Recombinant Human Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G (i) subunit alpha-1 (GNAI1)
-
货号:CSB-YP009588HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009588HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP009588HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP009588HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Adenylate cyclase inhibiting G alpha protein; Adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein; Adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G alpha protein; G protein alpha inhibiting 1; G protein alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1; Gi; Gi inhibitory G protein; Gi1 protein alpha subunit; GNAI 1; GNAI1; GNAI1_HUMAN; Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein) alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1; Guanine nucleotide binding protein alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1; Guanine nucleotide binding protein G(i) alpha 1 subunit; Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1; OTTHUMP00000161319; OTTHUMP00000208047
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-354
-
氨基酸序列GCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID RNLREDGEKA AREVKLLLLG AGESGKSTIV KQMKIIHEAG YSEEECKQYK AVVYSNTIQS IIAIIRAMGR LKIDFGDSAR ADDARQLFVL AGAAEEGFMT AELAGVIKRL WKDSGVQACF NRSREYQLND SAAYYLNDLD RIAQPNYIPT QQDVLRTRVK TTGIVETHFT FKDLHFKMFD VGGQRSERKK WIHCFEGVTA IIFCVALSDY DLVLAEDEEM NRMHESMKLF DSICNNKWFT DTSIILFLNK KDLFEEKIKK SPLTICYPEY AGSNTYEEAA AYIQCQFEDL NKRKDTKEIY THFTCATDTK NVQFVFDAVT DVIIKNNLKD CGLF
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in numerous signaling cascades. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state. Signaling by an activated GPCR promotes GDP release and GTP binding. The alpha subunit has a low GTPase activity that converts bound GTP to GDP, thereby terminating the signal. Both GDP release and GTP hydrolysis are modulated by numerous regulatory proteins. Signaling is mediated via effector proteins, such as adenylate cyclase. Inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, leading to decreased intracellular cAMP levels. The inactive GDP-bound form prevents the association of RGS14 with centrosomes and is required for the translocation of RGS14 from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Required for normal cytokinesis during mitosis. Required for cortical dynein-dynactin complex recruitment during metaphase.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- using cryo-electron microscopy, it is shown that the major interactions between activated rhodopsin and Gi are mediated by the C-terminal helix of the Gi alpha-subunit, which is wedged into the cytoplasmic cavity of the transmembrane helix bundle and directly contacts the amino terminus of helix 8 of rhodopsin PMID: 29899450
- 3.5 A resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the mu-opioid receptor (muOR) bound to the agonist peptide DAMGO and nucleotide-free Gi; these results shed light on the structural features that contribute to the Gi protein-coupling specificity of the microOR PMID: 29899455
