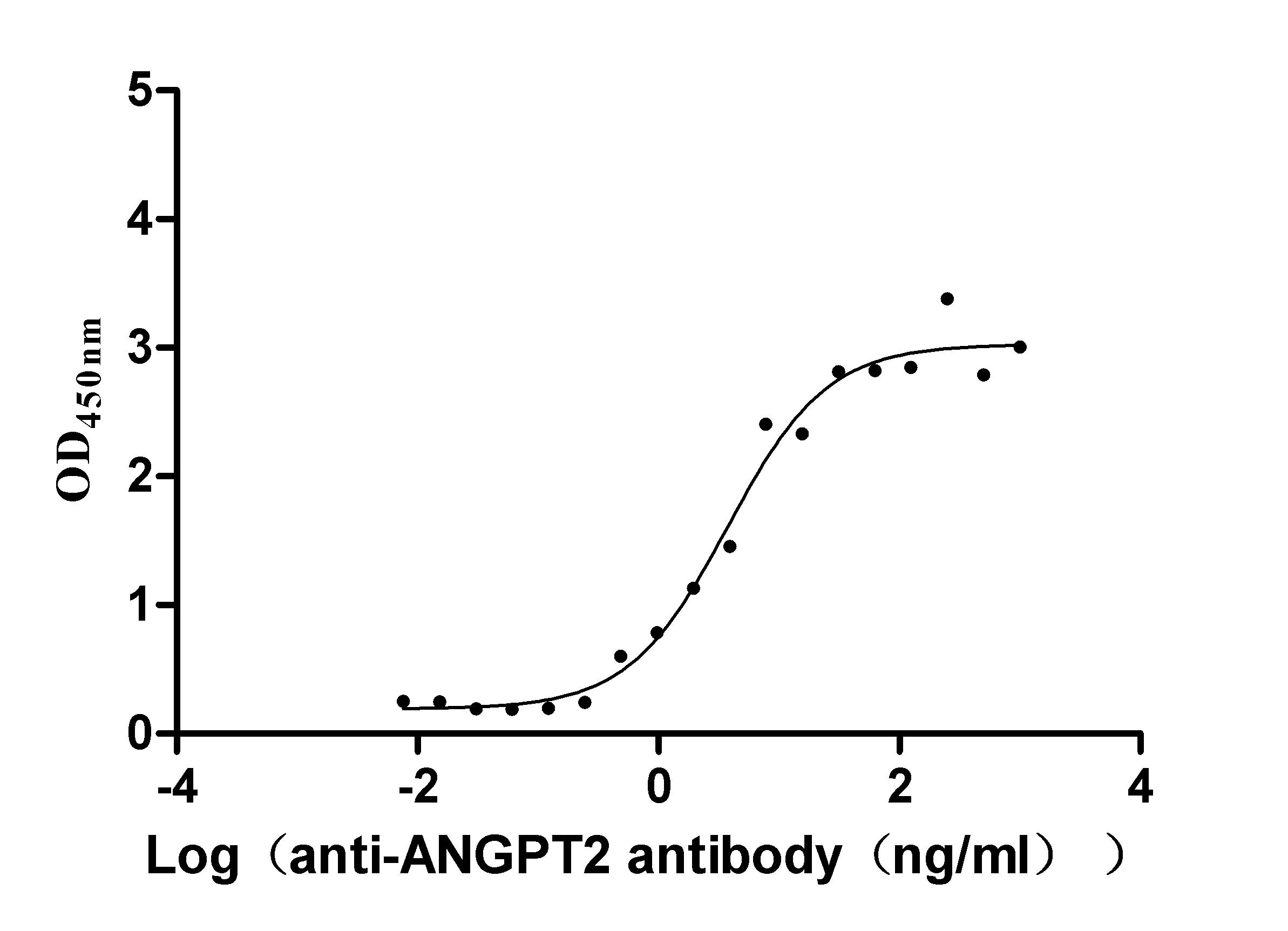
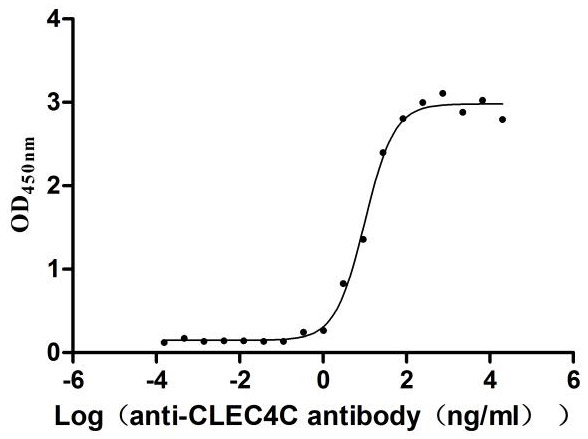
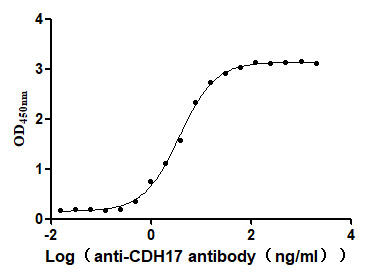
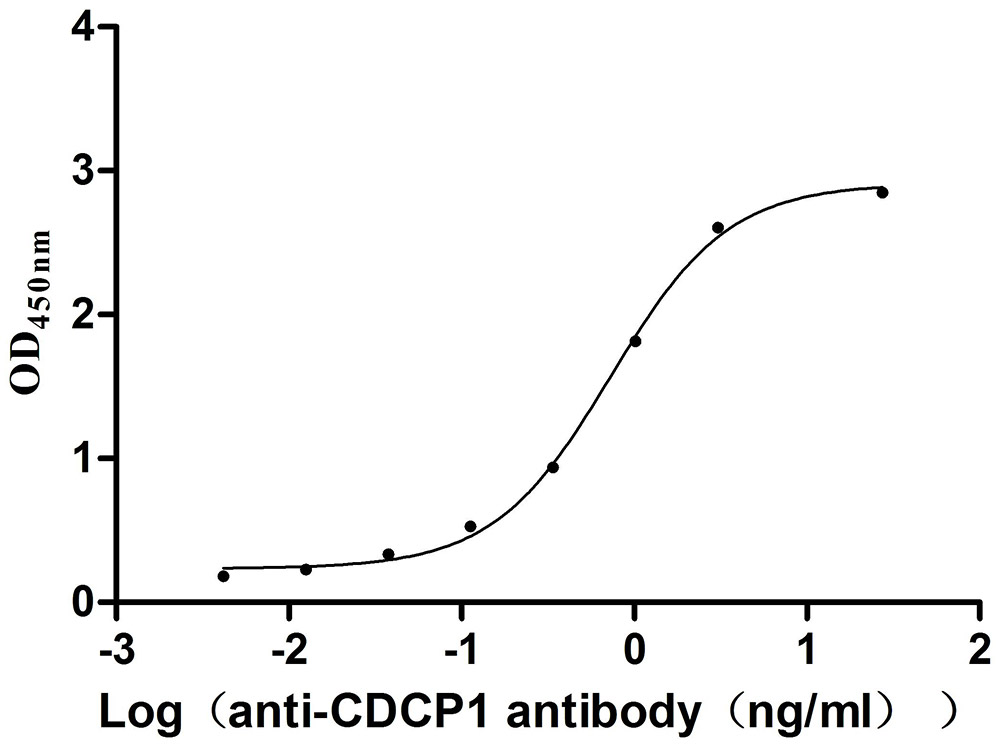
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein (TRADD)
-
货号:CSB-YP621879HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP621879HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP621879HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP621879HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:9130005N23Rik; AA930854; TNFR1 associated DEATH domain protein; TNFR1-associated DEATH domain protein; TNFRSF1A associated via death domain; TNFRSF1A-associated via death domain; tradd; TRADD_HUMAN; Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1 associated DEATH domain protein; Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-312
-
氨基酸序列MAAGQNGHEE WVGSAYLFVE SSLDKVVLSD AYAHPQQKVA VYRALQAALA ESGGSPDVLQ MLKIHRSDPQ LIVQLRFCGR QPCGRFLRAY REGALRAALQ RSLAAALAQH SVPLQLELRA GAERLDALLA DEERCLSCIL AQQPDRLRDE ELAELEDALR NLKCGSGARG GDGEVASAPL QPPVPSLSEV KPPPPPPPAQ TFLFQGQPVV NRPLSLKDQQ TFARSVGLKW RKVGRSLQRG CRALRDPALD SLAYEYEREG LYEQAFQLLR RFVQAEGRRA TLQRLVEALE ENELTSLAED LLGLTDPNGG LA
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Adapter molecule for TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 that specifically associates with the cytoplasmic domain of activated TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 mediating its interaction with FADD. Overexpression of TRADD leads to two major TNF-induced responses, apoptosis and activation of NF-kappa-B. The nuclear form acts as a tumor suppressor by preventing ubiquitination and degradation of isoform p19ARF/ARF of CDKN2A by TRIP12: acts by interacting with TRIP12, leading to disrupt interaction between TRIP12 and isoform p19ARF/ARF of CDKN2A. ...显示更多
-
基因功能参考文献:
- potential biological significance of TRADD mediated inflammatory response in the development of uterine leiomyoma, is reported. PMID: 28698006
- we found that ORF3 protein downregulates TLR3-mediated NF-kappaB signaling via TRADD and RIP1. Our findings provide a new perspective on the cellular response in HEV infection and expand our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of Hepatitis E virus (HEV) pathogenesis in innate immunity. PMID: 27270888
- In conclusion, for the first time, we report that TRADD, TRAF2, RIP1 and TAK1 play a role in the regulating TNF-alpha signalling in human myometrium. These findings are of significance given the central role of TNF-alpha in the processes of human labour and delivery. PMID: 28337828
