Recombinant Human RNA-binding protein FUS (FUS)
-
中文名称:人FUS重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP009069HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人FUS重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP009069HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人FUS重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP009069HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人FUS重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP009069HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:FUS
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:75 kDa DNA pairing protein; 75 kDa DNA-pairing protein; ALS6; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 6; fus; FUS CHOP; Fus like protein; FUS_HUMAN; FUS1; Fused in sarcoma; Fusion (involved in t(12,16) in malignant liposarcoma); Fusion derived from t(12,16) malignant liposarcoma; Fusion gene in myxoid liposarcoma; Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein P2; hnRNP P2; hnRNPP2; Oncogene FUS; Oncogene TLS; POMp75; RNA binding protein FUS; RNA-binding protein FUS; TLS; TLS CHOP; Translocated in liposarcoma; Translocated in liposarcoma protein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-526
-
氨基酸序列MASNDYTQQA TQSYGAYPTQ PGQGYSQQSS QPYGQQSYSG YSQSTDTSGY GQSSYSSYGQ SQNTGYGTQS TPQGYGSTGG YGSSQSSQSS YGQQSSYPGY GQQPAPSSTS GSYGSSSQSS SYGQPQSGSY SQQPSYGGQQ QSYGQQQSYN PPQGYGQQNQ YNSSSGGGGG GGGGGNYGQD QSSMSSGGGS GGGYGNQDQS GGGGSGGYGQ QDRGGRGRGG SGGGGGGGGG GYNRSSGGYE PRGRGGGRGG RGGMGGSDRG GFNKFGGPRD QGSRHDSEQD NSDNNTIFVQ GLGENVTIES VADYFKQIGI IKTNKKTGQP MINLYTDRET GKLKGEATVS FDDPPSAKAA IDWFDGKEFS GNPIKVSFAT RRADFNRGGG NGRGGRGRGG PMGRGGYGGG GSGGGGRGGF PSGGGGGGGQ QRAGDWKCPN PTCENMNFSW RNECNQCKAP KPDGPGGGPG GSHMGGNYGD DRRGGRGGYD RGGYRGRGGD RGGFRGGRGG GDRGGFGPGK MDSRGEHRQD RRERPY
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:DNA/RNA-binding protein that plays a role in various cellular processes such as transcription regulation, RNA splicing, RNA transport, DNA repair and damage response. Binds to nascent pre-mRNAs and acts as a molecular mediator between RNA polymerase II and U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein thereby coupling transcription and splicing. Binds also its own pre-mRNA and autoregulates its expression; this autoregulation mechanism is mediated by non-sense-mediated decay. Plays a role in DNA repair mechanisms by promoting D-loop formation and homologous recombination during DNA double-strand break repair. In neuronal cells, plays crucial roles in dendritic spine formation and stability, RNA transport, mRNA stability and synaptic homeostasis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- loss of nuclear FUS caused DNA nick ligation defects in motor neurons. PMID: 30206235
