Recombinant Human Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 (LCP2)
-
货号:CSB-YP622635HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP622635HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP622635HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP622635HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP622635HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
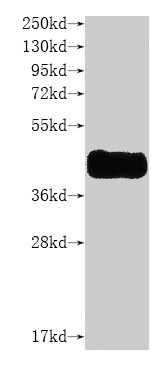
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:76 kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein; CG8697; LCP 2; LCP2; LCP2_HUMAN; Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2; SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein 76 KD ; SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 76kD; SH2 domain containing leukocyte protein of 76kDa; SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa; SLP 76; SLP 76 tyrosine phosphoprotein; SLP-76; SLP-76 tyrosine phosphoprotein; SLP76; SLP76 tyrosine phosphoprotein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-533
-
氨基酸序列MALRNVPFRS EVLGWDPDSL ADYFKKLNYK DCEKAVKKYH IDGARFLNLT ENDIQKFPKL RVPILSKLSQ EINKNEERRS IFTRKPQVPR FPEETESHEE DNGGWSSFEE DDYESPNDDQ DGEDDGDYES PNEEEEAPVE DDADYEPPPS NDEEALQNSI LPAKPFPNSN SMYIDRPPSG KTPQQPPVPP QRPMAALPPP PAGRNHSPLP PPQTNHEEPS RSRNHKTAKL PAPSIDRSTK PPLDRSLAPF DREPFTLGKK PPFSDKPSIP AGRSLGEHLP KIQKPPLPPT TERHERSSPL PGKKPPVPKH GWGPDRREND EDDVHQRPLP QPALLPMSSN TFPSRSTKPS PMNPLPSSHM PGAFSESNSS FPQSASLPPY FSQGPSNRPP IRAEGRNFPL PLPNKPRPPS PAEEENSLNE EWYVSYITRP EAEAALRKIN QDGTFLVRDS SKKTTTNPYV LMVLYKDKVY NIQIRYQKES QVYLLGTGLR GKEDFLSVSD IIDYFRKMPL LLIDGKNRGS RYQCTLTHAA GYP
