Recombinant Human Dynamin-1 (DNM1), partial
-
货号:CSB-BP007062HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP007062HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP007062HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:Name:DNM1 Synonyms:DNM
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:B dynamin; D100; DNM 1; DNM; DNM1; DYN1_HUMAN; Dynamin; Dynamin-1; Dynamin1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Microtubule-associated force-producing protein involved in producing microtubule bundles and able to bind and hydrolyze GTP. Most probably involved in vesicular trafficking processes. Involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The twin siblings exhibit mild to moderate intellectual disability and autistic symptoms but no epileptic encephalopathy. Exome sequencing revealed a genetic variant, c.1603A>G (p.Lys535Glu), in the PH domain of dynamin 1. The twin sisters studied here share the de novo variant, c.1603A>G (p.Lys535Glu) in exon 15 of DNM1, classified as likely pathogenic. PMID: 29397573
- The data show that the dynamin-amphiphysin helices are rearranged to form clusters upon GTP hydrolysis and membrane constriction occurs at protein-uncoated regions flanking the clusters. PMID: 29357276
- Together, these observations suggest that while endophilin helps shape endocytic tubules and recruit dynamin to endocytic sites, it can also block membrane fission when present in excess by inhibiting inter-dynamin interactions. PMID: 28933693
- The s show that in fibroblasts, dynamin GTP hydrolysis occurs as stochastic bursts, which are randomly distributed relatively to the peak of dynamin assembly. Thus, dynamin disassembly is not coupled to GTPase activity, supporting that the GTP energy is primarily spent in constriction. PMID: 29022874
- Dynamin isoforms differentially regulate the endocytosis and apoptotic signaling downstream of TRAIL-death receptor (TRAIL-DR) complexes in cancer cells. TRAIL stimulation activates ryanodine receptor-mediated calcium release from endoplasmic reticulum stores, leading to calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation and activation of Dyn1, TRAIL-DR endocytosis, and increased resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. PMID: 28049841
- Three genes in our epilepsy cohort (COQ4, DNM1, and PURA), accounting for 14% (3/21) of all novel genetic etiologies identified in patients with epilepsy, were subsequently confirmed in independent publications. PMID: 26795593
- Study delineates the phenotypic spectrum of DNM1 encephalopathy, an emerging disease of synaptic vesicle fission characterized by severe to profound developmental delay, infantile-onset epilepsy beginning with infantile spasms, and movement disorder. The genetic landscape of DNM1 encephalopathy is notable for the recurrent c.709C>T (p.Arg237Trp) variant and localization of mutations to specific domains of the protein. PMID: 28667181
- CLCb/Dyn1-dependent adaptive clathrin-mediated endocytosis selectively altered EGF receptor trafficking. PMID: 28171750
- Down-regulation of Dyn1 activity enhances extracellular Nme1 in human colon tumor cell lines. PMID: 27449069
- Hypoxic down-regulation of constitutive endocytosis is HIF-independent, and involves caveolin-1-mediated inhibition of dynamin-dependent, membrane raft endocytosis. PMID: 27094744
- study reports 2 patients with early onset epileptic encephalopathy possessing de novo DNM1 mutations; detected the novel mutation c.127G>A (p.Gly43Ser) in a patient with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and a recurrent mutation c.709C>T (p.Arg237Trp) in a patient with West syndrome PMID: 26611353
- The rare variants in DNM1 were significantly associated with smoking status. PMID: 25450229
- Data indicate that stimulation of the dynamin GTPase activity by SH3 domains is determined by its middle domain. PMID: 26659814
- molecular simulations corroborate the bimodal character of dynamin action and indicate radial and axial forces as dominant, although not independent, drivers of hemi-fission and fission membrane- transformations, respectively PMID: 26123023
- Data indicate the dynamics of a dynamin 1-catalysed GTP hydrolysis and tube-severing reaction in real time using fluorescence microscopy. PMID: 26479317
- This study identified and confirmed DNM1 protein changes within the postsynaptic density in schizophrenia. PMID: 25048004
- findings support a role for HTT on dynamin 1 function and ER homoeostasis. Proteolysis-induced alteration of this function may be relevant to disease. PMID: 26165689
- CRISPR-Cas9n-mediated knockout and reconstitution studies establish that dynamin-1 is activated by Akt/GSK3beta signaling in H1299 non-small lung cancer cells. PMID: 26139537
- Data suggest that by binding to both clathrin and F-actin, mammalian actin-binding protein 1 (mAbp1; HIP-55 or SH3P7) is specifically recruited at a late stage of clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) formation, which subsequently recruits dynamin to CCPs. PMID: 25690657
- Dynamin 1 and dynamin 2 activity are not essential for Chlamydia trachomatis internalization but is required for normal development. PMID: 25116793
- activity-dependent acceleration is only prominent at physiological temperature and that the mechanism of this modulation is based on the dephosphorylation of dynamin 1 PMID: 23908769
- determined the alpha-synuclein-binding domain of beta-III tubulin and demonstrated that a short fragment containing this domain can suppress alpha-synuclein accumulation in the primary cultured cells PMID: 25031323