- The herein presented data uncover a novel mechanism by which the fusion oncogene FUS-CHOP actively promotes invasion in myxoid and round cell liposarcoma through the activation of a SRC/FAK/RHO/ROCK signaling axis. PMID: 29190494
- When FUS was overexpressed and then de novo synthesis was blocked with ActD, the decay rate of LATS1/2 was slower in the FUS-overexpressed cells than in control cells. PMID: 30308519
- Motor neuron cultures exposed to mutant FUS (mutFUS)conditioned medium (ACM), but not wild-type FUS ACM, undergo significant cell loss, which is preceded by progressive degeneration of neurites. We found that Tumor TNFalpha is secreted into ACM of mutFUS-expressing astrocytes. Accordingly, mutFUS astrocyte-mediated motor neuron toxicity is blocked by targeting soluble TNFalpha with neutralizing antibodies. PMID: 29380416
- the abnormal stable complex of FUS-R521C/PRMT1/Nd1-L mRNA could contribute to neurodegeneration upon oxidative stress. PMID: 28094300
- more selective group of neurons appears to be affected in frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD)-TDP and FTLD-FUS than in FTLD-tau PMID: 28984110
- Taken together, FUS RNA-recognition motif appears to play a crucial role in exaggerating the physiological/reversible self-assembly into pathological/irreversible fibrillization, thus contributing to manifestation of FUS cytotoxicity. PMID: 28432364
- Fus is a binding partner of FMRP. PMID: 28424484
- Study demonstrates that FUS mutants, but not WT forms, impair fast axonal transport (FAT) in brain tissue of patients with ALS, through a mechanism dependent on activation of p38 MAPK. PMID: 28273913
- In human stem cell-derived motor neurons, the RNA profile associated with concomitant loss of both TAF15 and FUS resembles that observed in the presence of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-associated mutation FUS R521G, but contrasts with late-stage sporadic ALS patients. PMID: 27378374
- FUS P525L mutation alters transcriptome and microRNA pathways in motor neurons with implications for ALS pathogenesis. PMID: 28988989