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in T-cell antigen receptor mediated signaling.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data are consistent with a model in which bivalent recruitment of a GADS/SLP-76 complex is required for costimulation by CD6. PMID: 28289074
- LAT and SLP-76 are randomly dispersed throughout the clusters that form upon T cell receptor engagement. PMID: 27875277
- SLP76 is ectopically expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells where it plays a role in B-cell receptor signaling. PMID: 27443285
- findings identify ACK1 as a novel SLP-76-associated protein-tyrosine kinase that modulates early activation events in T cells. PMID: 28188290
- Data strongly suggest that chemokine-stimulated associations between Vav1, SLP-76, and ADAP facilitate Rac1 activation and alpha4beta1-mediated adhesion, whereas Pyk2 opposes this adhesion by limiting Rac1 activation. PMID: 26202465
- immune cell adaptor SLP-76 binds directly to SUMO-RanGAP1 of cytoplasmic fibrils of the nuclear pore complex, and this interaction is needed for optimal NFATc1 and NF-kappaB p65 nuclear entry in T cells PMID: 26321253
- SLP-76 N-terminal tyrosine residues regulate a dynamic signaling equilibrium involving feedback of proximal T-cell receptor signaling PMID: 25316710
- analysis of a costimulatory mechanism by which CXCL12 and antigen converge at SLP-76 microcluster formation to enhance T cell responses PMID: 23901140
- Multipoint binding of SLP-76 to ADAP facilitates the assembly of SLP-76 microclusters. PMID: 23979596
- Data indicate a role for the SAM domain in mediating SLP-76 self-association for T-cell function. PMID: 23935094
- Unique modes of regulation of positive and negative feedback pathways in T cells by SLP-76. PMID: 23071622
