Recombinant Human Methionine synthase reductase (MTRR)
-
中文名称:人MTRR重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP890659HU
-
规格:¥1344
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
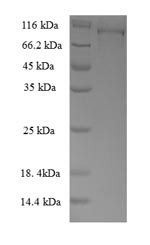
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:MTRR
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:MTRR; Methionine synthase reductase; MSR; EC 1.16.1.8
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:107.4kDa
-
表达区域:1-725aa
-
氨基酸序列MGAASVRAGARLVEVALCSFTVTCLEVMRRFLLLYATQQGQAKAIAEEICEQAVVHGFSADLHCISESDKYDLKTETAPLVVVVSTTGTGDPPDTARKFVKEIQNQTLPVDFFAHLRYGLLGLGDSEYTYFCNGGKIIDKRLQELGARHFYDTGHADDCVGLELVVEPWIAGLWPALRKHFRSSRGQEEISGALPVASPASSRTDLVKSELLHIESQVELLRFDDSGRKDSEVLKQNAVNSNQSNVVIEDFESSLTRSVPPLSQASLNIPGLPPEYLQVHLQESLGQEESQVSVTSADPVFQVPISKAVQLTTNDAIKTTLLVELDISNTDFSYQPGDAFSVICPNSDSEVQSLLQRLQLEDKREHCVLLKIKADTKKKGATLPQHIPAGCSLQFIFTWCLEIRAIPKKAFLRALVDYTSDSAEKRRLQELCSKQGAADYSRFVRDACACLLDLLLAFPSCQPPLSLLLEHLPKLQPRPYSCASSSLFHPGKLHFVFNIVEFLSTATTEVLRKGVCTGWLALLVASVLQPNIHASHEDSGKALAPKISISPRTTNSFHLPDDPSIPIIMVGPGTGIAPFIGFLQHREKLQEQHPDGNFGAMWLFFGCRHKDRDYLFRKELRHFLKHGILTHLKVSFSRDAPVGEEEAPAKYVQDNIQLHGQQVARILLQENGHIYVCGDAKNMAKDVHDALVQIISKEVGVEKLEAMKTLATLKEEKRYLQDIWS
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal GST-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Key enzyme in methionine and folate homeostasis responsible for the reactivation of methionine synthase (MTR/MS) activity by catalyzing the reductive methylation of MTR-bound cob(II)alamin. Cobalamin (vitamin B12) forms a complex with MTR to serve as an intermediary in methyl transfer reactions that cycles between MTR-bound methylcob(III)alamin and MTR bound-cob(I)alamin forms, and occasional oxidative escape of the cob(I)alamin intermediate during the catalytic cycle leads to the inactive cob(II)alamin species (Probable). The processing of cobalamin in the cytosol occurs in a multiprotein complex composed of at least MMACHC, MMADHC, MTRR and MTR which may contribute to shuttle safely and efficiently cobalamin towards MTR in order to produce methionine. Also necessary for the utilization of methyl groups from the folate cycle, thereby affecting transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. Also acts as a molecular chaperone for methionine synthase by stabilizing apoMTR and incorporating methylcob(III)alamin into apoMTR to form the holoenzyme. Also serves as an aquacob(III)alamin reductase by reducing aquacob(III)alamin to cob(II)alamin; this reduction leads to stimulation of the conversion of apoMTR and aquacob(III)alamin to MTR holoenzyme.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- 12 articles were included in this study. The pooled results did not reveal a significant association of the MTRR A66G polymorphism (G vs. A: OR = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.82-1.18, p = 0.72) with Nonsyndromic Cleft Lip With or Without Cleft Palate risk PMID: 30004262
- The gene polymorphism of MTRR A66G may not be an independent genetic risk factor in deep venous thrombosis in China. PMID: 29927730
- The genotypes of three women having spina bifida fetuses from two unrelated Chinese families were screened in candidate alleles. A trinucleotide deletion (c.4_6delAGG) was found in the first exon of MTRR only in the affected women, but not in their siblings with healthy babies or in controls. The Arg2del variant's subcellular localization and catalysis was unchanged, but it failed to efficiently activate MTR. PMID: 28712006
- Our results suggest an association between underweight and early childhood caries; in addition it is suggested that MTRR is a common genetic risk factor for early childhood caries and underweight PMID: 28118645
- higher frequency of 66GG genotype and 66G allele of MTRR 66A > G polymorphism observed in the women with pre-eclampsia compared to control group PMID: 27806663
- An association between the MTRR A66G polymorphism and LC ( p = 0.042) was found. In addition, this allele was observed more frequently in smokers compared to nonsmokers ( p = 0.030). In contrast, the distribution of the MTR 2756A>G and the MTRR 524 C> T allele frequencies were similar in the subject cases and controls. PMID: 28537809
- Meta-analysis suggests that MTRR 66A>G polymorphism may be associated with oligoasthenozoospermia risk. PMID: 28436330
- Study in Egyptian children showed that MTRR A66G and C524T polymorphisms were associated with a higher congenital heart diseases risk in the homozygote comparison of wild and mutant genotypes and also in heterozygote and mutant comparison. PMID: 28778621
- study widens the clinical, molecular, metabolic, and cytological knowledge of deficiency MTRR enzyme. PMID: 25978498
- The present study suggests that the G allele of MTR A2756G polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of autism. PMID: 28094822
- These findings indicate that the alternatively spliced form of MS expressed in SH-SY5Y human neuronal cells is sensitive to inhibition by thimerosal and neurotoxic metals, and lower GSH levels contribute to their inhibitory action. PMID: 26989453
- MTRR genetic polymorphisms are risk factor for predicting cardiovascular manifestations in Marfan syndrome. PMID: 26063524
- no association of rs1801394 with non-obstructive azoospermia PMID: 26196053
- an association between MTRR 66 and SHMT1 1420 polymorphisms and spaceflight-induced vision changes PMID: 26316272
- Results identified an allelic variant in the first intron of MTRR that is associated with increased risk of anencephaly in neural tube defects cases. PMID: 26045171
- Findings indicate an association between the single-nucleotide polymorphism A66G in the synthase reductase (MTRR A66G) gene and male infertility, particularly in oligoasthenozoospermia males. PMID: 25966116
