Recombinant Human Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1 (HSD17B1)
-
货号:CSB-YP010766HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP010766HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP010766HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP010766HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:HSD17B1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:17 beta HSD 1; 17 beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1; 17-beta-HSD 1; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1; 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; 20-alpha-HSD; DHB1_HUMAN; E17KSR; E2DH; EDH17B1; EDH17B2; EDHB17; Estradiol 17 beta dehydrogenase 1; Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1; HSD17; HSD17B1; Hydroxysteroid (17 beta) dehydrogenase 1; MGC13814; Placental 17 beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; Placental 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; SDR28C1; Short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 28CE,member 1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-328
-
氨基酸序列ARTVVLITG CSSGIGLHLA VRLASDPSQS FKVYATLRDL KTQGRLWEAA RALACPPGSL ETLQLDVRDS KSVAAARERV TEGRVDVLVC NAGLGLLGPL EALGEDAVAS VLDVNVVGTV RMLQAFLPDM KRRGSGRVLV TGSVGGLMGL PFNDVYCASK FALEGLCESL AVLLLPFGVH LSLIECGPVH TAFMEKVLGS PEEVLDRTDI HTFHRFYQYL AHSKQVFREA AQNPEEVAEV FLTALRAPKP TLRYFTTERF LPLLRMRLDD PSGSNYVTAM HREVFGDVPA KAEAGAEAGG GAGPGAEDEA GRGAVGDPEL GDPPAAPQ
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Favors the reduction of estrogens and androgens. Converts estrone (E1) to a more potent estrogen, 17beta-estradiol (E2). Also has 20-alpha-HSD activity. Uses preferentially NADH.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Our genetic study demonstrated HSD17B1 937 G variant as a risk factor for infertility in women with stage I and II endometriosis in Polish Caucasian patients. PMID: 28405865
