Recombinant Measles virus Fusion glycoprotein F0 (F), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP301654MCQ
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP301654MCQ
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP301654MCQ
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:F
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:FFusion glycoprotein F0 [Cleaved into: Fusion glycoprotein F2; Fusion glycoprotein F1]
-
种属:Measles virus (strain Edmonston) (MeV) (Subacute sclerose panencephalitis virus)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Class I viral fusion protein. Under the current model, the protein has at least 3 conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and plasma cell membrane fusion, the heptad repeat (HR) regions assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of viral and plasma cell membranes. Directs fusion of viral and cellular membranes leading to delivery of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. This fusion is pH independent and occurs directly at the outer cell membrane. The trimer of F1-F2 (F protein) probably interacts with H at the virion surface. Upon HN binding to its cellular receptor, the hydrophobic fusion peptide is unmasked and interacts with the cellular membrane, inducing the fusion between cell and virion membranes. Later in infection, F proteins expressed at the plasma membrane of infected cells could mediate fusion with adjacent cells to form syncytia, a cytopathic effect that could lead to tissue necrosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Cell-to-Cell Measles Virus Spread between Human Neurons Is Dependent on Hemagglutinin and Hyperfusogenic Fusion Protein. PMID: 29298883
- L454W F mutant is activated independently of H or the cell receptor that enabled the efficient spread in the central nervous system. PMID: 25670774
- Acquisition of enhanced fusion activity through substitutions in the extracellular domain of the F protein may be crucial for measles virus to the extensive spread in the central nervous system and development of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. PMID: 25520515
- Complementation of F mutants with a monomeric, fusion-inactive F variant enriched the F oligomers for heterotrimers containing a single disulfide bond, without affecting fusion complementation profiles compared with standard F protein. PMID: 25157143
- F maturation prepares for complex separation after triggering, and the H head domains in prereceptor-bound conformation prevent premature stalk rearrangements and F activation. PMID: 25392208
- Thermodynamically stabilized by the N465H substitution, the F protein required elevated temperature as high as 40 degrees C to promote cell-cell fusion, whereas all five DIII mutations caused destabilization of the F protein PMID: 25479085
- s demonstrate that the measles virus H stalk represents the effector domain for measles virus F triggering. PMID: 23966411
