Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Virion infectivity factor (vif)
-
货号:CSB-EP303185HKM
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP303185HKM-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP303185HKM
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP303185HKM
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Name:vif
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:vifVirion infectivity factor; Vif; SOR protein) [Cleaved into: p17; p7]
-
种属:Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BRU/LAI) (HIV-1)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-192
-
氨基酸序列MENRWQVMIV WQVDRMRIRT WKSLVKHHMY VSGKARGWFY RHHYESPHPR ISSEVHIPLG DARLVITTYW GLHTGERDWH LGQGVSIEWR KKRYSTQVDP ELADQLIHLY YFDCFSDSAI RKALLGHIVS PRCEYQAGHN KVGSLQYLAL AALITPKKIK PPLPSVTKLT EDRWNKPQKT KGHRGSHTMN GH
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Counteracts the innate antiviral activity of host APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. Forms a complex with host APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G thus preventing the entry of these lethally hypermutating enzymes into progeny virions. Recruits an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex composed of elongin BC, CUL5, and RBX2 to induce polyubiquitination of APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F. In turn, they are directed to the 26S proteasome for degradation. Vif interaction with APOBEC3G also blocks its cytidine deaminase activity in a proteasome-independent manner, suggesting a dual inhibitory mechanism. May interact directly with APOBEC3G mRNA in order to inhibit its translation. Seems to play a role in viral morphology by affecting the stability of the viral nucleoprotein core. Finally, Vif also contributes to the G2 cell cycle arrest observed in HIV infected cells.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- two stem-loop structures within the 5'-untranslated region of A3G mRNA are crucial for translation inhibition by Vif in HIV-infected cells, and most Vif alleles neutralize A3G translation efficiently PMID: 27996044
