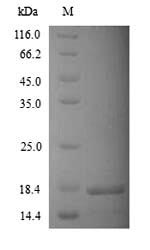
Recombinant Human Potassium channel subfamily K member 2 (KCNK2), partial
-
中文名称:人KCNK2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP012070HU
-
规格:¥1500
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:KCNK2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:hTREK 1c; hTREK 1e; K2p2.1; K2P2.1 potassium channel; KCNK 2; Kcnk2; KCNK2_HUMAN; MGC126742; MGC126744; Outward rectifying potassium channel protein TREK 1; Outward rectifying potassium channel protein TREK-1; Outward rectifying potassium channel protein TREK1; Potassium channel subfamily K member 2; Potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily K member 2; Tandem pore domain potassium channel TREK 1; Tandem pore domain potassium channel TREK1; TPKC1; TREK 1; TREK 1 K(+) channel subunit; TREK; TREK-1 K(+) channel subunit; TREK1; TWIK related potassium channel 1; Two pore domain potassium channel TREK 1 ; Two pore domain potassium channel TREK-1; Two pore domain potassium channel TREK1; Two pore potassium channel 1; Two pore potassium channel TPKC1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:Yeast
-
分子量:17.7kDa
-
蛋白标签:N-terminal His-tagged/Tag-Free
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Ion channel that contributes to passive transmembrane potassium transport. Reversibly converts between a voltage-insensitive potassium leak channel and a voltage-dependent outward rectifying potassium channel in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. In astrocytes, forms mostly heterodimeric potassium channels with KCNK1, with only a minor proportion of functional channels containing homodimeric KCNK2. In astrocytes, the heterodimer formed by KCNK1 and KCNK2 is required for rapid glutamate release in response to activation of G-protein coupled receptors, such as F2R and CNR1.; Does not display channel activity but reduces the channel activity of isoform 1 and isoform 2 and reduces cell surface expression of isoform 2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- data reveal a druggable K2P site that stabilizes the C-type gate 'leak mode' and provide direct evidence for K2P selectivity filter gating PMID: 28693035
