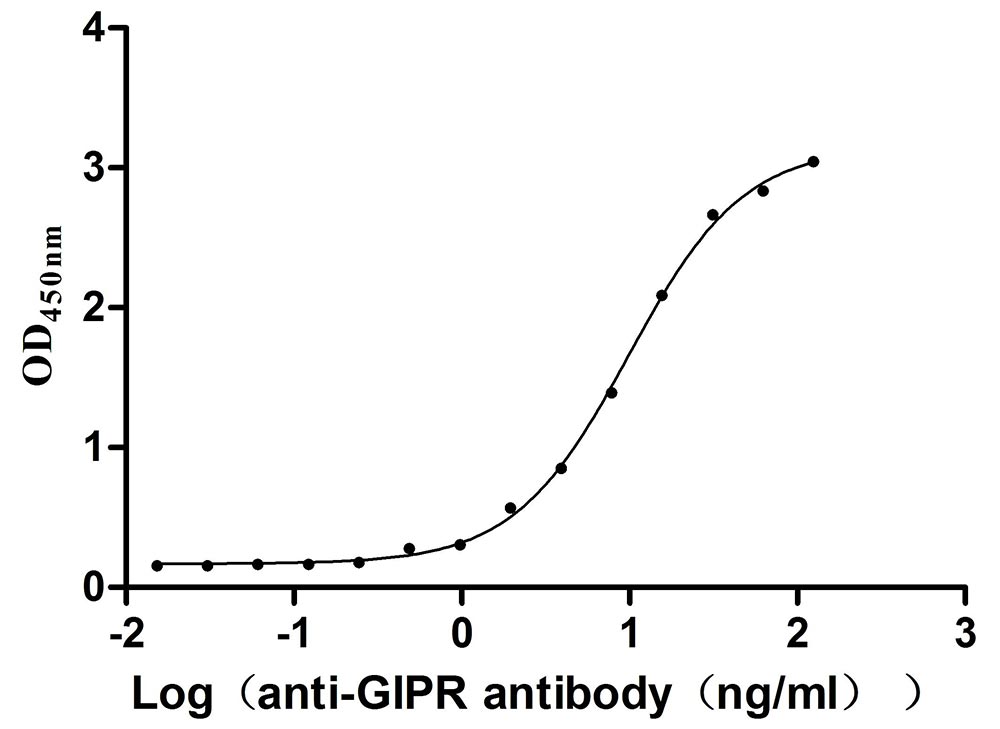
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
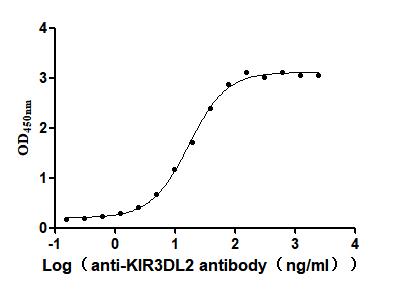
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
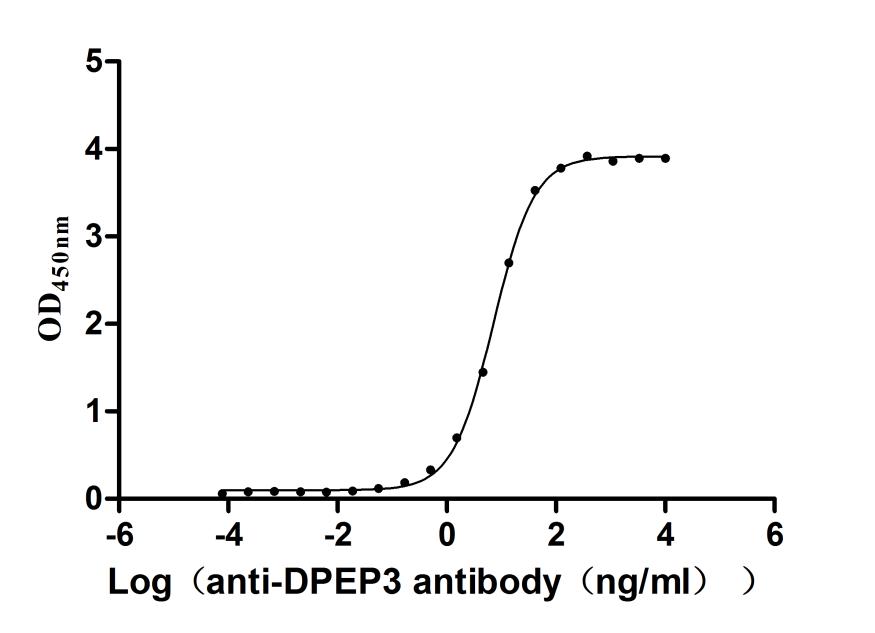
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)