Recombinant Human Glucose-6-phosphatase (G6PC), partial
-
中文名称:人G6PC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP009118HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人G6PC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP009118HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人G6PC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP009118HU1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人G6PC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP009118HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人G6PC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP009118HU1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:AW107337; G-6-Pase; G6Pase; G6Pase-alpha; g6pc; G6PC_HUMAN; G6PT; Glucose-6-phosphatase alpha; Glucose-6-phosphatase; glucose-6-phosphatase; catalytic subunit; GSD1; GSD1a; MGC163350; MGC93613; RP23-281C18.19
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Hydrolyzes glucose-6-phosphate to glucose in the endoplasmic reticulum. Forms with the glucose-6-phosphate transporter (SLC37A4/G6PT) the complex responsible for glucose production in the terminal step of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Hence, it is the key enzyme in homeostatic regulation of blood glucose levels.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Microarrays revealed that G6PC mRNA was upregulated following GDNF-mediated dopaminergic differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells. Array association analysis showed three downregulated microRNAs that could possibly influence G6PC translation. Although qRT-PCR results were not significant, they did support the microarray findings with regard to trend. Western blotting also confirmed increased G6PC protein expression following GDNF PMID: 28829278
- 3'-UTR SNP rs2229611 in G6PC1 affects mRNA stability, expression and Glycogen Storage Disease type-Ia risk PMID: 28502559
- crystal structures of the FoxO1 DNA binding domain in complex with the G6PC1 promoter PMID: 28223045
- Notch1 expression is reduced and glucose-6-phosphatase and perilipin-5 (G6PC/PLIN5) are upregulated in liver biopsies from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients. PMID: 27428080
- Mutation analysis of the G6PC gene revealed that GSD Ia accounted for 11% in GSD patients with involvement of liver. Three patients were homozygous for R83C mutation. In addition, a novel stop mutation, Y85X, was identified in a patient with the typical features of GSD Ia. PMID: 28360385
- Post-translational regulation of the glucose-6-phosphatase complex by cyclic AMP is a crucial determinant of endogenous glucose production and is controlled by the glucose-6-phosphate transporter. PMID: 26958868
- ApoA-IV colocalizes with NR4A1, which suppresses G6Pase and PEPCK gene expression at the transcriptional level, reducing hepatic glucose output and lowering blood glucose. PMID: 26556724
- By direct DNA sequencing, three novel G6PC variations were identified which expanded the G6PC mutation spectrum, and provided conclusive genetic evidences for the definitive diagnosis of the Chinese patients. PMID: 24980439
- This study is the first to demonstrate a functional relationship between the critical gluconeogenic and glycogenolytic enzyme G6PC with the metabolic adaptations during glioblastoma invasion. PMID: 25001192
- The spectrum of mutations in the G6PC gene. PMID: 24355556
- Lipopolysaccharide and monophosphoryl lipid A also up-regulated G6PC and PCK1 transcript abundance in a TLR4-dependent manner. PMID: 23465595
- Both GSD-1a and G6PT strongly colocalised in perinuclear membranes. showed that GSD1 mutations did neither alter the G6PC or G6PT chimera localisation, nor the interaction between G6PT termini. PMID: 21983240
- results reveal a novel link between glucose metabolism and the DNA damage signaling pathway and suggest a possible role for PEPCK and G6P in the DNA damage response PMID: 21733854