- decreased TREK-1 expression in the aganglionic and ganglionic bowel observed in Hirschsprung's disease may alter intestinal epithelial barrier function leading to the development of enterocolitis PMID: 27384506
- Atrial TREK-1 expression was reduced in atrial fibrillation patients with concomitant severe heart failure PMID: 28005193
- The s identified a heterozygous point mutation in the selectivity filter of the stretch-activated K2P potassium channel TREK-1 (KCNK2 or K2P2.1). This mutation introduces abnormal sodium permeability and stretch-activation hypersensitivity to TREK-1. PMID: 28242754
- downregulated in overactive detrusor PMID: 28539337
- The M2-glycine hinge controls the macroscopic currents of TREK1 channels. PMID: 28676394
- TREK-1 overexpression suppresses CHO cell proliferation by inhibiting the activity of PKA and p38/MAPK signaling pathways and subsequently inducing G1 phase cell arrest. PMID: 27397543
- Trek1 expression facilitates the restoration of intestinal epithelial barrier functions in an allergic environment. PMID: 25683610
- presence of TREK-1 variants correlated to reduced TREK-1 activity, suggesting a pathological role for TREK-1 variants in preterm labor PMID: 26400398
- Data suggest that potassium channel protein TREK-1 (TREK-1) might be a biomarker in castration resistance free survival (CRFS) judgment of prostate cancer (PCa), as well as a potential therapeutic target. PMID: 25962960
- During conductance simulation experiments, both TASK-3 and TREK-1 channels were able to repolarise the membrane once AP threshold was reached PMID: 25482670
- How ion channels sense mechanical force: insights from mechanosensitive K2P channels TRAAK, TREK1, and TREK2. PMID: 26332952
- We conclude that Trek1 is critical to maintain the nasal epithelial barrier function. PMID: 25778785
- Nasal epithelia express Trek1 that can be suppressed by allergic response. PMID: 25529528
- Modulation of K2P 2.1 and K2P 10.1 K(+) channel sensitivity to carvedilol by alternative mRNA translation initiation PMID: 25168769
- Response of the human detrusor to stretch is regulated by TREK-1 PMID: 24801307