- HSD17B1 is a promising marker to predict EC prognosis. PMID: 27923582
- Macronutrient intakes were associated with serum estradiol level, and these associations may be modified by HSD17B1 polymorphism in postmenopausal Japanese women. PMID: 28980890
- the effect of 17beta-HSD1 expression on breast cancer cell transcript profile in steroid-deprived condition, was investigated. PMID: 27544780
- Mutation in the 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene is associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. PMID: 28207417
- Substrate inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 in tumor epithelial cells and regulation of 17beta-HSD7 by 17beta-HSD1 knockdown has been demonstrated. PMID: 28554725
- 10 natural products were evaluated leading to inhibition of the activity of 17beta-HSD1 at the concentration of 25 muM, and six of them inhibit the activity over 50%. PMID: 27933483
- The structure of human 17beta-HSD1 and biological function have been studied extensively in the last two decades. In humans, the enzyme is expressed in placenta, ovary, endometrium and breast; high activity of estrogen activation provides the basis of 17beta-HSD1's implication in estrogen-dependent diseases, such as breast cancer, endometriosis and non-small cell lung carcinomas. [Review] PMID: 27102893
- These findings suggested that the HSD17B1 Ser312Gly polymorphism might confer genetic cancer susceptibility in an ethnic-dependent manner, especially among Caucasians. PMID: 26923943
- The rs605059 polymorphism of the HSD17B1 gene is associated with increased risk of recurrent spontaneous abortion. PMID: 25394609
- Review/Meta-analysis: HSD17B1 rs605059 polymorphisms were not associated with the risks of endometrial cancer or endometriosis. PMID: 26261478