- These data for the first time identifies miR-485-5p/TRADD axis in hydrogen sulfide protecting against TNF-alpha-induced neuronal cell apoptosis. PMID: 27562714
- By reducing the levels of TRADD, wild type CFTR suppresses downstream proinflammatory NFkappaB signaling. PMID: 27960153
- NPM-RAR binding to TRADD selectively inhibits caspase activation, while allowing activation of NFkappaB and JNK PMID: 25791120
- The release of extracellular vesicles was triggered by TNFA from BEAS-2b cells.TNFA-triggered extracellular vesicles contained TNFR1 and TRADD. PMID: 26475675
- MicroRNA-30c-2-3p negatively regulates NF-kappaB signaling and cell cycle progression through downregulation of TRADD and CCNE1 in breast cancer. PMID: 25732226
- domains of calmodulin mediate FADD and TRADD interaction PMID: 25643035
- PA induced the apoptosis of HUVECs by initiating the death pathway (TNF-R1/TRADD/caspases 8 pathway), whereas AA enhanced cell survival to protect vascular endothelial cells by activating the survival pathway (TNF-R1/RIP/NF-kappaB 50/NF-kappaB 65). PMID: 25230327
- Biologic assessment found that NPM-RAR expression impaired TNF-induced signaling through TRADD, blunting TNF-mediated activation of caspase-3 (CASP3) and caspase-8 (CASP8), to ultimately block apoptosis. PMID: 25033841
- TRADD gene expression was knocked down by an antisense oligonucleotide. PMID: 24070137
- structure-based mutations of TNFR-1 (P367A and P368A), TRADD (F266A), and RIP1 (M637A and R638A) disrupted formation of the death domain (DD) complex and prevented stable interactions among those DDs PMID: 24361886
- Data indicate that the ASK1-FoxO3a-TRADD-caspase 8 pathway is present in neural tube defects (NTDs)-affected tissues. PMID: 23982205
- we demonstrated that the association between DR6 and TRADD was enhanced upon DQM3 stimulation and TRADD was involved in DR6-induced signaling activation PMID: 24374337
- Data indicate that silencing tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1)-associated death domain protein (TRADD) in glioma cells results in decreased NF-kappaB activity, decreased proliferation of cells, and increased sensitivity to temozolomide. PMID: 23908590
- death domains in several proteins, including TRADD, FADD, RIPK1 and TNFR1, were directly inactivated by NleB, an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) type III secretion system effector known to inhibit host nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signalling PMID: 23955153
- rpS3 appears to be recruited to the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) to induce apoptosis by interacting TRADD in response to extracellular stresses. PMID: 22510408