- This study showed that in fibroblasts of FUS P525L mutation carriers, FUS mislocalized to the cytoplasm where it redistributed into stress granules with likely a dose effect. PMID: 29035885
- Results find that mutant but not wild-type FUS decreased dendritic growth, mRNA levels, and protein synthesis in dendrites. These data suggest that cytoplasmic FUS aggregates trap mRNA and its transporters, impairing dendritic mRNA trafficking and translation, in turn leading to the disruption of dendritic homeostasis and the development of frontotemporal dementia phenotypes. PMID: 28928015
- activation of the IGF-IR/PI3K/Akt signaling system is a common pattern in MLS which appears to be transcriptionally controlled, at least in part by induction of IGF2 gene transcription in a FUS-DDIT3-dependent manner. PMID: 28637688
- SOD1 mutations were present in 20% of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients and 1.9% of sporadic ALS patients, while FUS mutations were responsible for 13.3% of familial ALS cases, and TARDBP mutations were rare in either familial or sporadic ALS cases. PMID: 27604643
- Depletion of SAFB1 reduced FUS's localization to chromatin-bound fraction and splicing activity, suggesting SAFB1 could tether FUS to chromatin compartment thorough N-terminal DNA-binding motif. Moreover, FUS interacts with another nuclear matrix-associated protein, Matrin3. PMID: 27731383
- A molecular docking and dynamics study concluded that R521C and R521H mutations in FUS result in weak binding with Karyopherin-beta2 leading to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 27381509
- both FUS and TDP43 colocalize with active RNA polymerase II at sites of DNA damage along with the DNA damage repair protein, BRCA1, and FUS and TDP43 participate in the prevention or repair of R loop-associated DNA damage, a manifestation of aberrant transcription and/or RNA processing PMID: 27849576
- FUS mutations were significantly more common among mainland Chinese patients than those among Caucasian populations (p=6.8x10-3). The high frequency of FUS mutations in FALS and SALS in mainland China is another genetic feature distinct from Caucasians. PMID: 26519472
- The impairment of PARP-dependent DNA damage response (DDR) signaling due to mutations in the FUS nuclear localization sequence induces additional cytoplasmic FUS mislocalization which in turn results in neurodegeneration and FUS aggregate formation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 29362359