- HL-60 neutrophil-like cells expressing Rap1a(G12V) or Radil have an elongated phenotype because of enhanced uropod adhesion as they attempt to migrate on fibronectin. This elongated phenotype driven by Rap1a(G12V) or Radil is reversed by Galphai1(Q204L), but not by WT Galphai1 expression, suggesting that Galphai-GTP also regulates adhesion in immune cells at the level of, or downstream of, Radil. PMID: 29259127
- complex between M2R and holo-Gi1 is an octamer comprising four copies of each, and that activation is accompanied by a decrease in the oligomeric size of Gi1 PMID: 27494760
- GIV is a bifunctional modulator of G proteins; it serves as a guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) for Galphas using the same motif that allows it to serve as a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for Galphai PMID: 27621449
- The s demonstrate that Glu53, Glu60, and Glu118 of human Ngb are crucial for both the neuroprotective activity and interaction with Gi. Moreover, they show that Lys46, Lys70, Arg208, Lys209, and Lys210 residues of Gi are important for binding to human Ngb. PMID: 27109834
- GTP analogs leads to a rigid and closed arrangement of the Galphai1, whereas the apo and GDP-bound forms are considerably more open and dynamic. PMID: 27298341
- The results show ZIP9 is a specific Gi coupled-membrane AR mediating testosterone-induced MAP kinase and zinc signaling in PC3-ZIP9 cells. PMID: 28219737
- These data indicate that, unlike in taste cells, TAS2Rs couple to the prevalent G proteins, Galphai1, Galphai2, and Galphai3, with no evidence for functional coupling to Galphagust. PMID: 28145731
- testosterone rapidly increased whole-cell HCAEC SKCa and BKCa currents via a surface androgen receptor, Gi/o protein, and protein kinase A PMID: 28223151
- These findings suggest that Gi1 interacts only with active GPCRs and that the well known high speed of GPCR signal transduction does not require preassembly between G proteins and GPCRs. PMID: 28438833
- Silencing of Galphai1 expression blocked the inhibitory effects of G-1 on prostate cancer cell growth PMID: 27908592
- biochemical and computational data indicate that the interactions between alpha5, alpha1, and beta2-beta3 are not only vital for GDP release during G protein activation, but they are also necessary for proper GTP binding (or GDP rebinding). PMID: 27462082
- In activation cluster I, helices alpha1 and alpha5 pack against strands beta1-beta3 to stabilize the nucleotide-bound states. PMID: 26258638
- The loss-of-function mutations of GNAI loci are rare or nonexistent in familial pituitary adenomas. PMID: 25291362
- Employed time-resolved FTIR difference spectroscopy to investigate the molecular reaction mechanisms of Galphai1. Mutants of the intrinsic arginine finger (Galphai1-R178S) affected exclusively the hydrolysis reaction. PMID: 25979337
- Data indicate that hydroxyurea (HU) induces SAR1 protein expression, which in turn activates gamma-globin expression, predominantly through the Gialpha/JNK/Jun pathway. PMID: 24914133