- De novo mutations in synaptic transmission genes including DNM1 cause epileptic encephalopathies. PMID: 25262651
- Data show that the classical dynamin DNM1 and DNM3 genes reach their maximum expression levels (100% of maximal expression) in all normal central nervous system tissues studied. PMID: 24673776
- Alternate pleckstrin homology domain orientations regulate dynamin-catalyzed membrane fission. PMID: 24478459
- Dynamin1 is associated with both preserved cognition and regenerative responses in older people with cerebrovascular disease and may represent a novel treatment target. PMID: 24486840
- findings show NDPKs (NM23-H1/H2/H4) interact with and provide GTP to dynamins, allowing these motor proteins to work with high thermodynamic efficiency for membrane remodeling PMID: 24970086
- Data suggest that dynorphin A (DynA) is ligand for opioid receptor kappa (KOR); upon DynA binding, only small chemical shifts observed in second extracellular loop of KOR; chemical shift changes of DynA show conclusively that DynA interacts with KOR. PMID: 24616919
- The discovery that the pre-mRNA sequence of dnm1 in humans has sequence features similar to that of the alternative splicing patterns observed in insects greatly expands the applicability of the docking site-selector sequence pairing model to bilaterian animals. PMID: 23793749
- analysis of how the membrane interactions of disease-related dynorphin A variants cause differences in cell toxicity PMID: 23705820
- dyn1 affects amyloid generation through regulation of BACE-1 subcellular localization and therefore its enzymatic activities. PMID: 23024787
- Herpes simplex virus type 1 can enter human keratinocytes by alternative entry pathways that require dynamin and host cholesterol. PMID: 22022400
- Study presents the GMPPCP-bound structures of the truncated human dynamin 1 helical polymer at 12.2 A and a fusion protein, GG, linking human dynamin 1's catalytic G domain to its GTPase effector domain (GED) at 2.2 A. PMID: 21962517
- crystal structure of human dynamin 1 in the nucleotide-free state with a four-domain architecture comprising the GTPase domain, the bundle signalling element, the stalk and the pleckstrin homology domain. PMID: 21927000
- A new role for the dynamin-1 GTPase in the regulation of fusion pore expansion PMID: 21460182
- In conclusion, Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin is endocytosed by dynamin-dependent mechanisms and we provide evidence for involvement of clathrin and Rho. PMID: 20690924
- 2.0 A resolution crystal structure of a human dynamin 1-derived minimal GTPase-GED fusion protein, which was dimeric in the presence of the transition state mimic GDP.AlF(4)(-) PMID: 20428113
- Endocytosis of FcalphaR is clathrin- and dynamin-dependent, but is not regulated by Rab5, and the endocytic motif is not located in the cytoplasmic domain of FcalphaR. PMID: 19859085
- Data suggest that the components of the GTPase-GED interface act as an intramolecular signaling module, which we term the bundle signaling element, that can modulate dynamin function in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 19515832
- Results demonstrate that, in concert with dynamin-1 self-assembly, pleckstrin homology domain membrane insertion is essential for fission and vesicle release in vitro and for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in vivo. PMID: 19776347
- These findings suggest that dynamin is part of a protein network that controls nucleation of actin from membranes. PMID: 11782545
- dynamin-dependent endocytosis is inhibited by syntaphilin PMID: 12896979
- serglycin-bound granzyme B in high-molecular-weight degranulate material from cytotoxic T lymphocytes predominantly followed a dynamin-dependent pathway to kill target cells PMID: 14739229
- Point mutations were made in the GTPase effector/assembly domain (GED)of dynamin 1 and tested for their effects on self-assembly and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. PMID: 15004222
- dynamin-1 interacts with Sumo-1, Ubc9, and PIAS-1, all of which are members of the sumoylation machinery PMID: 15123615
- Dynamin GTPase domain is important for GTP binding, GTP hydrolysis, and clathrin-mediated endocytosis PMID: 15262989
- dynamin, Cbl, and Src coordinately participate in signaling complexes that are important in the assembly and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, leading to changes in osteoclast adhesion, migration, and resorption PMID: 15872089
- S-nitrosylation of dynamin regulates endocytosis through nitric oxide PMID: 16432212
- PLD functions as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) through its phox homology domain (PX), which directly activates the GTPase domain of dynamin and increased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytosis at physiological EGF concentrations. PMID: 16622417
- Data show that swapping the highly homologous GTPase domain of dynamin-2 into dynamin-1 is sufficient to confer caspase-3 activation. PMID: 16938290
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 31 (EIEE31)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Note=Microtubule-associated.
-
蛋白家族:TRAFAC class dynamin-like GTPase superfamily, Dynamin/Fzo/YdjA family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2972
OMIM: 602377
KEGG: hsa:1759
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000362014
UniGene: Hs.522413
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
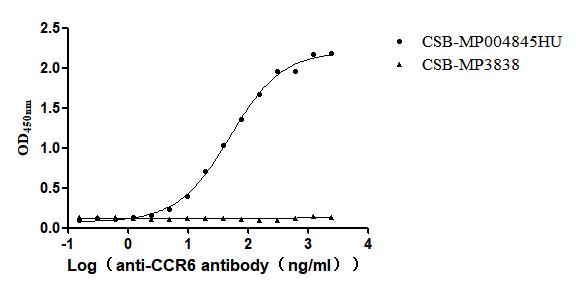
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)