- PLD2, but not PLD1, directly binds to the C terminus of TREK1 and TREK2. PMID: 25197053
- results suggest that the TREK-1e splice variant may interfere with the vesicular traffic of full-length TREK-1 channels from the ER to the plasma membrane. PMID: 24196565
- TREK-1 deficient alveolar epithelial cells have less F-actin and are more deformable making them more resistant to stretch-induced injury. PMID: 24586773
- Activation of K(2)P channel-TREK1 mediates the neuroprotection induced by sevoflurane preconditioning. PMID: 24154701
- High TREK-1 expression is associated with epithelial ovarian cancer. PMID: 23479219
- A number of mutations that affect TREK1 channel gating occlude the action of fenamates but only in the longer form of TREK1. PMID: 24509840
- In human embryonic kidney (HEK-293) cells stably expressing TREK-1, outward currents at 80 mV increased from 91.0 +/- 23.8 to 247.5 +/- 73.3 pA/pF. PMID: 23804201
- study analyzed the role of TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (TREK1)in endothelial cells and the blood-brain barrier(BBB); blocking TREK1 increased leukocyte transmigration; TREK1 activation had the opposite effect PMID: 23933981
- TASK and TREK-1 are involved in regulation of cell proliferation and in control of resting membrane potentials in endometrial epithelial cells. PMID: 23305490
- we report the expression of Trek-1 in human alveolar epithelial cells and propose that Trek-1 deficiency may alter both IL-6 translation and transcription in AECs without affecting Ca(2+) signaling PMID: 23275623
- each of four TREK-1 splice variants interacts with full-length wild-type TREK-1 and in vivo, such interactions may contribute to a preterm labor phenotype. PMID: 22811574
- TREK-1 is expressed by both nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus cells of the human intervertebral disc. PMID: 22563662
- Cochlin interacts with TREK-1 and annexin A2. PMID: 21886777
- the important role of selectivity filter gating in the regulation of TREK-1 by the extracellular K(+) and proton. PMID: 21965685
- These results demonstrate that the primary activation mechanisms in TREK-1 reside close to, or within the selectivity filter and do not involve gating at the cytoplasmic bundle crossing. PMID: 21822218