- We observed increased expression of Galphai1/3 in wounded human skin and keloid skin tissues, suggesting the possible involvement of Galphai1/3 in wound healing and keloid formation. PMID: 25078664
- Gi alpha subunit was found to be a key modulator of GABAB-receptors signaling in analgesia. PMID: 25242222
- AC5, by binding active Galphai1, interferes with G-protein deactivation and reassembly and thereby might sensitize its own regulation. PMID: 23841650
- Data indicate that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation and cell migration require Src, Gi/Go, COX-2 and LOXs activities. PMID: 23179791
- resistin contributes to the pro-inflammatory state of SMC by the up-regulation of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 expression via a mechanism involving NF-kB, AP-1, and STAT1/3 transcription factors, (2) resistin employs TLR4 and Gi-protein signaling. PMID: 23086480
- leucine can directly facilitate insulin signaling through a Galphai protein-dependent intracellular signaling pathway PMID: 23404499
- Data suggest that chemokine binding to CCX-CKR (a) recruits Gi proteins and beta-arrestin (beta-arr) with high affinity. PMID: 23341447
- This study support a role for RGS proteins as negative regulators of opioid supraspinal antinociception and also reveal a potential novel function of RGS proteins as positive regulators of opioid spinal antinociceptive pathways. PMID: 23467353
- Galpha(o) protein contributes to maximally efficient mu-opioid receptor signaling and antinociception in Galpha(o) null transgenic mice. PMID: 21654736
- CXCL12 signaling via CXCR7 is Gialpha independent. PMID: 22070874
- RGS14 can form complexes with GPCRs in cells that are dependent on Galpha(i/o) and these RGS14.Galpha(i1).GPCR complexes may be substrates for other signaling partners such as Ric-8A PMID: 21880739
- analysis of a novel Gi, P2Y-independent signaling pathway mediating Akt phosphorylation in response to thrombin receptors PMID: 20586915
- Data reveal a change in the repertoire of Galpha(i/o) subunits during T cell differentiation and suggest functional equivalence among Galpha(i/o) subunits irrespective of their relative abundance. PMID: 20829352
- The RET combination analysis revealed that stimulation of the alpha(2A)-adrenergic receptor (alpha(2A)AR) leads to the recruitment of GRK2 at a receptor still associated with the Galpha(i1)beta(1)gamma(2) complex. PMID: 20696855
- AGS3 receptor coupling to both Galphabetagamma and GPR-Galpha(i) offer additional flexibility for systems to respond and adapt to challenges and orchestrate complex behaviors PMID: 20716524
- Nucleobindin 1 is a calcium-regulated guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor of G{alpha}i1. PMID: 20679342
- The chemotaxis signal pathway induced by chemokines CKbeta8 and CKbeta8-1 is mediated via the Gi/Go protein, phospholipase C (PLC) and protein kinase C delta (PKC delta). PMID: 19951712
- Structural determinants for GoLoco-induced inhibition of nucleotide release by Galpha subunits PMID: 11976690