- the HSD17B1 transcript and protein were identified in HeLa, SiHa, Ca Ski and C-33A cervical cancer cells. PMID: 26054693
- Increased expression of HSD17B1 in NSCLC may contribute to an elevated intratissue level of E2 and consequently may support the development and spread of cancer. PMID: 25564397
- The key enzymes of ovarian steroidogenesis, CYP 19 and 17beta-HSD, are active in the ovaries of postmenopausal women. PMID: 24855493
- 17beta-HSD1 and 17beta-HSD7 are principal reductive 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and major players in the viability of estrogen-dependent breast cancer cells. PMID: 25257817
- E1-induced ERELuc activity in the inhibitor-treated uterus was reduced by the HSD17B1 inhibitor. PMID: 25617485
- Single nucleotide polymorphism in HSD17B1 gene is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 24563232
- Onset of epileptiform discharges is modestly delayed in slices from ovariectomized rats replaced with physiologically relevant doses of EB, but the number of discharges is not affected. PMID: 24113171
- results demonstrated that HSD17B1 expression and its ability to convert the weak estrogen E1 to the more potent E2 can be associated with DNA methylation in the 5' flanking region in GC cells. PMID: 23916544
- analysis of intratumoral localization and activity of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in non-small cell lung cancer PMID: 23837683
- We found the presence of HSD17B1 transcripts and proteins in human Jurkat acute T cell leukemia, Hut-78 and Raji B lymphoma cells PMID: 23540283
- HSD17B1-mediated decreased conversion of estrone to estradiol may reduce the estrogenic effects, thereby reducing the risk of developing breast cancer during long-term hormone replacement therapy use. [Meta-analysis] PMID: 23430226