- These findings reveal a novel role for SLP-76 in CXCR4-mediated T lymphocyte trafficking. PMID: 22806433
- a novel regulation mechanism of SLP-76 by ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of activated SLP-76, which is mediated by Ser-376 phosphorylation, leading to down-regulation of TCR signaling. PMID: 22902619
- Complementary phosphorylation sites in the adaptor protein SLP-76 promote synergistic activation of natural killer cells. PMID: 22786724
- Nef employs a dual mechanism to disturb early TCR signaling by limiting the communication between LAT and SLP-76 PMID: 22802418
- both T cell activation and the association between SLP-76 and Nck. After T cell receptor stimulation, SLP-76 was phosphorylated, which enabled the binding of Nck. PMID: 22534133
- our studies demonstrate a novel role for the adaptor molecule SLP-76 in regulating HIV-1 infection in T cells PMID: 22323535
- Combining regulated deletion of endogenous SLP-76 with transgenic expression of a SLP-76 SH2 domain mutant demonstrates that the SLP-76 SH2 domain is required for peripheral T cell activation and positive selection of thymocytes. PMID: 21949020
- The spatial correlation between kinase ZAP70 and adaptor SLP76 microclusters (MC) at the cell periphery and the effects of F-actin on MC assembly, were analysed. PMID: 21887278
- findings demonstrate the critical role of SLP-76-mediated signaling in initiating T-cell-directed immune responses both in vitro and in vivo PMID: 21469089
- LAT recruits Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte 76 kDa protein (SLP-76) following T-cell receptor ligation and membrane translocation of Akt and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)phosphorylation in Jurkat cells, activating Akt signaling. PMID: 21282515