- Vif was also unable to induce G2/M cell cycle arrest in other nonhuman cell types, including cells derived from nonhuman primates, leading to propose that one or more human-specific cofactors underpin Vif's ability to modulate the cell cycle. PMID: 29321323
- Moreover, using a CBF-beta loss-of-function mutant, the s demonstrated that the interaction between CBF-beta and Vif was not sufficient for Vif assistance; a region including F68 in CBF-beta was also required for the stability and function of Vif. PMID: 28516844
- Here, the s show that APOBEC3G polyubiquitination is essential for its HIV-1 vif-induced degradation. PMID: 27297094
- cyclin F functions as an intrinsic cellular regulator of HIV-1 Vif and has a negative regulatory effect on the maintenance of viral infectivity by restoring APOBEC3G expression. PMID: 28184007
- The overall conclusion from this study is that it may not be possible to select Vif-null viruses capable of replicating in relevant HIV target cells in vivo thus highlighting the critical role of Vif for HIV-1 replication. PMID: 28131088
- Vif stabilization by CBFbeta is mainly caused by impairing MDM2-mediated degradation. PMID: 27758855
- using novel human A3G transgenic mouse models that express varying levels of A3G as is seen in humans, this study clearly demonstrates that polymorphic vif alleles can have differential anti-A3G activity in vivo PMID: 27363431
- The s found that multiple Vif residues are involved in the extensive N-terminal Vif-CBFbeta interaction and that the (5)WQVMIVW(11) region of Vif is the major determinant. PMID: 28302150
- HIV-1 Vif has evolved to utilize three dispersed surfaces for recognizing three types of interfaces on APOBEC3h proteins under certain structural constraints. PMID: 28336404
- virus adaptation and computational studies to interrogate the APOBEC3F-Vif interface and build a robust structural model; taken together with mutagenesis results, propose a wobble model to explain how HIV-1 Vif has evolved to bind different APOBEC3 enzymes PMID: 26628363
- Identified Vif mRNA as a new substrate for Pokeweed antiviral protein and demonstrate that derepression of innate immunity against HIV-1 contributes to its antiviral activity. PMID: 26275799