- An age-induced increase in G alpha i may have a role in depressing cardiac function in aged human atria. PMID: 14576516
- region of the third cytoplasmic loop of Dopamine D2 receptor is crucial for determining G(i) protein coupling specificity. PMID: 14581469
- Gi has a role in insulin attenuation of platelet functions by interfering with cAMP suppression along with IRS-1 PMID: 14602724
- Gi, but not Gq or G12/13, signaling pathways are required for activation of Akt in platelets PMID: 14623889
- Gi has a role in CXCL16 signaling that induces cell-cell adhesion and aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation PMID: 14625285
- the G(alpha)o/i-coupled cannabinoid receptor, by regulating the proteasomal degradation of Rap1GAPII, activates Rap1 to induce neurite outgrowth. PMID: 15657046
- Gialpha and Gbeta subunits both define selectivity of G protein activation by alpha2-adrenergic receptors. PMID: 16371464
- Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) reduces cell surface levels of eight different members of the CC- and CXC-family of Chemokine receptors (CKRs) by up to 92%. PMID: 16775006
- autotaxin induces uPA expression via the Gi-PI3K-Akt-NF-kappaB signaling pathway that might be critical for autotaxin-induced tumor cell invasion and metastasis PMID: 17013094
- Data show that Gi and RGS proteins provide biochemical control of androgen receptor exclusion from the cell nucleus. PMID: 17416965
- Selective induction of G alpha inhibiting subunit 1 (Gi alpha1) expression is a novel downstream event in hypertrophic signaling that may be a critical factor leading to cellular electrophysiological remodeling of the Ras transgenic mouse heart. PMID: 17646583
- Heretotrimeric G protein subunit Galphai is associated with mitochondria. PMID: 18037379
- The potency and efficacy of LPA-mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity was enhanced in cells expressing RGSi G(i) (mutant) proteins as compared to RGSwt G(i). PMID: 18083345
- MUPP1 binds to the G protein-coupled MT(1) melatonin receptor and directly regulates its G(i)-dependent signal transduction PMID: 18378672
- analysis of structural determinants underlying the temperature-sensitive nature of a Galpha mutant PMID: 18519563
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:G-alpha family, G(i/o/t/z) subfamily
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 4384
OMIM: 139310
KEGG: hsa:2770
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000343027
UniGene: Hs.134587
Most popular with customers
-
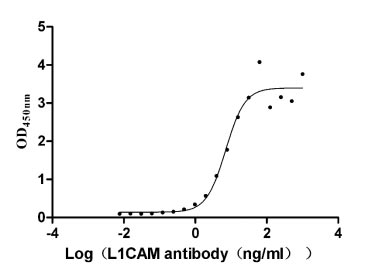
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
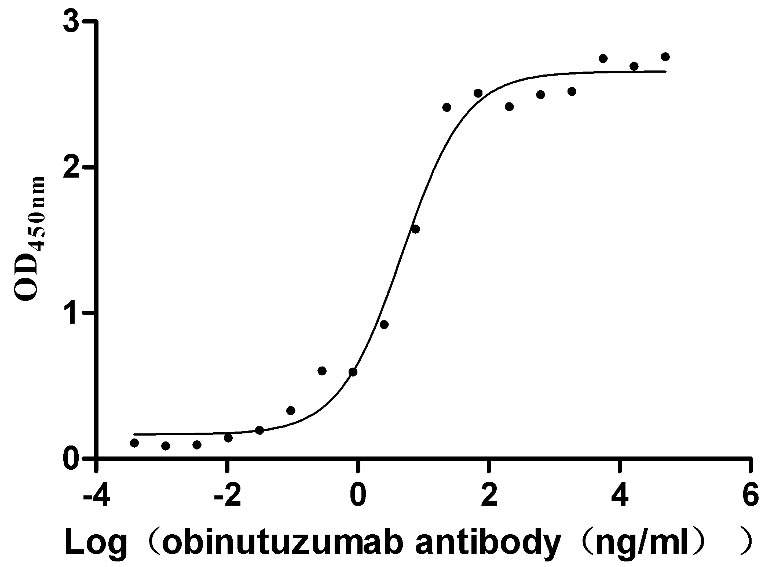
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
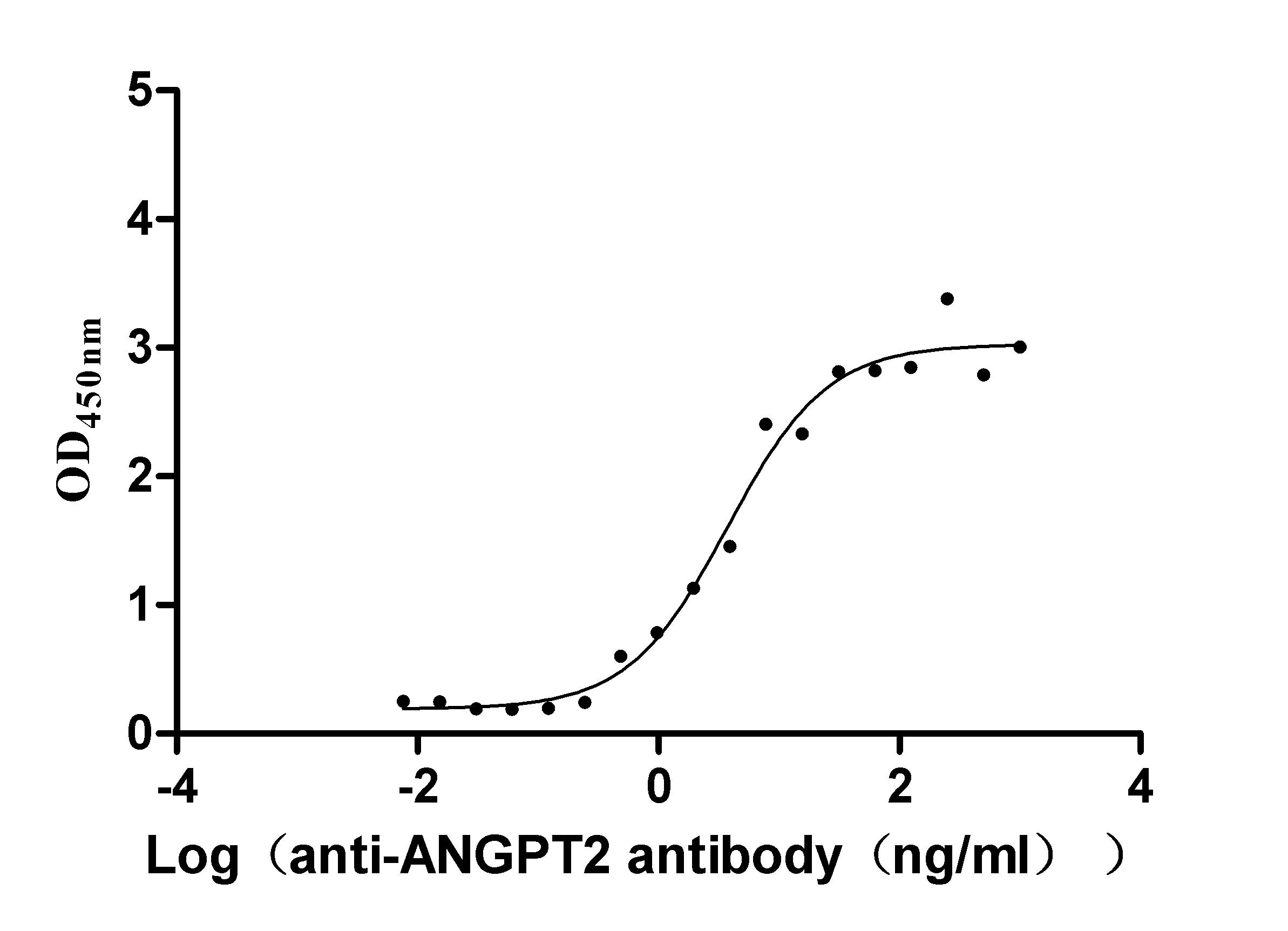
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
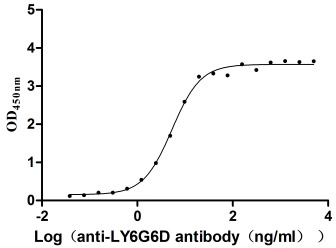
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
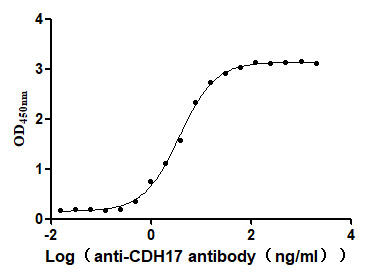
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
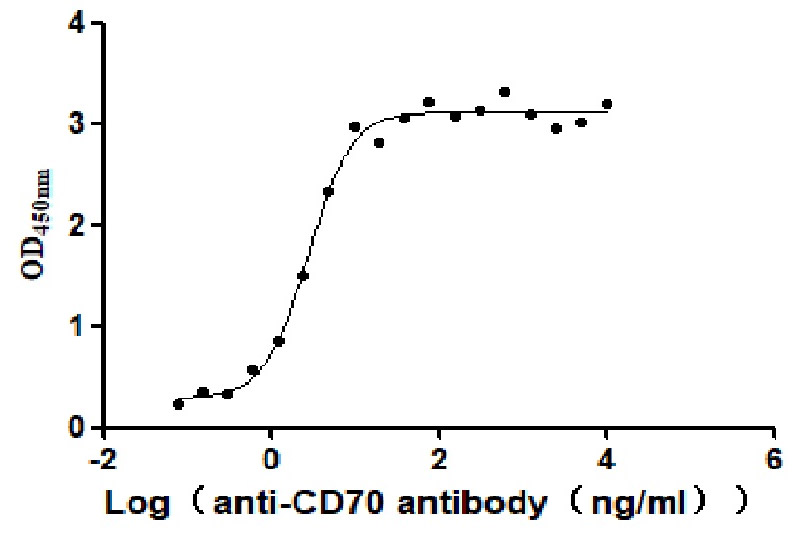
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)