- Results define the composition, stoichiometry and specificity of interactions in the SLP-76, Nck and VAV1 complex, which is crucial for regulation of the actin machinery after T-cell activation. PMID: 20562827
- findings reconfigure the TCR signaling pathway by showing SLP-76 back-regulation of ZAP-70, an event that could ensure that signaling components are in balance for optimal T cell activation PMID: 20534575
- The results show that Bcr-Abl regulates the actin cytoskeleton and non-apoptotic membrane blebbing via a GADS/Slp-76/Nck1 adaptor protein pathway. PMID: 20079431
- Shb links SLP-76 and Vav with the CD3 complex in Jurkat T cells (SLP-76) PMID: 12084069
- SLP-76 is essential for NF-kappa B activation and lipid raft translocation of protein kinase C theta and the I kappa B kinase complex. PMID: 12496421
- SLP-76 is required for intracellular calcium ion mobilization in response to SDF-1alpha/CXCL12-induced prolonged activation of extracellular signal-related protein kinase in Jurkat T cells. PMID: 12817019
- SLP-76 is necessary for T cell receptor stimulation-induced polarization of the T cell's microtubule-organizing center, as it moves toward the interface of the T cell and antigen-presenting cell. PMID: 12847255
- Study provides the first data to address the mechanisms controlling SLP-76 transcription by providing evidence for several key cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region. PMID: 14662865
- the proline-rich domain in SLP-76 has a role in subcellular localization and T cell function PMID: 14722089