- Six residues located within the conserved HIV-1 Vif F1-, F2-, and F3-box motifs are essential for both APOBEC3C and APOBEC3F degradation, and an additional four residues are uniquely required for APOBEC3F degradation. PMID: 26537685
- This study identifies a new cellular complex, HDAC6/A3G, involved in the autophagic degradation of Vif, and suggests that HDAC6 represents a new antiviral factor capable of controlling HIV-1 infectiveness by counteracting Vif and its functions. PMID: 26105074
- The existence and persistence of both types of HIV-1 Vif variant suggests the importance of APOBEC3H suppression and cell cycle regulation for HIV-1's survival in vivo. PMID: 25590520
- stable APOBEC3H haplotypes present as in vivo barriers to HIV-1 replication, that Vif is capable of adapting to these restrictive pressures, and that an evolutionary equilibrium has yet to be reached. PMID: 25411794
- This study unveils that HIV-1 Vif inhibits autophagy via interaction with LC3B independently of its action on APOBEC3G and, therefore, suggest a new function of this viral protein in restricting innate antiviral mechanisms. PMID: 25490467
- Vif continues to protect HIV-1 from the deleterious effects of APOBEC3G, even after packaging of APOBEC3G has occurred. PMID: 25304135
- These results provide important information on the assembly of the Vif-CUL5-E3 ubiquitin ligase and identify a new viV binding interface with CBF-beta at the C-terminus of HIV-1 Vif. PMID: 25424878
- HIV-1 Vpr and Vif were shown to bind to TBK1 and inhibit its autophosphorylation by binding of these proteins leading to a block in type I and III interferon induction. PMID: 25855743
- The human APOBEC3G N-terminal domain is bound by HIV-1 Vif. PMID: 25984970
- CBF-beta promoted steady-state levels of HIV-1 Vif by inhibiting the degradation of HIV-1 Vif through the proteasome pathway. PMID: 25582776
- No single viral polymorphism could explain the reduced anti-APOBEC3G activity of elite controllers-derived Vif, suggesting that various combinations of minor polymorphisms may underlie these effects. PMID: 25717111
- Results indicate that Vif has potent RNA chaperone activity and provide direct evidence for an important role of the unstructured C-terminal domain of Vif in this capacity. PMID: 25144404