- Taken together, these findings reveal that the morbillivirus H protein must lower the activation energy barrier of metastable prefusion F for fusion triggering. PMID: 23077316
- The F genes of measles virus isolated in china had no significant genetic variation. PMID: 20084883
- The F genes of measles virus in China during 1999-2003 had no sig-nificant changes. PMID: 20077667
- residues located in the head domain of the F trimer and the HR-B region contribute jointly to controlling F conformational stability PMID: 16415028
- findings show that both M (a fraction of which is modified by ubiquitination) & F proteins individually promote formation of virus-like particles, but they do not act in synergy; we propose that M & F act separately in particle morphogenesis and release PMID: 17374768
- These findings suggest a common molecular mechanism and a key role of the F protein for syncytium formation in cells expressing an unidentified third receptor for MV. PMID: 17825451
- Tyrosine-based targeting motifs in the H and F glycoproteins play a crucial role for MV replication and spread within lymphocytes, the main target cells of acute MV infection. PMID: 18272759
- The partitioning of F, CD46 and CD55 molecules in different membrane microdomains could account for the ability of F to escape complement regulation by the CD55 and CD46 regulators. PMID: 18455798
- Alanine-scanning mutagenesis revealed that an F protein with a single mutation of a central TM region leucine (L507A) was more fusogenic than the unmodified F protein while retaining similar kinetics of proteolytic processing. PMID: 18786999
- The H-protein and the F-protein mediates the virus cell entry. PMID: 19198562
- findings argue against specific protein-protein contacts between the H head & F head domains; support a docking model characterized by short-range contacts between prefusion F head & attachment protein stalk, possibly involving H residues 111, 114 & 118 PMID: 19656895
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Virion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host cell membrane; Single-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Paramyxoviruses fusion glycoprotein family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: vg:1489800
Most popular with customers
-
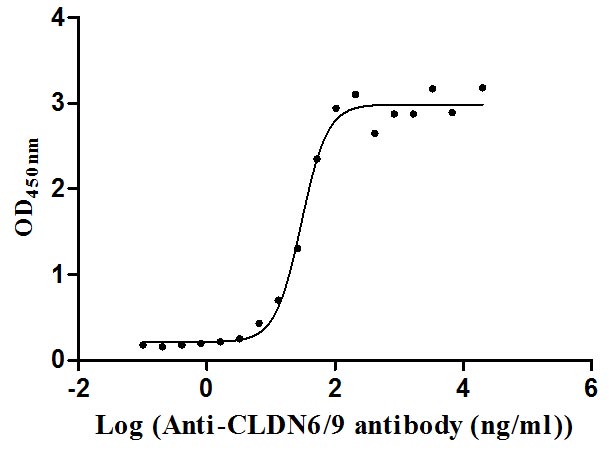
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
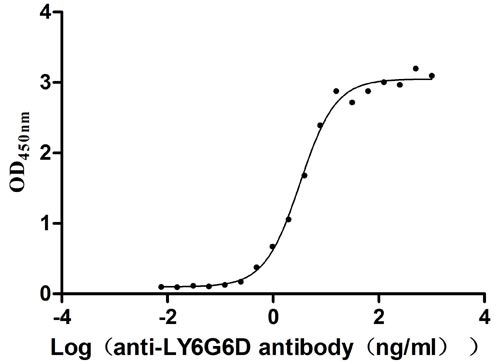
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
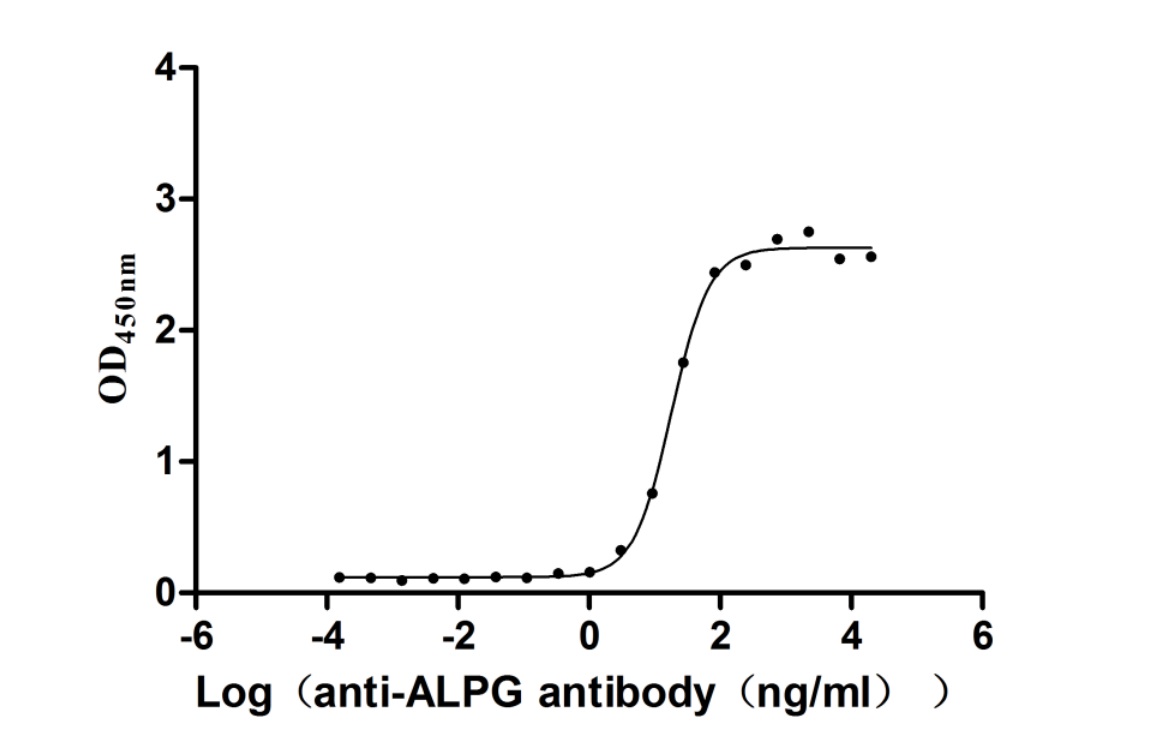
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
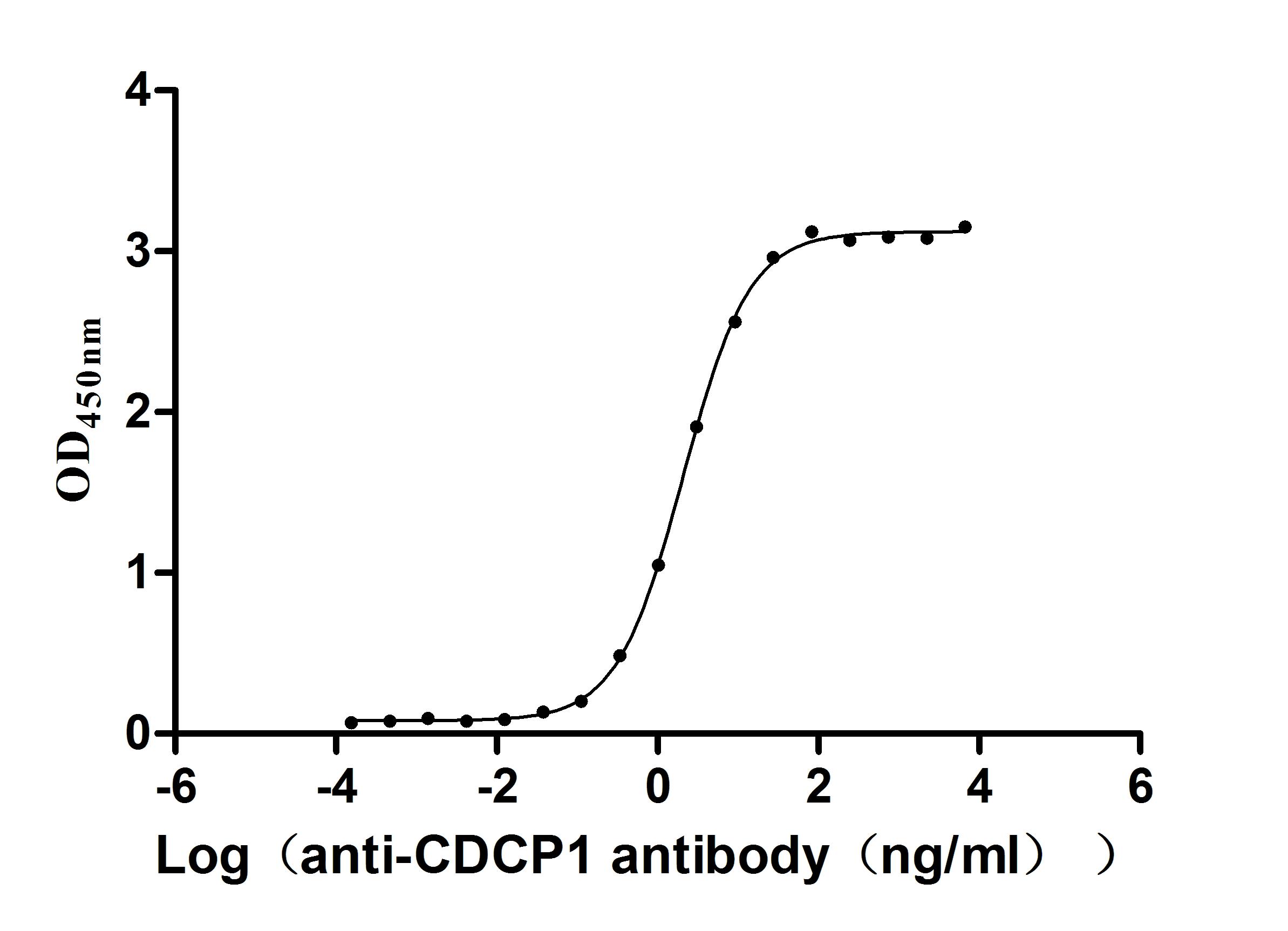
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
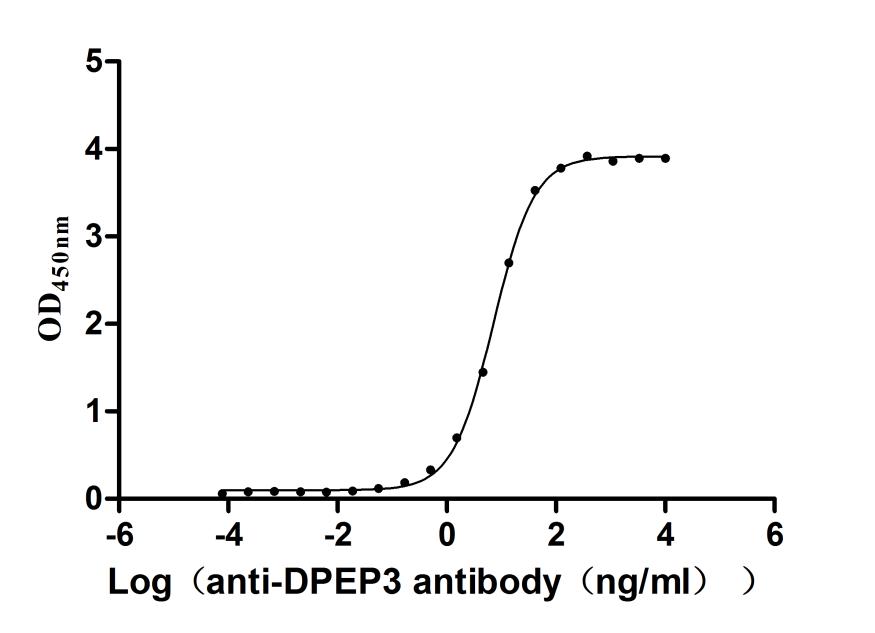
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
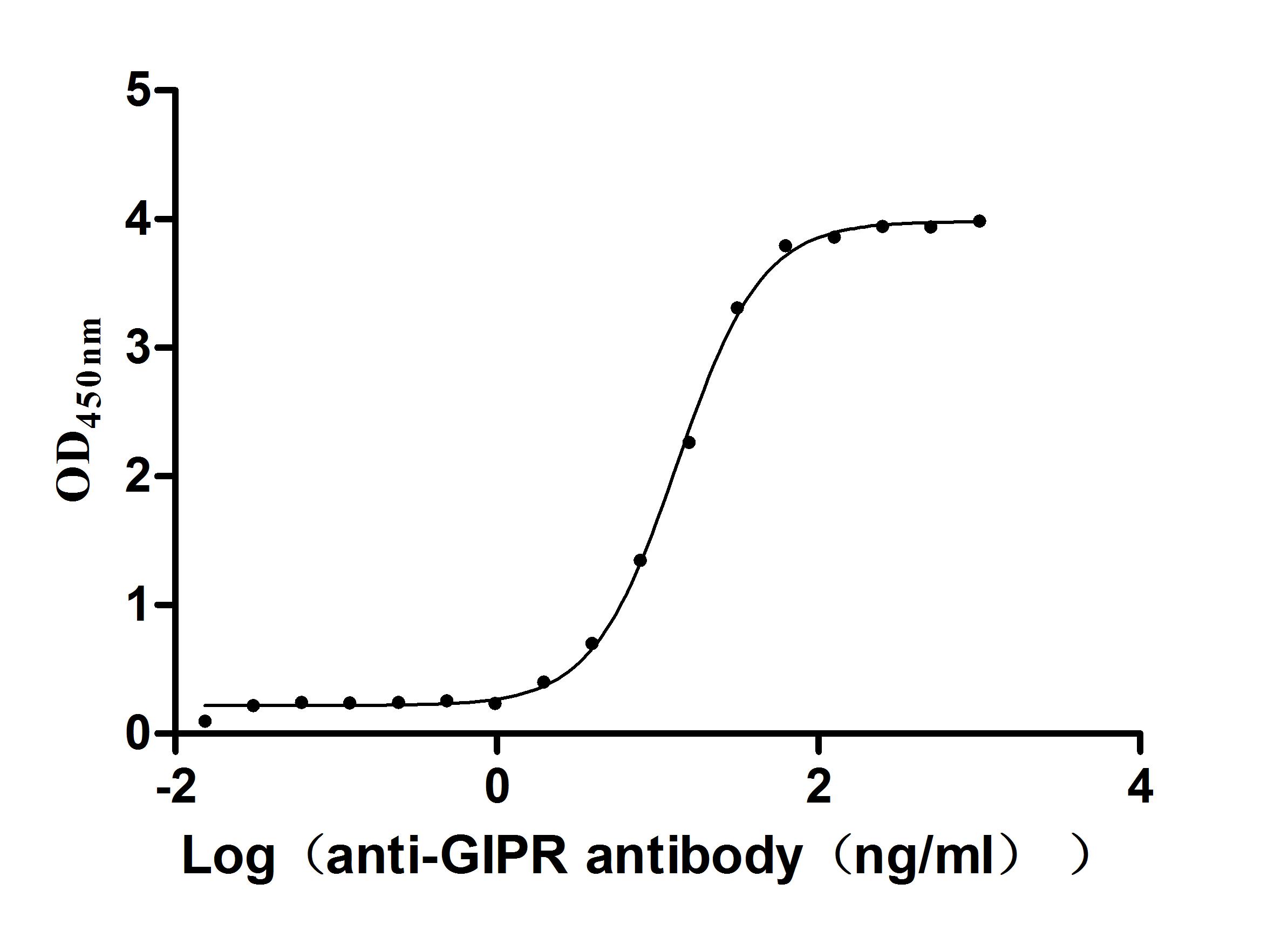
Recombinant Macaca Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)