- The data of this study suggested that TREK-1 is associated with NSC proliferation and probably is a modulator of the effect that fluoxetine attenuates the inhibitory neurogenesis induced by glucocorticoid hormones. PMID: 21069514
- inhibition of TREK1 current by fluoxetine is found to be accompanied by dissociation of the C-terminal domain from the membrane. PMID: 21262820
- role for TREK-1 in contributing to uterine quiescence during gestation PMID: 20811500
- these data suggest that beta-COP plays a critical role in the forward transport of TREK1 channel to the plasma membrane. PMID: 20362547
- Results describe the regulation of neuronal K(2P)2.1 (KCNK2, TREK-1) channel activity by resting membrane potential. PMID: 19837167
- These findings indicate that TREK1 genotypes are associated with individual differences in reward-related brain activity. PMID: 19621370
- TREK-1 channels may function as sensors that couple the metabolic state of the cell to membrane potential, perhaps through an associated ATP-binding protein PMID: 12368289
- During hypoxia, modulation of hTREK1 cannot be accomplished by parameters known to be perturbed in brain ischemia. hTREK1 regulation in brain will be more relevant during alkalosis than during ischemia or acidosis. PMID: 14522822
- TREK-1 is inhibited by fluoxetine and norfluoxetine. PMID: 15685212
- hypoxic inhibition: (a) requires the C-terminal domain of the channel; (b) does not involve redox modulation of the C-terminal domain cysteine residues C365 and C399; and (c) is critically dependent on the glutamate residue at position 306 PMID: 15883010
- receptor- and kinase-induced inhibition of TREK-1 background potassium channels is mediated by sequential phosphorylation PMID: 16006563
- human osteoblasts functionally express TREK-1 and that these channels contribute, at least in part, to the resting membrane potential of human osteoblast cells. We hypothesise a possible role for TREK-1 in mechanotransduction, leading to bone remodelling. PMID: 16250016
- VOCCs and TREK channels have been implicated in mechanotransduction signaling pathways in numerous connective tissue cell types. PMID: 17035301