- data mitigate against G6PD deficiency contributing to stroke risk in individuals with sickle cell anemia. PMID: 21328436
- description of G6PC mutations in Thailand patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia PMID: 19832742
- we report the results of structure and function studies of the 48 missense mutations and the DeltaF327 codon deletion mutation, grouped as active site, helical, and nonhelical mutations PMID: 11739393
- active site of G6Pase: role of HIS176 as the nucleophile forming the phosphohistidine-enzyme intermediate during catalysis PMID: 12093795
- homozygosity for one G6PC mutation, G188R, seems to be associated with a glycogen storage disease type I non-a phenotype and homozygosity for the 727G>T mutation may be associated with a milder phenotype but an increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma PMID: 12373566
- The amino-terminal domain of G6PT is required for optimal glucose-6-phosphate uptake activity. PMID: 12444104
- maximum repression of basal glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit (G6Pase) gene transcription by insulin requires two distinct promoter regions, designated that together form an insulin response unit. PMID: 12556524
- Five mutants lack microsomal G6P uptake activity and one retains residual activity, suggesting that in G6PT the signature motif is a functional element required for microsomal glucose-6-phosphate transport. PMID: 12560945
- a novel, widely expressed G6Pase-related protein, PAP2.8/UGRP, renamed here G6Pase-beta couples with the G6P transporter to form an active G6Pase complex that can hydrolyze G6P to glucose PMID: 13129915
- Glc-6-Pase-alpha and Glc-6-Pase-beta share a similar active site structure, topology, and mechanism of action PMID: 14718531
- G6pc expression was functionally silenced by adenovirus-mediated delivery of short hairpin RNA. PMID: 14759518
- Findings suggest that the screening for 727G-->T and R83H mutations of glucose-6-phosphatase gene in conjunction with the 1176 polymorphism linkage analysis is a good method for gene and prenatal diagnosis of glycogen storage disease Ia. PMID: 15696478
- HNF4alpha, CREM, HNF1alpha, and C/EBPalpha have roles in transcriptional regulation of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene by cAMP/vasoactive intestinal peptide in the intestine PMID: 16893891
- G6PC1 hepatic activity was abnormally low in 98 SIDS (preterm, n=13; term, n=85), and non-SIDS preterm infants (n=35) compared to term non-SIDS infants (n=29) and adults (n=9) PMID: 17354259
- analysis of mutation spectrum of glycogen storage disease type Ia in Tunisia PMID: 18008183
- summary of the reported G6PC mutations and review what mutagenesis studies have revealed about the structure and function of the G6PC catalytic unit [review] PMID: 18449899
- EGF also inhibits hepatic G6Pase gene expression in vivo PMID: 18847435
- Identification of a risk conferring single nucleotide polymorphism in G6PC for type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. PMID: 19082990
- Increased transcriptional expression of PEPCK1 and G6Pc does not account for increased gluconeogenesis and fasting hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 19587243
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Glycogen storage disease 1A (GSD1A)
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Glucose-6-phosphatase family
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 4056
OMIM: 232200
KEGG: hsa:2538
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000253801
UniGene: Hs.212293
Most popular with customers
-
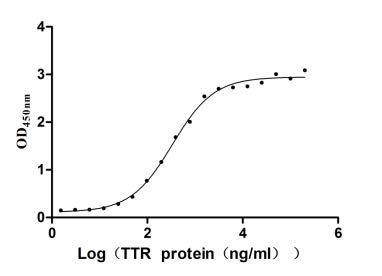
Recombinant Human Transthyretin (TTR) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
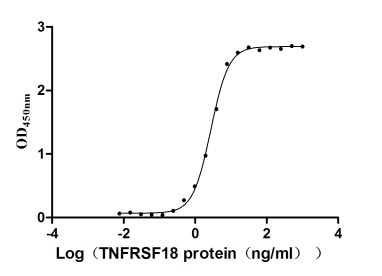
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
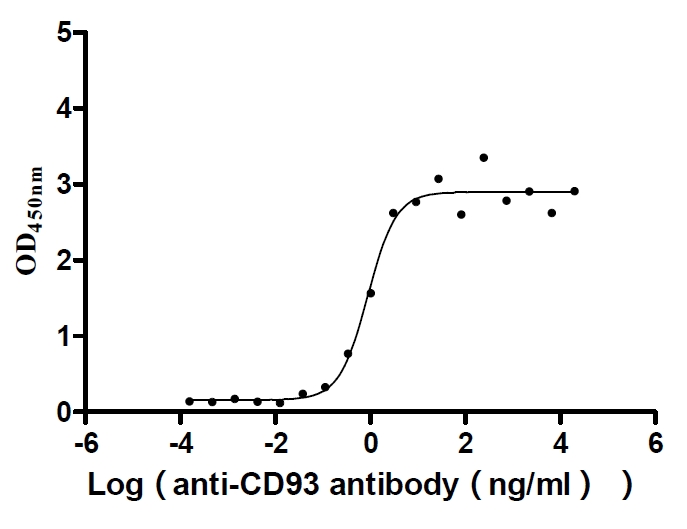
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
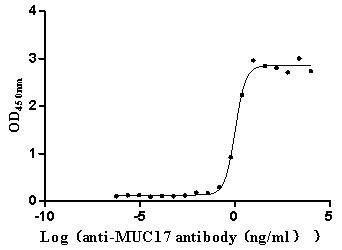
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)