- study demonstrated that 17beta-HSD1 increases breast cancer cell migration, in spite of its positive regulation of the antimetastatic gene NM23 PMID: 22691413
- In this review, the results suggest that HSD17B1 and PR polymorphism may play a role in the risk of endometriosis PMID: 22613790
- Frequencies of rs605059 AA genotype and A allele were significantly increased in Chinese patients with uterine leiomyoma compared to healthy controls. PMID: 22546946
- Data suggest that HSD17B1 is overexpressed in endometrial cancer tissue; HSD17B1 appears responsible for shift toward reductive metabolism (i.e., greater reduction of estrone to 17-beta-estradiol; lesser oxidation of 17-beta-estradiol to estrone). PMID: 22362820
- Breast cancer cells T47D, MCF-7, BT 20, and JEG 3 as control cells, were chosen to evaluate the contribution of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and type 2 to the estradiol/estrone ratio. PMID: 22253796
- reduced HSD17B1 expression can be associated with DNA methylation in the 5' flanking region of HSD17B1 in CRC from the proximal colon. PMID: 22176788
- HSD17B1 gene may contribute to sex steroid-mediated effects on colorectal cancer development. PMID: 21317201
- SNPs (HSD17B1 (rs2010750, rs598126 and rs676387), COMT (rs4680), UGT1A1 (rs8175347) and ESR1 (rs9340799)) seem to be related to mammographic density in the same direction of their associations with breast cancer risk PMID: 22199302
- Data show that in 17beta-HSD1 inhibitors are placed in the substrate-binding site and they occupy an apolar subpocket consisting of the following amino acids: Gly94, Leu95, Leu96, Asn152, Tyr155, and Phe192. PMID: 21857977
- HSD17B1 upregulation by sodium butyrate is associated with increased conversion of E1 to E2 in colorectal cancer cells. PMID: 21563966
- Obese women with selected CYP19 and 17-beta HSD gene variants had remarkably different E2 trajectories around the the final menstrual period, resulting in different postmenopausal E2 levels. PMID: 21198743