- NSP 5a3a induces apoptosis in Head and Neck cell line HN30 through p73-DAXX and TRAF2-TRADD. PMID: 22170762
- Death domain SXXE/D motifs are phosphorylated, as is required for stable TNFR1-TRADD complex formation and subsequent activation of NF-kappaB in inflamed mucosa. PMID: 21724995
- TRADD contains a nuclear export and import sequence that allows shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. It induces apoptosis via different mechanisms. PMID: 12045187
- chemotherapeutic drugs exhibited their cytotoxic effects in part by down-regulating Akt signaling following TRADD expression PMID: 12446787
- Diphtheria toxins induce apoptosis by activating components of the death receptor pathway in a receptor-independent manner. PMID: 12576460
- TRADD is involved in the p75(NTR)-mediated antiapoptotic activity of nerve growth factor in breast cancer cells PMID: 12604596
- TRAD binds with keratin 14 and has a role in susceptibility of keratinocytes to caspase-8-mediated apoptosis PMID: 14660619
- TRADD activates distinct mechanisms of apoptosis from the nucleus and the cytoplasm. PMID: 15761471
- TRADD employs a Pelle-like surface to interact with its binding partners, either receptor TNFR1 or adaptor FADD. PMID: 16006552
- PAK4 has a role in TNF-alpha induced cell survival pathyways by facilitating TRADD binding to the TNF Receptor PMID: 16227624
- TRADD and RIP1 compete for recruitment to the TNFR1 signaling complex and the distinct programs of cell death. PMID: 16611992
- These findings suggest that EMAP-II sensitises endothelial cells to apoptosis by facilitating TNF-R1 apoptotic signalling via TRADD mobilization. PMID: 17051333
- The expression of TRADD in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was significantly decreased in SLE patients. PMID: 17235653
- The structure of TRADD DD was solved by NMR. PMID: 17922260
- unique interaction of LMP1 with TRADD encodes the transforming phenotype of viral TRADD signaling and masks TRADD's pro-apoptotic function PMID: 18198944
- Mutations in the TRADD gene may contribute to the development of different hematological diseases. PMID: 18661484
- glomerular and tubular expression of TNF-alpha, (TNF receptor-associated death domain protein)TRADD, RIP(receptor-interacting protein) and TRAF-2 (TNF receptor-associated factor-) was significantly up-regulated in Lupus nephritis PMID: 19151112
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
-
组织特异性:Found in all examined tissues.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 12030
OMIM: 603500
KEGG: hsa:8717
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000341268
UniGene: Hs.460996


-AC1.jpg)