- TREK1, the most thoroughly studied K(2P) channel, has a key role in the cellular mechanisms of neuroprotection, anaesthesia, pain and depression--{REVIEW} PMID: 17375039
- These findings indicate that genetic variation in KCNK2 may identify individuals at risk for treatment resistance. More broadly, they indicate the utility of animal models in identifying genes for pharmacogenetic studies of antidepressant response. PMID: 18288090
- voltage-dependent C-type gating acceleration by protons represents a novel mechanism for K2P2.1 outward rectification. PMID: 18474599
- (Review) KCNK2, the gene encoding K2P2.1, can generate either full-length or K2P2.1D1-56 via alternative translation initiation, a mechanism which increases protein diversity by giving rise to two or more proteins from a single mRNA strand. PMID: 18579071
- Both TASK-3 and TREK-1 are functionally operational in the adrenocortical H295R cell line, modulate membrane potential and aldosterone secretion. PMID: 18854423
- Results highlight the important role of K(2P)2.1 channels as receptors for mediators known to cause nociception. PMID: 19130888
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Isoform 4]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Two pore domain potassium channel (TC 1.A.1.8) family
-
组织特异性:Isoform 4 is detected in kidney, adrenal gland and brain where it is preferentially expressed in the amygdala but not found in thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus or substantia nigra.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6277
OMIM: 603219
KEGG: hsa:3776
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000394033
UniGene: Hs.497745
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
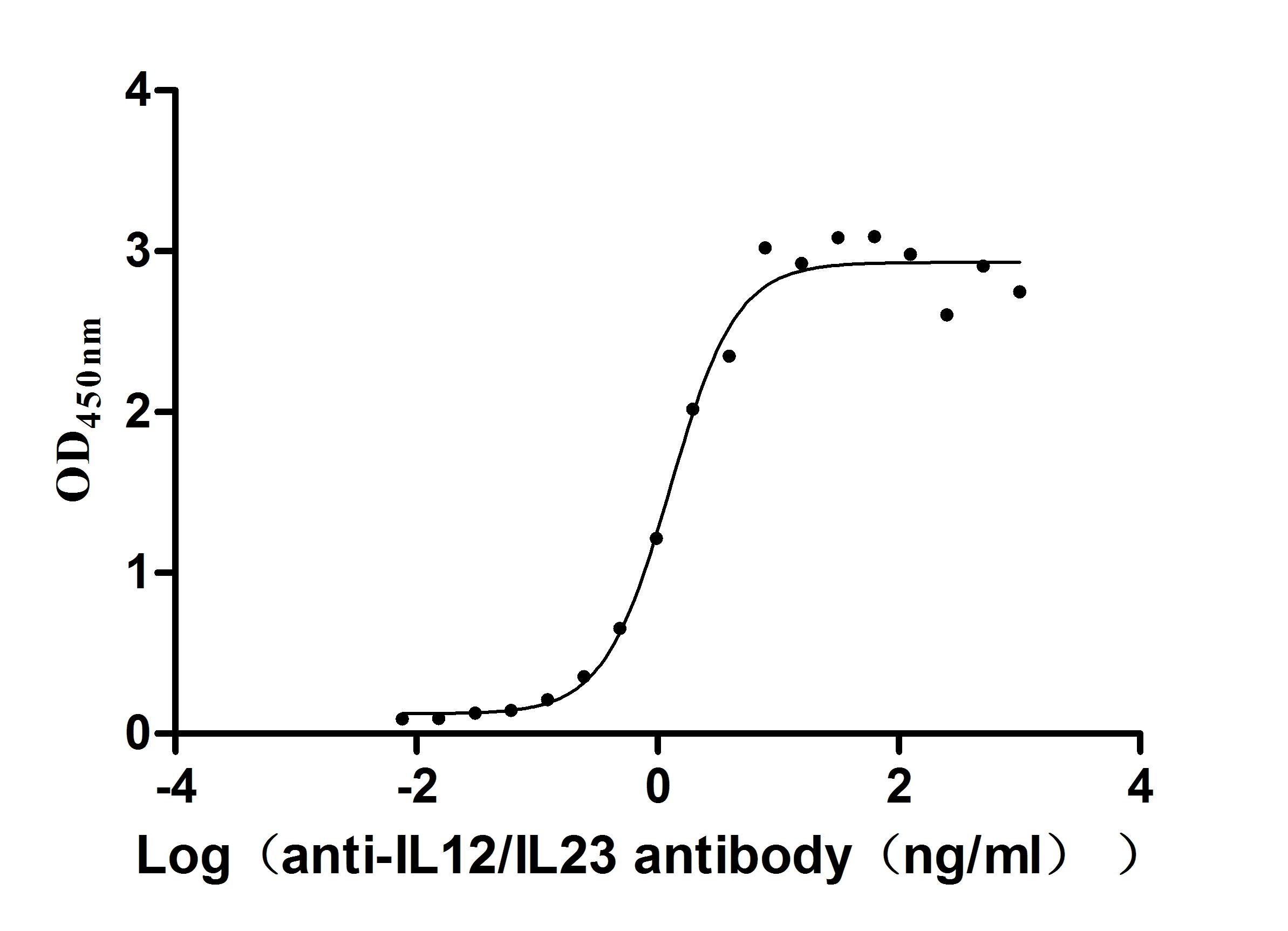
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
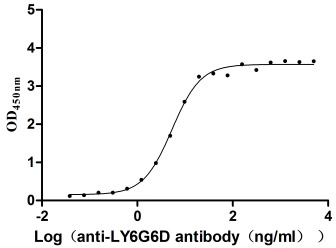
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
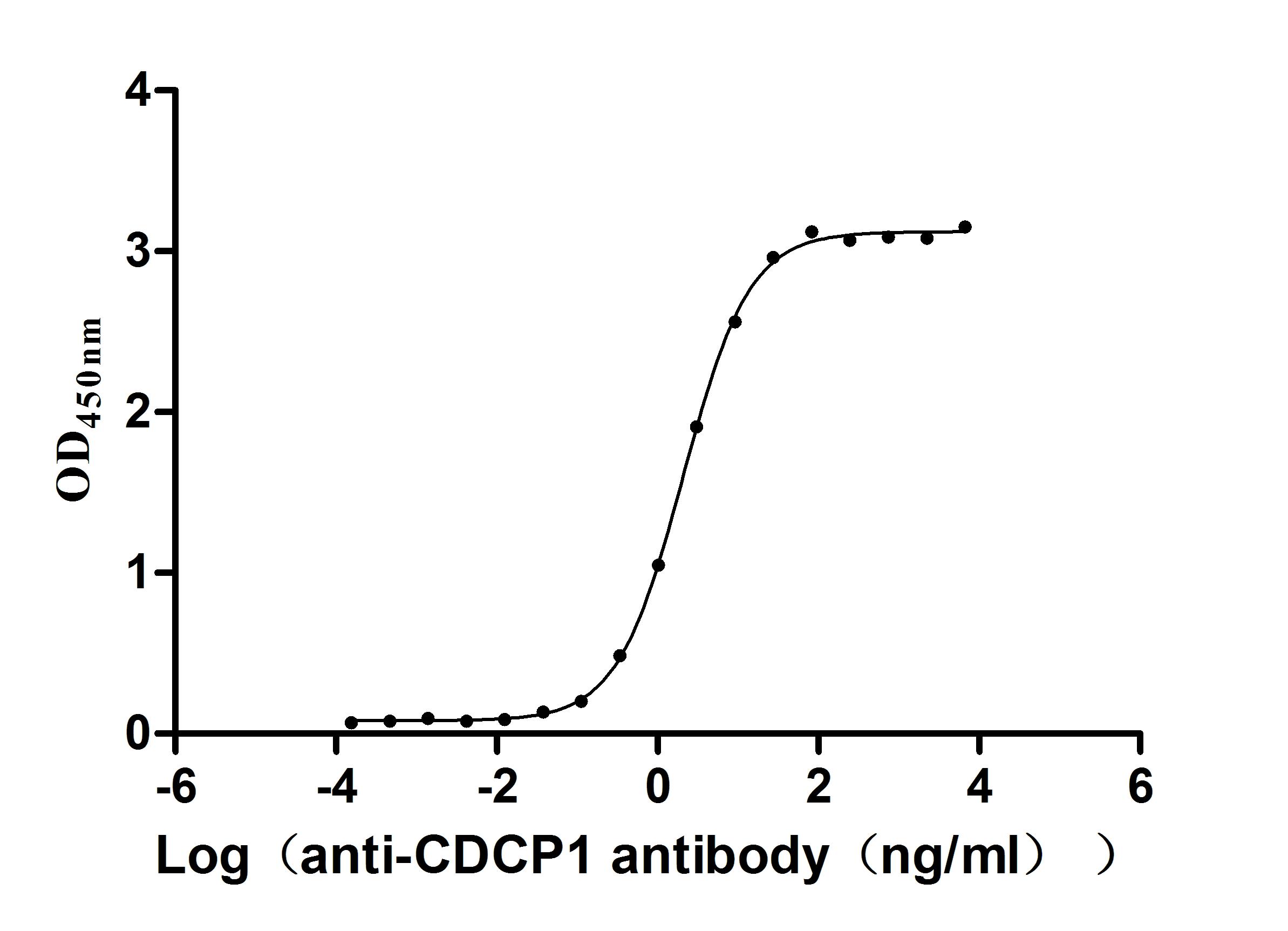
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
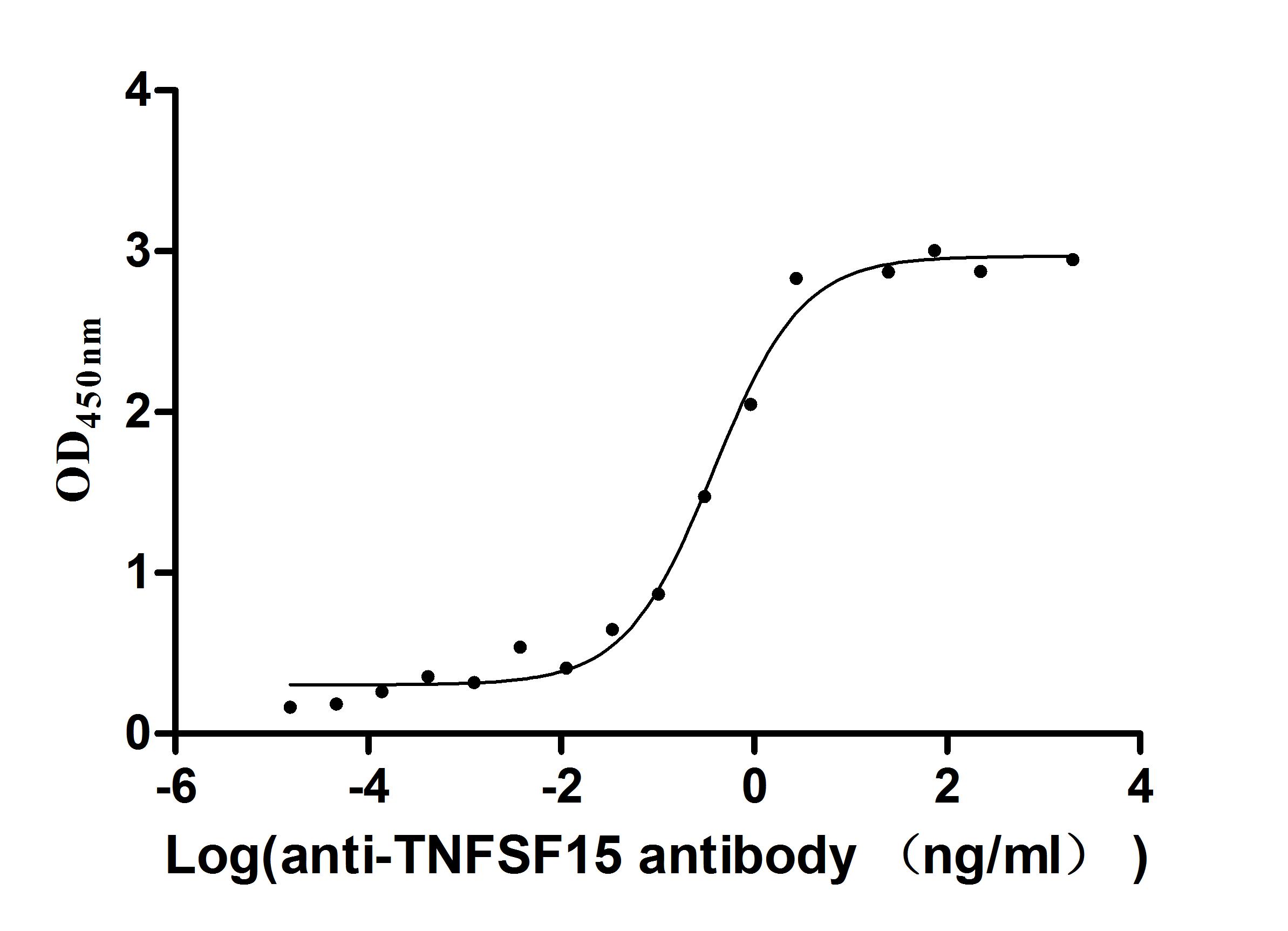
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)