- Genetic variants in ESR1, ESR2, and HSD17B1 genes could modify susceptibility to endometriosis and might influence the fertility status in endometriosis patients. PMID: 20586553
- This study suggests that HSD17B1 312Gly allele may be a protective factor for breast cancer development in Caucasians. PMID: 20151320
- CYP17 (T1931C) and HSD17beta1 (A1954G) polymorphisms may jointly increase the risk of breast cancer. PMID: 20193327
- genetic assiciation studies [Japan, Brazil]: data suggest SNP in 17beta-HSD1 gene may modify association between dietary isoflavone intake & breast cancer PMID: 20432167
- 17beta-HSD1 up-regulates breast cancer cell growth by a dual action on estradiol synthesis and dihydrotestosterone inactivation. PMID: 20172961
- A significant increment of 17beta-HSD1 followed exemestane neoadjuvant therapy of postmenopausal ER-positive breast carcinoma. This may represent the compensatory response of breast carcinoma tissues to estrogen depletion. PMID: 20151319
- An amino acid important for steroid/retinoid discrimination was identified and its significance was highlighted by the results of molecular modeling studies. PMID: 20382160
- Data report structures of the binary and ternary complexes of 17beta-HSD1 with a new inhibitor E2B, opening a new orientation of breast cancer treatment. PMID: 19929851
- increased activity in hypothalamic obesity PMID: 12519880
- possible hypothalamic mediators regulating adipose tissue 11 beta-HSD-1 might include down-regulation by CRH, ACTH, and alpha 2 sympathetic stimulation, and up-regulation by beta 2 sympathetic stimulation and by the cytokines TNFalpha and IL-1 beta PMID: 12519881
- examination of amplification in breast cancer PMID: 12527905