- ALS-associated mutations enhance FUS protein propagation in Drosophila neurons. PMID: 28429234
- juvenile ALS linked to FUS mutations represent a specific entity different from both classical juvenile ALS and adult ALS linked to FUS gene PMID: 28054830
- Motor neurons expressing FUS with the P525L or the R521H mutation showed cytoplasmic mislocalization of FUS, hypoexcitability, and axonal transport defects. PMID: 29021520
- Results suggest that RBM45 serves as a negative regulator to prevent FUS-mediated excessive recruitment of HDAC1 to the sites of DNA damage. PMID: 29140459
- The review describes the main physiological functions of FUS and considers evidence for each of the theories of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathogenesis. PMID: 28707655
- s used solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance methods to characterize the molecular structure of self-assembling fibrils formed by the LC domain of the fused in sarcoma (FUS) RNA-binding protein. From the 214-residue LC domain of FUS (FUS-LC), a segment of only 57 residues forms the fibril core, while other segments remain dynamically disordered. PMID: 28942918
- Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy demonstrates the intrinsically disordered structure of FUS's nearly uncharged, aggregation-prone, yeast prion-like, low sequence-complexity domain is preserved after phosphorylation. PMID: 28790177
- Long noncoding RNA SchLAH functions through interaction with fused in sarcoma protein (FUS). PMID: 28196303
- Focus on the recent advances on approaches to uncover the mechanisms of wild type and mutant FUS proteins during development and in neurodegeneration (review). PMID: 27033831
- FUS-induced reductions to ER-mitochondria associations and are linked to activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta), a kinase already strongly associated with ALS/FTD. PMID: 27418313
- Motor-neuron disease (MND)-linked RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), TDP-43, FUS, and hnRNPA2B1, bind to and induce structural alteration of UGGAAexp. These RBPs suppress UGGAAexp-mediated toxicity in Drosophila by functioning as RNA chaperones for proper UGGAAexp folding and regulation of pentapeptide repeat translation. PMID: 28343865