- The findings of this study provide evidence that multiple sclerosis spinal cord simultaneously lack Cbl, EGF, and PrPCs. PMID: 25888933
- Results from the case-control study and meta-analysis suggest that both of the two polymorphisms MTHFR C677T and MTRR A66G Polymorphisms are not associated with being overweight/obesity PMID: 26016497
- A decrease of placental expression was noted for MTRR by 50% in pre-eclamptic women as compared to control group. PMID: 25801727
- MTRR 66GG genotype showed strong negative association with the risk of childhood brain tumors. PMID: 25809864
- More specifically, variants in methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) are not likely associated with capecitabine efficacy. PMID: 25815774
- The MTRR polymorphism represents a risk factor for the birth of a child with Down Syndrome among white Caucasian women. [Meta-analysis] PMID: 24965145
- MSR 524C/T polymorphism is associated with essential hypertension in ethnic groups in China. PMID: 26252105
- Review/Meta-analysis: suggest an association between MTRR A66G polymorphism and colorectal cancer susceptibility among Caucasians. PMID: 26214647
- meta analysis demonstrated that MTRR A66G polymorphism is a risk factor for congenital heart defects PMID: 24913415
- Heterogeneity across alcohol consumption status of the associations between MTR/MTRR polymorphisms and these cancers indicates potential interactions between alcohol drinking and one-carbon metabolic pathway PMID: 25337902
- This meta-analysis suggests that MTRR A66G GG is associated with decreased risk of leukemia in a Caucasian population and in children, especially for ALL. PMID: 24261678
- MTRR A66G polymorphisms have not been found to affect the hemostatic system in adolescents with Essential Hypertension. PMID: 25518505
- MTRR A66G polymorphism was not associated with breast cancer susceptibility. PMID: 24815481
- Reciprocal active site substitutions in CPR (H322A) and MSR (A312H) were created. Interflavin electron transfer was inhibited in CPR H322A and accelerated in MSR A312H. PMID: 24589657
- MTRR A66G gene polymorphism is associated with meningioma. PMID: 23959833
- Single nucleotide polymorphism in MTRR gene with LINE-1 methylation is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 24130171
- The distribution of MTHFR A1298C and MTRR A66G genotypes were not different between the fertile and infertile groups. PMID: 24334125
- [meta-analysis] MTRR A66G polymorphisms are not associated with risks for neural tube defects in Caucasian children. PMID: 23425389
- The 66GG and AG genotypes were associated with decreased odds ratios for heart defects. This overall association was driven by decreased risk for ventricular septal defect for 66GG and AG and decreased odds ratio for aortic valve stenosis for 66AG. PMID: 22475273
- A review of the influences of genetic polymorphisms in methionine synthase reductase on the occurrence of adverse effects from methotrexate therapy. PMID: 23986219
- Haplotype analysis suggests an association between MTRR haplotypes and reduced risk of migraine with aura. PMID: 23430981
- genetic association studies in population in China: Data suggest that an SNP in MTRR (C524T; S175L; rs1801394) is associated with decreased risk of Down syndrome in this population. PMID: 22925068
- maternal MTRR 66A>G polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of having a DS child.[Meta-Analysis] PMID: 23094987
- Rs6893114 in MTRR and alcohol consumption are associated with lung cancer risk in current smokers. PMID: 23372658
- Results indicate the importance of four gastric cancer susceptibility polymorphisms of IL-10, NOC3L, PSCA and MTRR in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 22796266
- The MTRR+66AA genotype may correlate with the severity of HD. PMID: 23039890
- studies suggest that SNPs in CBS and MTRR have sex-specific associations with aberrant methylation in the lung epithelium of smokers that could be mediated by the affected one-carbon metabolism and transsulfuration in the cells PMID: 22665368
- Known common single-nucleotide polymorphisms in MTRR and BHMT genes may not be significant risk factors for cororonary artery disease. PMID: 22339686
- the single-nucleotide polymorphism A66G MTRR is not involved in the development of breast cancer. PMID: 22236648
- The variant allele and genotypic frequencies in MTRR A66G gene was significantly higher in patients with UC compared to healthy controls. PMID: 21947961
- MTRR A66G polymorphism is a potential biomarker for cancer risk. PMID: 21547363
- MTRR A66G and cSHMT C1420T polymorphisms influence CpG island methylator phenotype of BNIP3, thus epigenetically regulating BNIP3 in breast cancer PMID: 21987236
- We have demonstrated that the MTRR c.56+781 A>C variant is an important genetic marker for increased congenital heart disease risk because this variant results in functionally reduced MTRR expression at the transcriptional level. PMID: 22179537
- MTRR polymorphisms did not appear to be an important genetic factor predisposing to idiopathic infertility in Brazilian men. PMID: 21775772
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia, cblE complementation type (HMAE); Neural tube defects, folate-sensitive (NTDFS)
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform B]: Cytoplasm.; [Isoform A]: Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Found in all tissues tested, particularly abundant in skeletal muscle.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 7473
OMIM: 236270
KEGG: hsa:4552
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000264668
UniGene: Hs.481551
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)