- Evidence for association between the Ser312Gly polymorphism in HSD17B1 and endometriosis was found in a Japanese population PMID: 15640252
- the germline variants in HSD17B1 characterized by htSNPs do not substantially influence the risk of prostate cancer in U.S. and European whites PMID: 16311626
- Corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) increased whereas alpha-helical CRH decreased the mRNA levels of STS, CYP19A1, and HSD17B1, the key enzymes for estrogen synthesis. PMID: 16467490
- HSD17B1 is a multispecific enzyme. PMID: 16480815
- importance of 17HSD type 2 in breast cancer- & non-tumour breast cell lines; high or low expression affected oestradiol concentration significantly; response dependent on endogenous expression of 17HSD type 1 which seems to be dominant to 17HSD type 2 PMID: 16954436
- These results suggest that soy consumption may interact with polymorphisms in the 17beta-HSD1 gene in relation to endometrial cancer risk. PMID: 17301695
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 5210
OMIM: 109684
KEGG: hsa:3292
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000466799
UniGene: Hs.654385
Most popular with customers
-
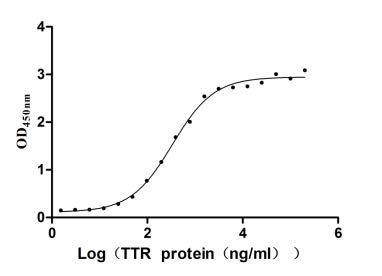
Recombinant Human Transthyretin (TTR) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
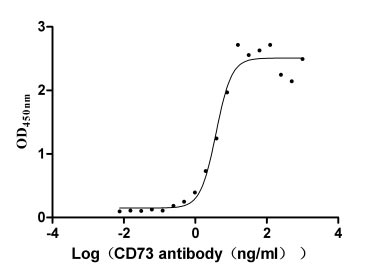
Recombinant Human 5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
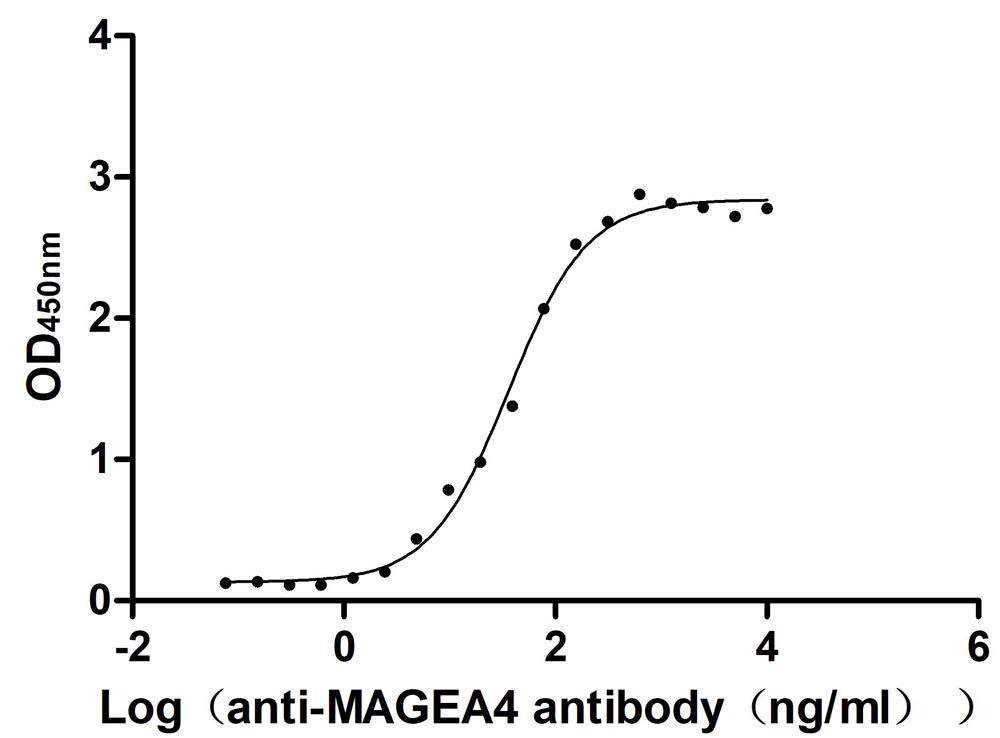
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
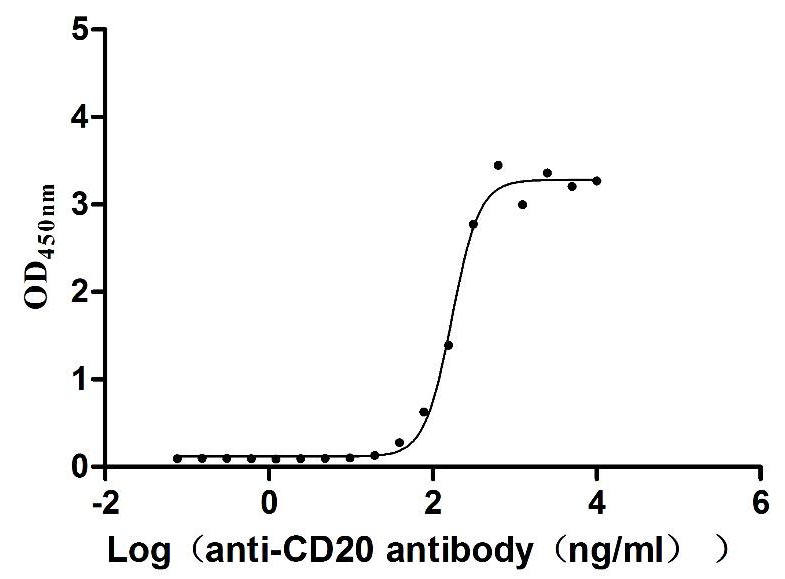
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
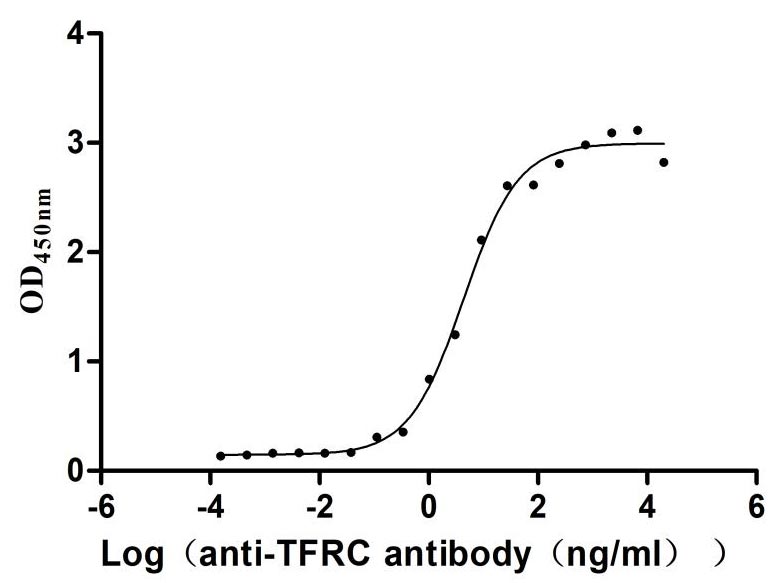
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
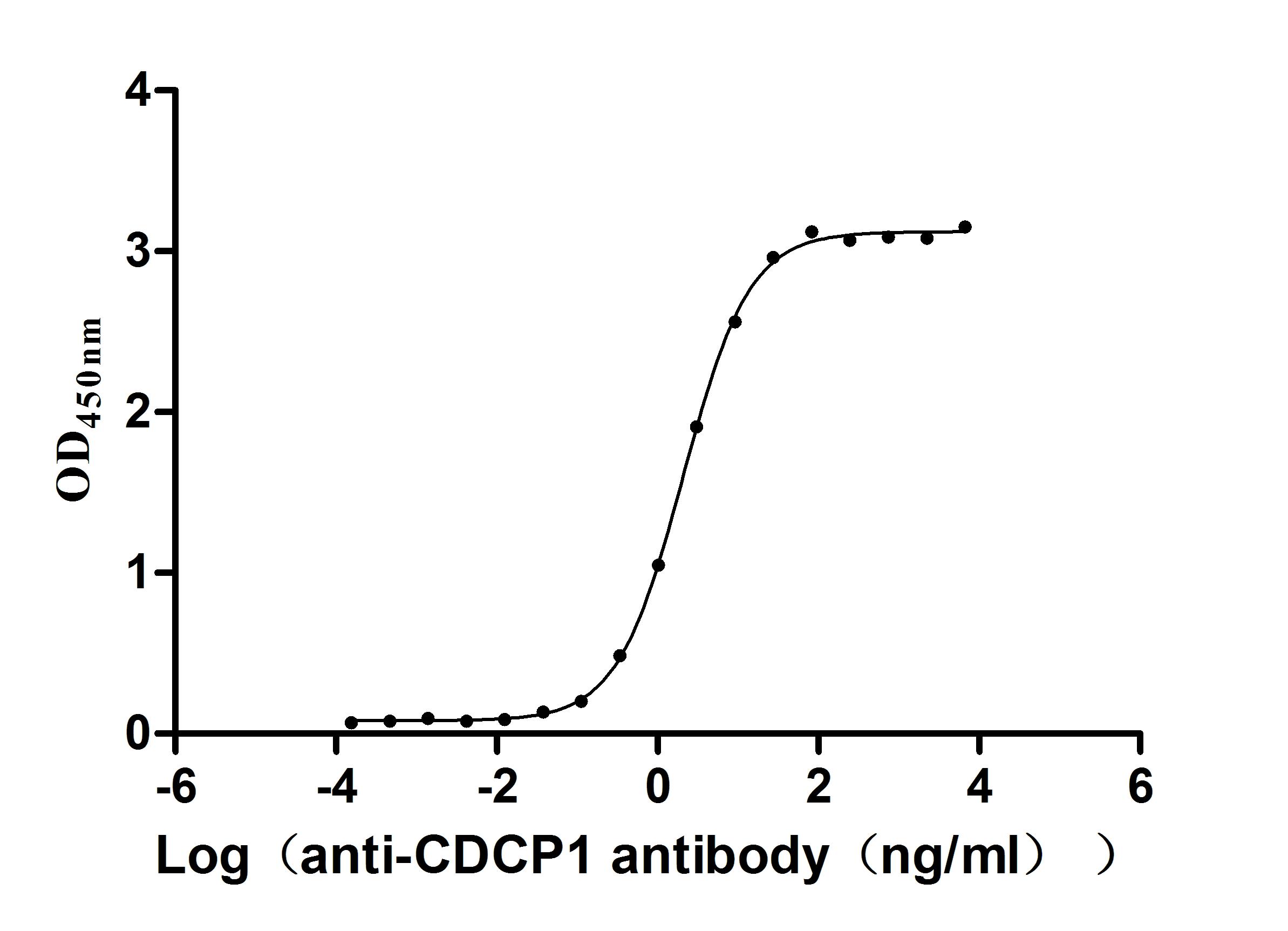
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
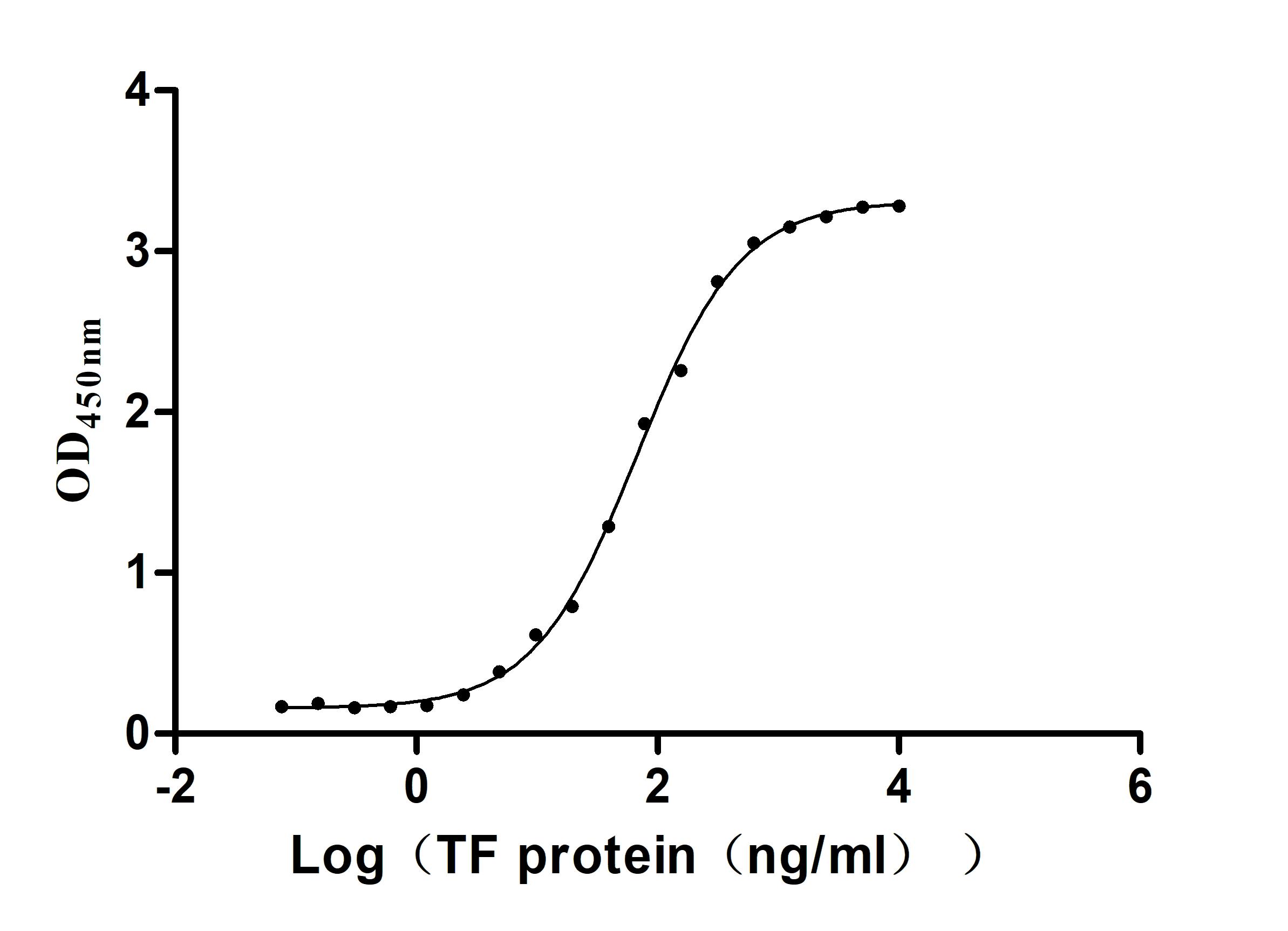
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)