- we analyzed fast axonal transport in larval motor neurons of Drosophila models of TARDBP (TDP-43), FUS and C9orf72. We also analyzed the effect of loss-of-function mutants of the Drosophila orthologs of TDP-43 and FUS, TBPH and caz, respectively. The motor activities of larvae and adults in these models were assessed to correlate potential defects in axonal transport with locomotor deficits PMID: 27056981
- These findings suggest a possible pathomechanism for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in which mutated FUS inhibits correct splicing of minor introns in mRNAs encoding proteins required for motor neuron survival. PMID: 27252488
- This study revealed a characteristic phenotype in FUS/TLS-linked FALS patients in Japan. PMID: 26823199
- The aim of this review will be to provide a general overview of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS proteins and to highlight their physiological functions--{REVIEW} PMID: 27015757
- Mouse model that overexpresses FUS without a nuclear localization signal (DeltaNLS-FUS) shows progressive motor deficits/ALS phenotype PMID: 27368346
- Possible role of deregulated DNA binding function of FUS in ALS. PMID: 27693252
- Our in vivo studies of the hFUS-Q290X mutation in Drosophila link motor dysfunction to impairment in the GABAergic pathway. Our findings would facilitate further efforts in unravelling the pathophysiology of Essential tremor PMID: 27395408
- FUS is glycosylated with a high stoichiometry not only in the neural cells but also in the non-neural cell lines. PMID: 27903134
- The results of this study suggested that FUS mutations are the most frequent genetic cause in early-onset sporadic ALS patients of Chinese origin. PMID: 26972116
- Data show that induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)-derived motor neurons mimicked several neurodegenerative phenotypes including mis-localization of fused-in sarcoma (FUS) gene product into cytosolic. PMID: 26997647
- miR-141 and the FUS gene, which are inversely correlated, play significant functional roles in regulating human neuroblastoma. PMID: 26936280
- pathological TDP-43 and FUS may exert motor neuron pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis through the initiation of propagated misfolding of SOD1 PMID: 26926802
- iNeurons may provide a more reliable model for investigating FUS mutations with disrupted NLS for understanding FUS-associated proteinopathies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis PMID: 26795035