- Data suggest that SLP-76 may play a role in signaling pathways by interacting with the p85 subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). PMID: 15388330
- SLP-76 need not interact with SH3(PLC) to activate PLC-gamma1, and the P-I region of SLP-76 serves a structural role that is sequence-independent and is not directly related to protein-protein interactions PMID: 15623534
- Data show that the adaptor molecules LAT and SLP-76 are specifically targeted by Yersinia to inhibit T cell activation. PMID: 15699071
- TCR-induced association of Vav3 with SLP-76 is required for its membrane/IS localization and function PMID: 15708849
- In T cells all SLP-76 proteins are in a approximately 400 kDa complex with the small adaptor protein Grb2-like adaptor protein Gads. PMID: 16356554
- findings show that retinoic acid(RA) induced the expression of SLP-76, which when co-expressed with an RA-induced receptor, c-FMS, enhanced RA-induced cell differentiation and G0 cell cycle arrest PMID: 16439309
- The costimulatory effect of CD6 is mediated through phosphorylation-dependent binding of a specific tyrosine residue, 662Y, in its cytoplasmic region to the adaptor SLP-76. PMID: 16914752
- The P-I region deletion disrupted Vav association and reduced SLP-76-associated kinase activity. PMID: 17148460
- The integrity of T-cell receptor signaling in vivo is sustained both by strong selection of SLP-76 for the Gads C-SH3 domain and by a capacity to buffer intrinsic crossreactivity. PMID: 17235283
- phosphorylation of the adaptor molecule SLP-76 is essential for recruitment of the exchange factor Vav leading to Ca(2+) flux and IL-2 production PMID: 17237383