- This approach identified the alpha3 and alpha4 helices of human APOBEC3F as important determinants of the interaction with HIV-1 Vif. PMID: 25142588
- The degradation efficiency of Vif correlated with both the binding strength of the APOBEC3-Vif interaction and the APOBEC3-Vif interface. PMID: 25275135
- N-terminal mutants of HIV-1 vif that demonstrated reduced Cul5 binding were also unable to degrade APOBEC3G as well as APOBEC3F. PMID: 24422669
- Vif-positive viruses with more host APOBEC3G expressed were found to have decreased virion infectivity ex vivo. PMID: 24146808
- Vif interaction with EloB-EloC may contribute to recruitment of CBF-beta to Vif, demonstrating that the EloB C-teminus may play a role in improving Vif function and that the over-expression of EloB results in Vif stabilization. PMID: 23988114
- study reports NMR solution structure of the Vif SOCS-ElonginBC (EloBC)complex; structure of the complex and biophysical studies provide insight into the function of Vif's proline-rich motif and reveal novel dynamic information on the Vif-EloBC interaction PMID: 24225024
- s propose that CBFbeta acts as a chaperone to stabilize HIV-1 Vif during and after synthesis and to facilitate interaction of Vif with cellular cofactors required for the efficient degradation of APOBEC3G. PMID: 24522927
- In the absence of CBFbeta, Vif does not bind Cul5, thus preventing the assembly of the E3 ligase complex. PMID: 24390320
- CBF-beta is critical for the formation of the Vif-ElonginB/ElonginC-Cul5 core E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. PMID: 24390335
- Catalytic activity of APOBEC3F is required for efficient restriction of Vif-deficient human immunodeficiency virus 1. PMID: 24503066
- Vif conserved residues E88/W89 are crucial for CBFbeta binding. PMID: 24418540
- data reveal the structural basis for Vif hijacking of the CBF-beta and CUL5 E3 ligase complex, laying a foundation for rational design of novel anti-HIV drugs PMID: 24402281
- Vif derived from a subtype C molecular clone was less effective at overcoming A3G-mediated inhibition than Vif derived from either subtype B or CRF02_AG molecular clones. PMID: 23689841