- A subset of juvenile-onset familial/sporadic ALS cases with FUS gene mutations reportedly demonstrates mental retardation or learning difficulty. PMID: 26984092
- Study implicates phosphorylation as an additional mechanism by which nuclear transport of FUS might be regulated and potentially perturbed in ALS and FTLD. PMID: 26403203
- Study identifies a common mechanism of transport into neurites of proteins linked to the pathology of Alzheimer's disease (i.e. sAPP) and ALS (i.e. FUS, TDP-43 and SOD1) PMID: 26605911
- RNA binding proteins TDP-43 and FUS do not consistently fit the currently characterised inclusion models suggesting that cells have a larger repertoire for generating inclusions than currently thought. PMID: 26293199
- Wild-type and mutant hFUS proteins induced neuronal degeneration with partial selectivity for motor neurons. Motor neuron loss was accompanied by abnormal neurite morphology and length. PMID: 26174443
- FUS mutation seems indicated in sporadic early-onset ALS patients especially if showing predominant bulbar symptoms and an aggressive disease course. PMID: 26362943
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH); Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 6, with or without frontotemporal dementia (ALS6); Tremor, hereditary essential 4 (ETM4)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:RRM TET family
-
组织特异性:Ubiquitous.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 4010
OMIM: 137070
KEGG: hsa:2521
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000254108
UniGene: Hs.46894
Most popular with customers
-
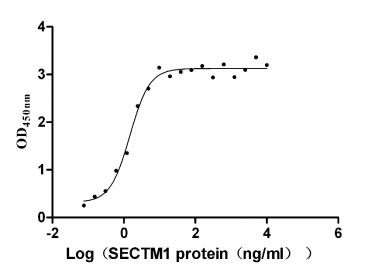
Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
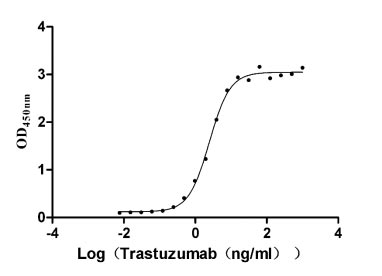
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
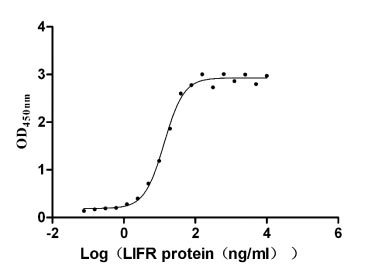
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
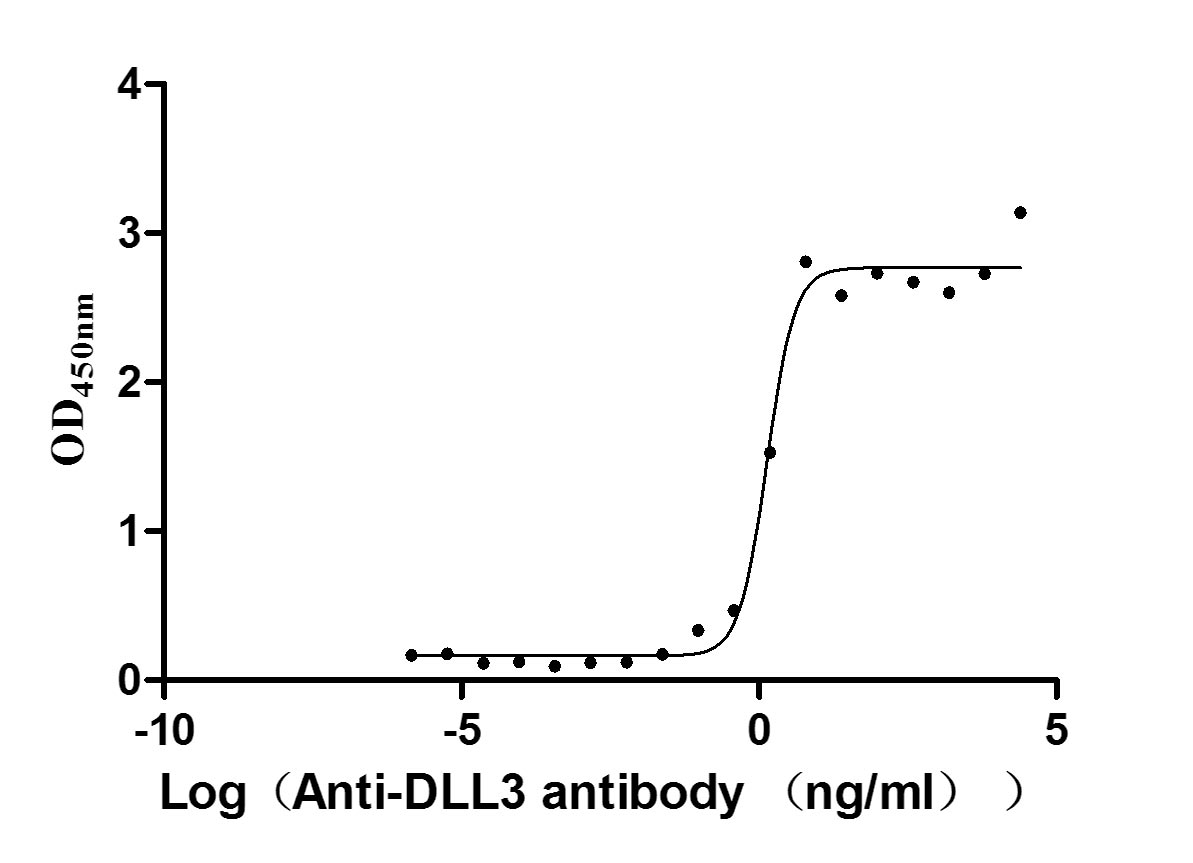
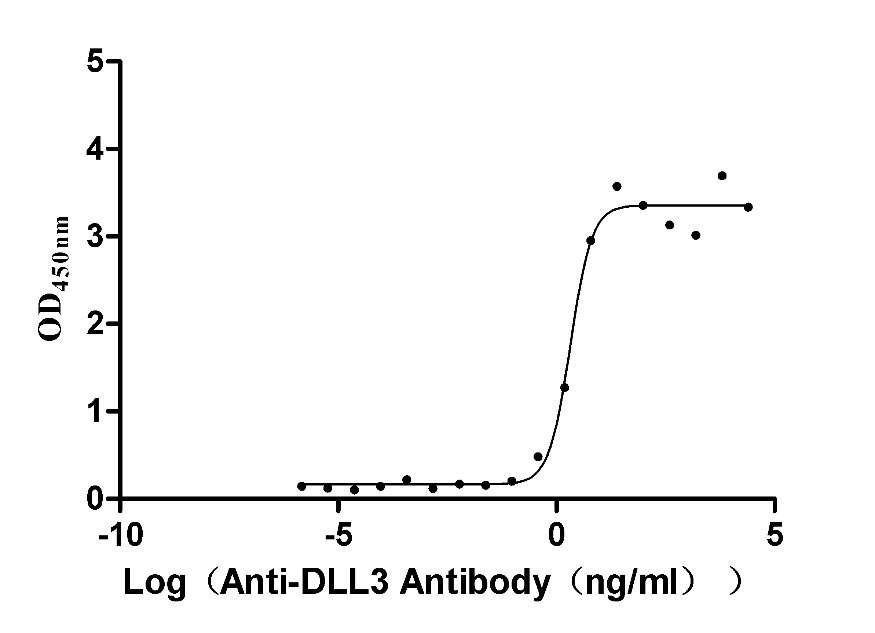
Recombinant Human Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Delta-like protein 3 (DLL3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
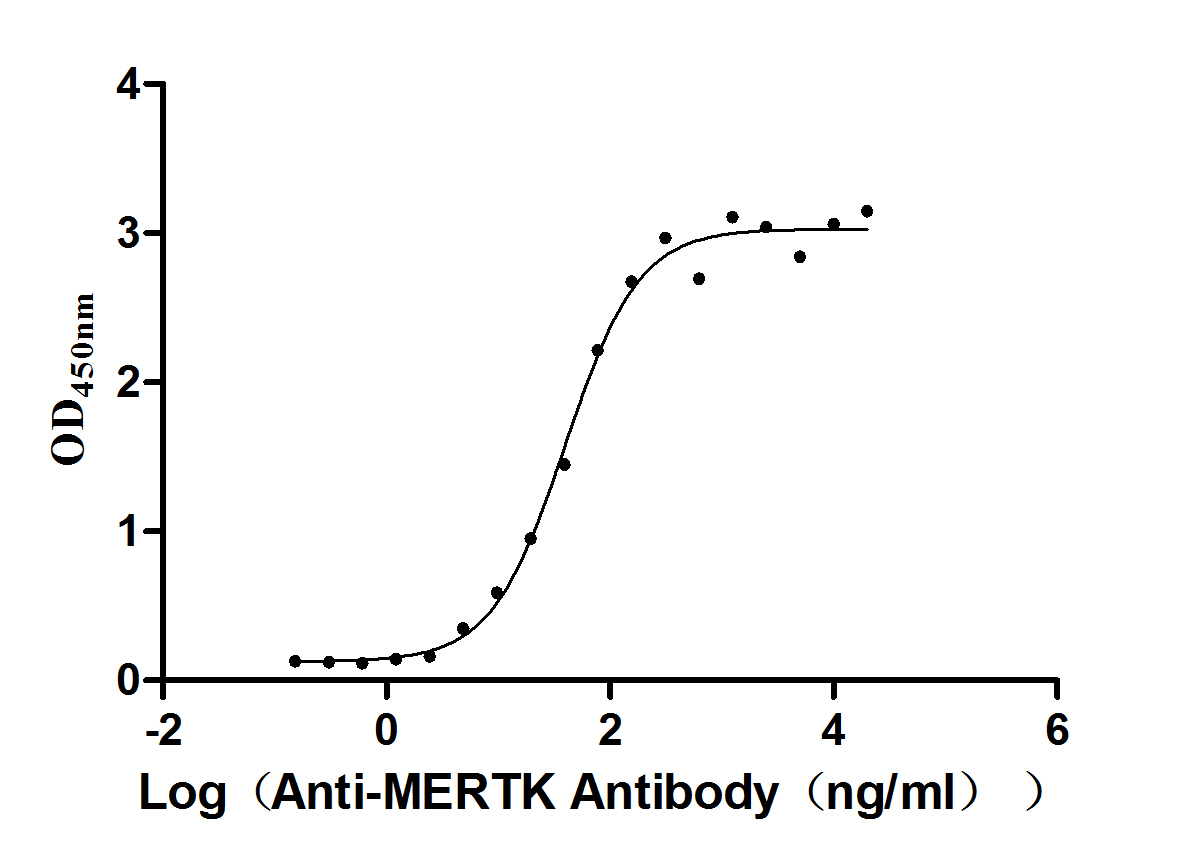
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
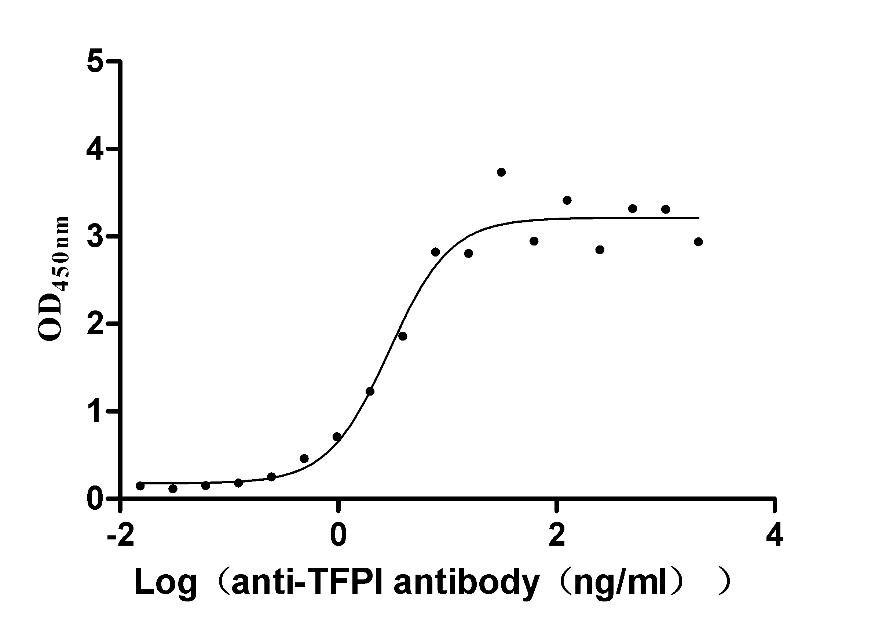
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
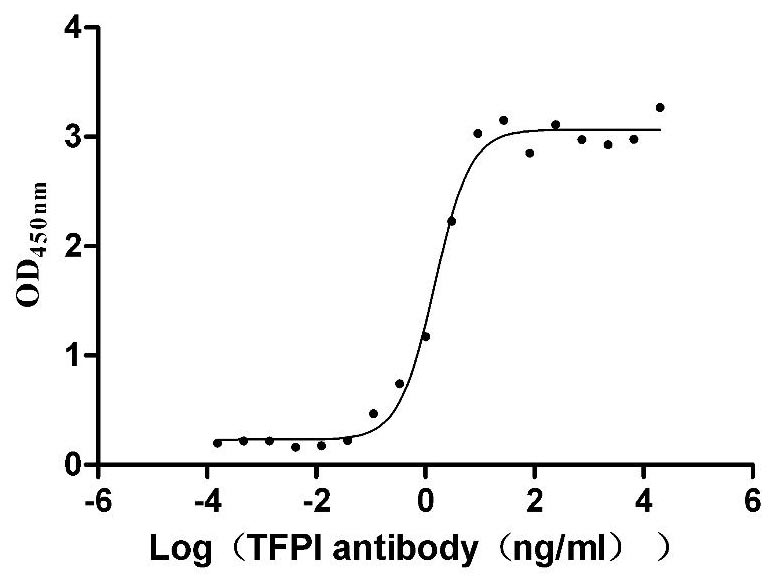
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)