- Required for activation of IL-2-inducible T cell kinase (ITK); furthermore, an ongoing physical interaction between SLP-76 and ITK is required to maintain ITK in an active conformation. PMID: 17420479
- SLP-76 relocalizes to integrin-initiated signaling complexes by a mechanism different from that employed during TCR signaling and that SLP-76 relocalization corresponds to SLP-76-dependent integrin function in T cells. PMID: 19667077
- SLP76 is differentially required for T cell receptor- compared to chemokine C-X-C receptor 4-mediated inside-out signaling pathways regulating T cell adhesion and migration in Jurkat T cells. PMID: 19812192
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in spleen, thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes. Highly expressed also in T-cell and monocytic cell lines, expressed at lower level in B-cell lines. Not detected in fibroblast or neuroblastoma cell lines.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6529
OMIM: 601603
KEGG: hsa:3937
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000046794
UniGene: Hs.304475
Most popular with customers
-
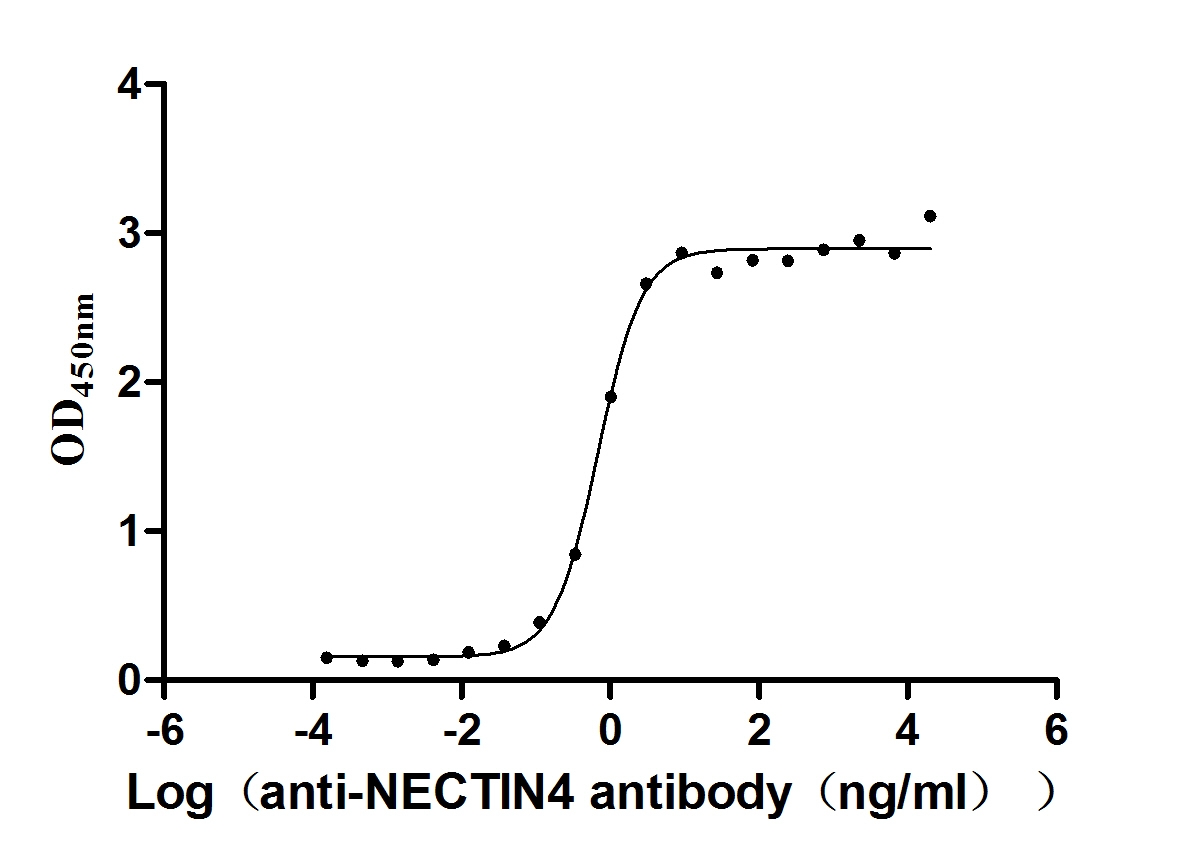
Recombinant Human Nectin-4 (NECTIN4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
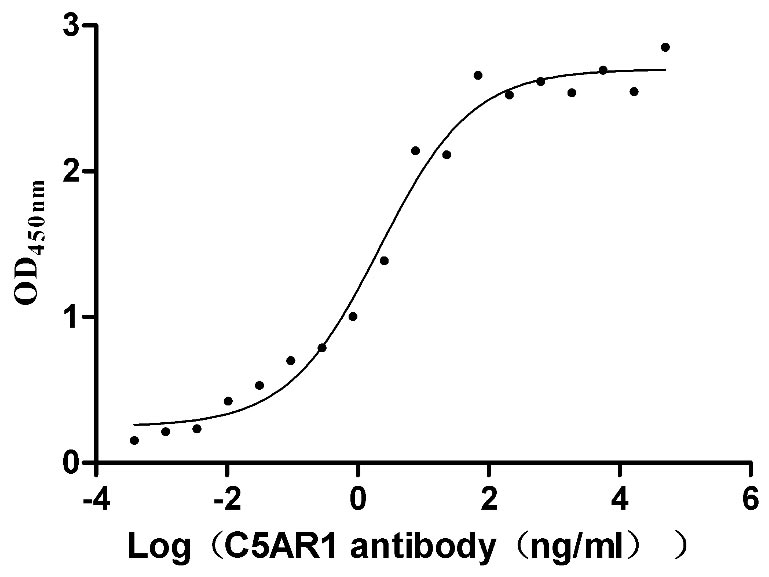
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
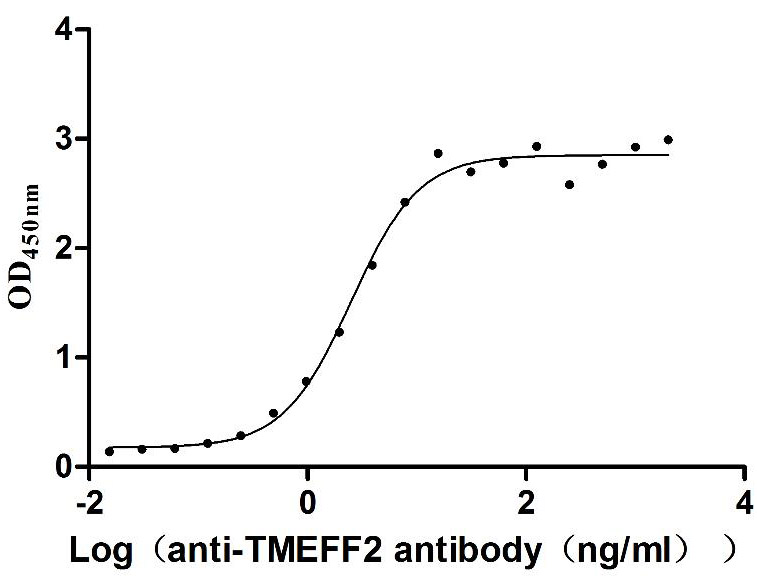
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
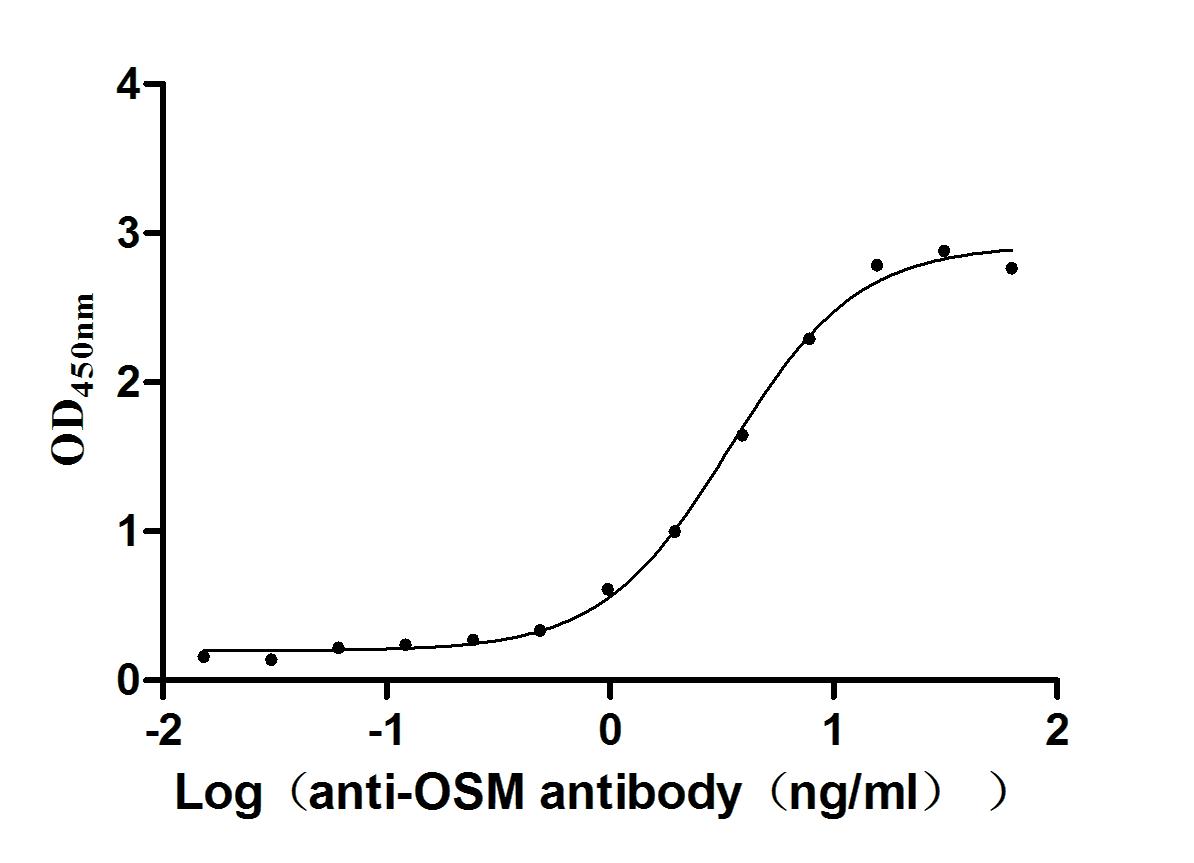
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
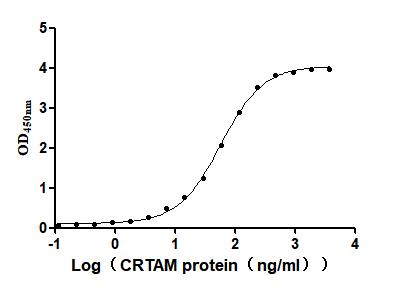
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
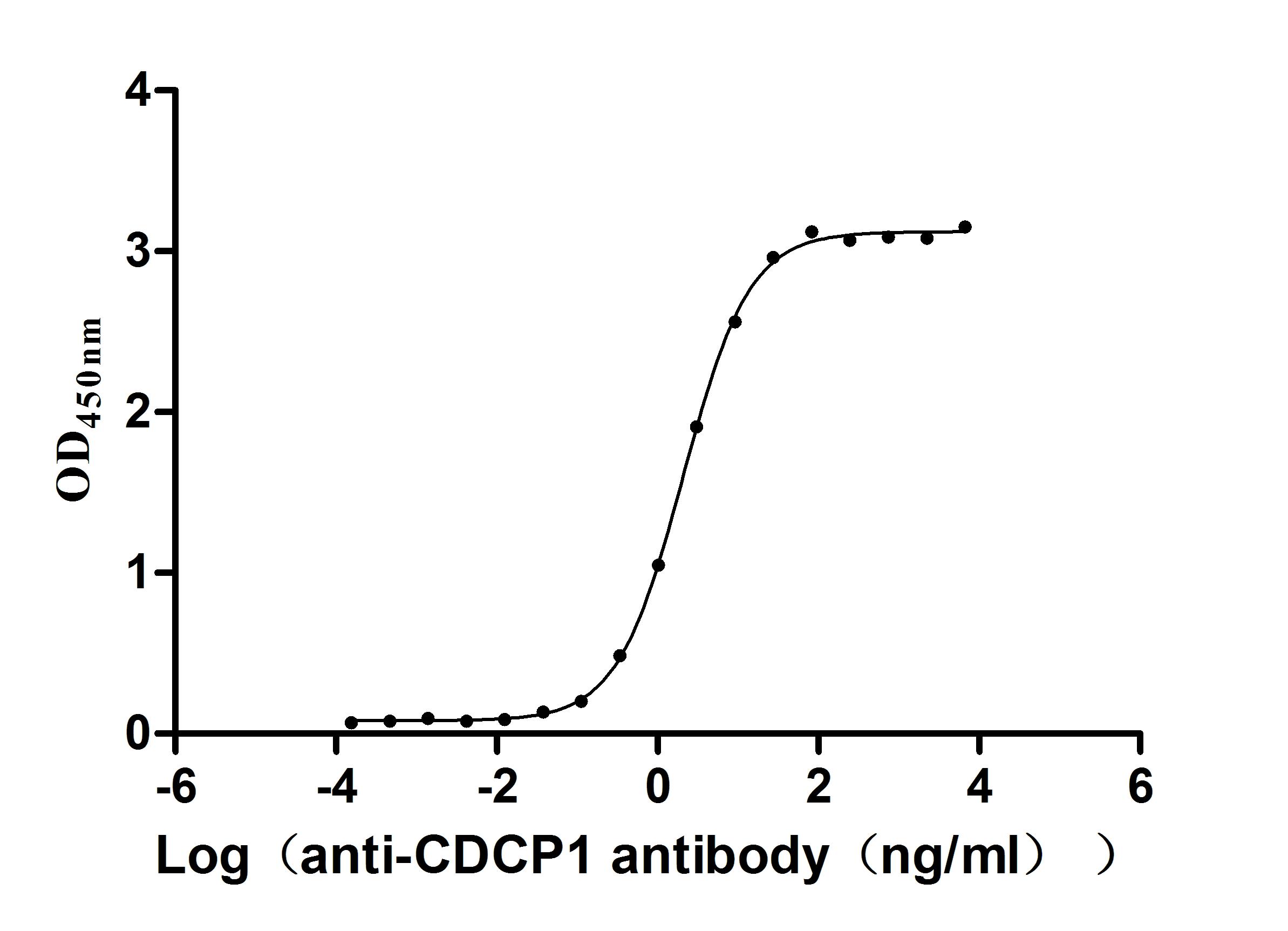
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(PLAU) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)