- Overall, the results of this study indicate that the HIV-1 Vif residue I107 is important for its anti-APOBEC3G activity and viral replication, which may have implications for viral fitness in vivo. PMID: 23707381
- A3H-hapII is resistant to NL4-3 Vif while it is efficiently degraded by LAI Vif. PMID: 23469063
- These data indicate the importance of the HIV accessory proteins nef and vif as factors that contribute to the outcome of AIDS. PMID: 23417613
- Cellular APOBEC3G impairs the multimerization of the HIV-1 Vif protein. PMID: 23576497
- Vif co-encapsidation with APOBEC3G can promote sublethal mutagenesis of HIV-1 proviral DNA. PMID: 23316055
- These separation-of-function mutants demonstrate that HIV-1 Vif and the RUNX transcription factors interact with cellular CBFbeta on genetically distinct surfaces. PMID: 22725134
- Unusual Vif substitutions may be linked to HIV-1 attenuation in patients infected perinatally. PMID: 23080486
- Vif specifically binds the TAR and DIS sequences in the low nanomolar range. PMID: 22767258
- s revealed that different lengths and regions are required for CBFbeta to assist HIV-1 Vif or RUNX1. PMID: 23175372
- Vif binding to human APOBEC3C protein PMID: 23001005
- CBFbeta prestabilizes Vif((1-192)) relative to Vif((95-192)), consistent with a stronger interaction of Cul5 with Vif's C-terminal Zn(2+)-binding motif. PMID: 23098073
- These data suggest that Vif and A3G are not serine/threonine phosphorylated in human cells and phosphorylation is not linked to their functional activities. PMID: 22894923
- Viral diversity and diversification of major non-structural genes vif, vpr, vpu, tat exon 1 and rev exon 1 during primary HIV-1 subtype C infection. PMID: 22590503
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Host cytoplasm. Host cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Virion.
-
蛋白家族:Primate lentivirus group Vif protein family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: vg:155459
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
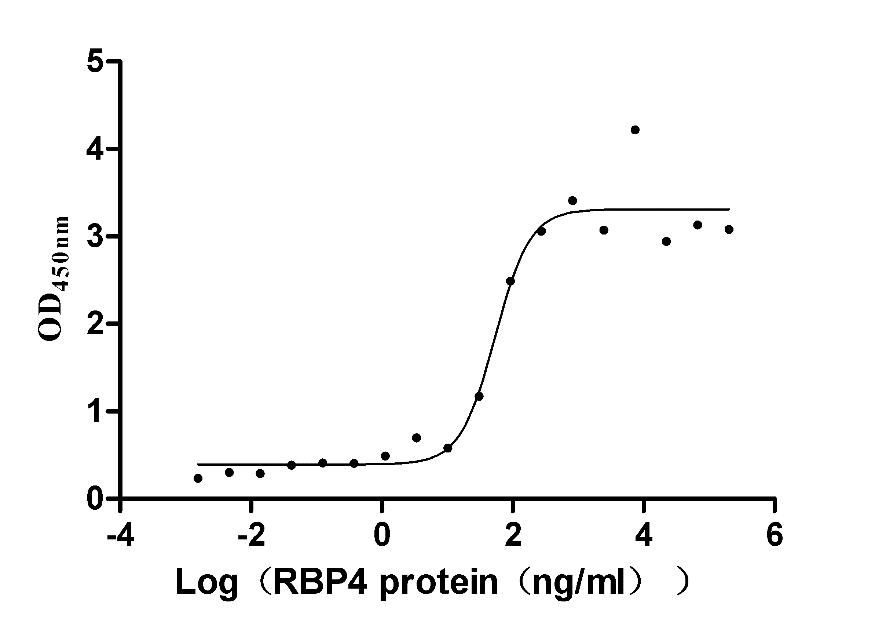
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
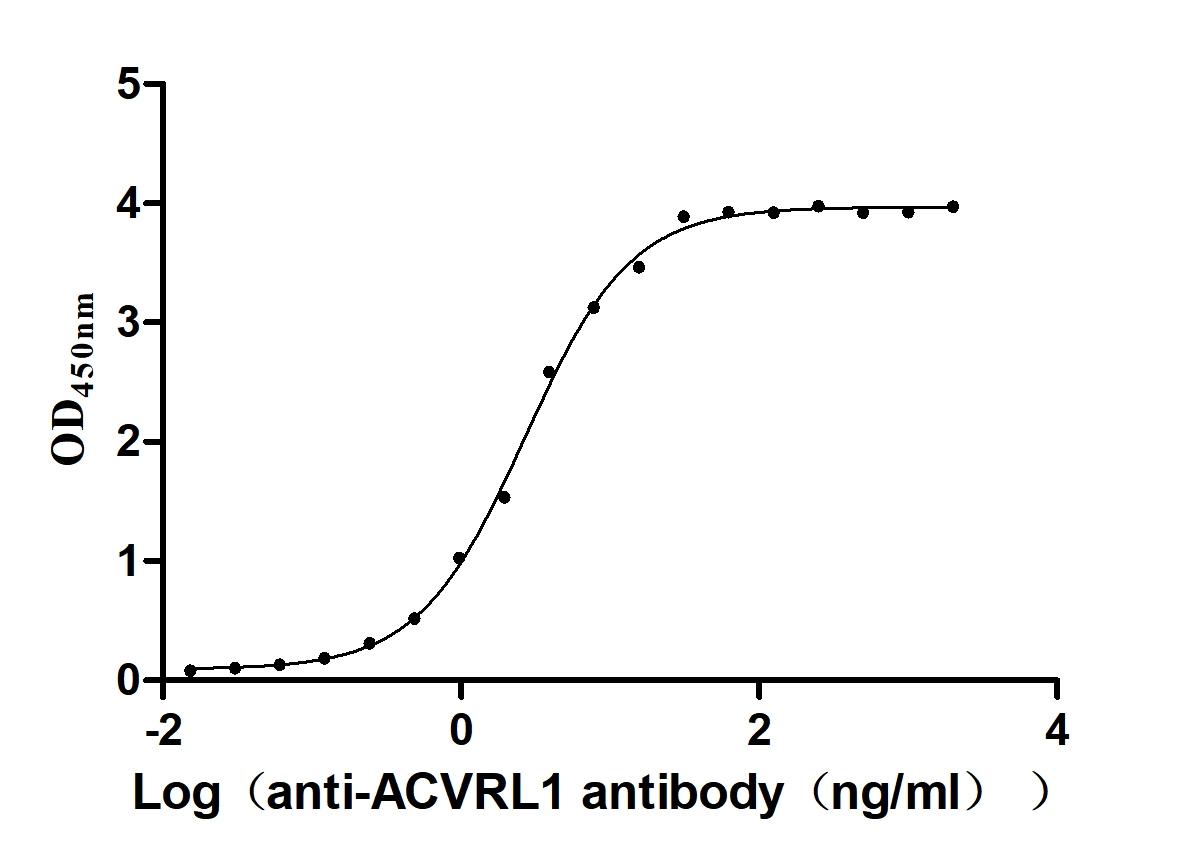
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
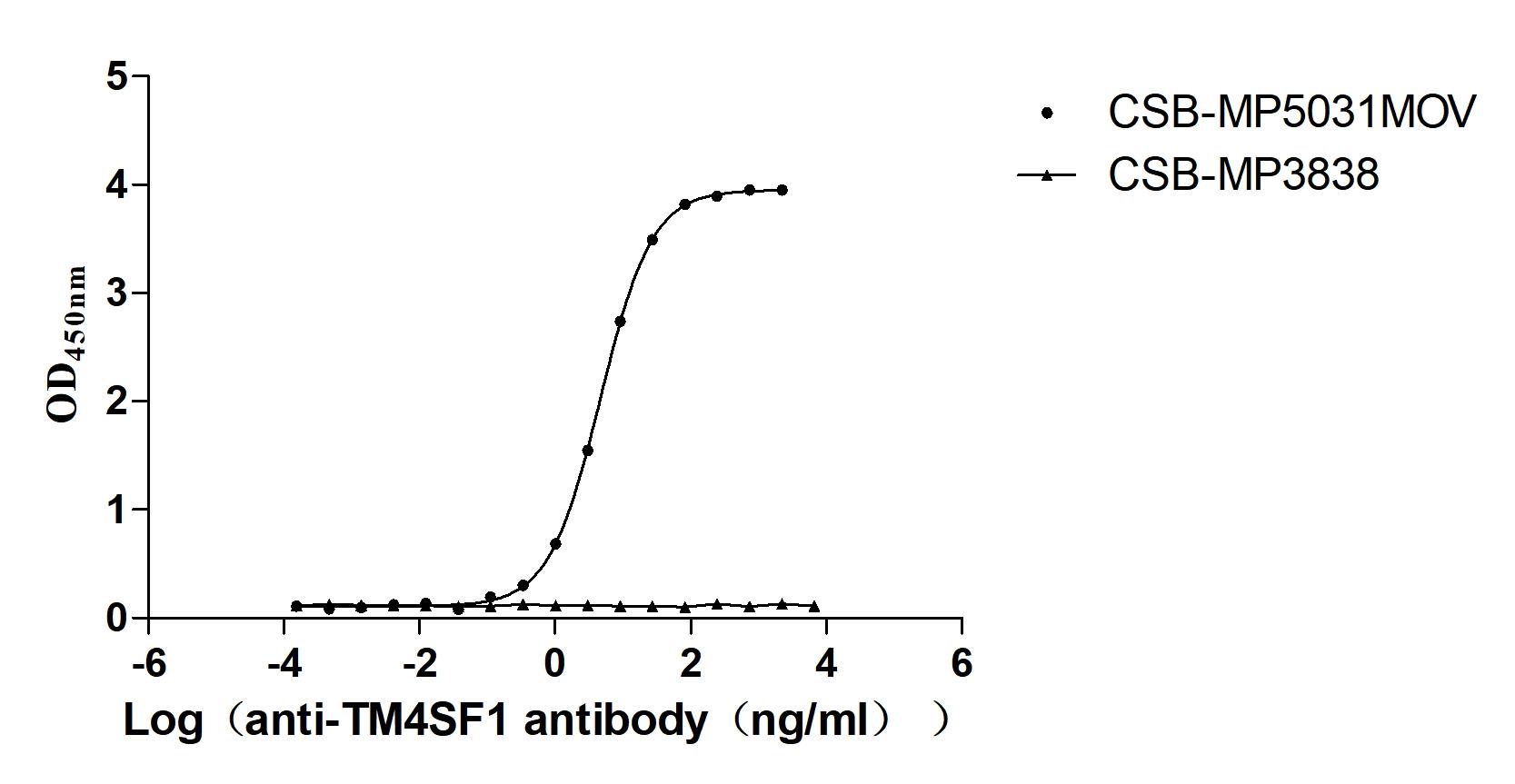
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)