Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc)
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein(Arc),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP001981MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein(Arc),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP001981MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein(Arc),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP001981MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein(Arc),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP001981MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein(Arc),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP001981MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Arc
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:ArcActivity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein; mArc; Activity-regulated gene 3.1 protein; ARC/ARG3.1; Arg3.1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-396
-
氨基酸序列MELDHMTTGG LHAYPAPRGG PAAKPNVILQ IGKCRAEMLE HVRRTHRHLL TEVSKQVERE LKGLHRSVGK LENNLDGYVP TGDSQRWKKS IKACLCRCQE TIANLERWVK REMHVWREVF YRLERWADRL ESMGGKYPVG SEPARHTVSV GVGGPEPYCQ EADGYDYTVS PYAITPPPAA GELPEQESVE AQQYQSWGPG EDGQPSPGVD TQIFEDPREF LSHLEEYLRQ VGGSEEYWLS QIQNHMNGPA KKWWEFKQGS VKNWVEFKKE FLQYSEGTLS REAIQRELEL PQKQGEPLDQ FLWRKRDLYQ TLYVDAEEEE IIQYVVGTLQ PKLKRFLRHP LPKTLEQLIQ RGMEVQDGLE QAAEPSGTPL PTEDETEALT PALTSESVAS DRTQPE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Master regulator of synaptic plasticity that self-assembles into virion-like capsids that encapsulate RNAs and mediate intercellular RNA transfer in the nervous system. ARC protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles that mediate the transfer of ARC mRNA into new target cells, where ARC mRNA can undergo activity-dependent translation. ARC capsids are endocytosed and are able to transfer ARC mRNA into the cytoplasm of neurons. Acts as a key regulator of synaptic plasticity: required for protein synthesis-dependent forms of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) and for the formation of long-term memory. Regulates synaptic plasticity by promoting endocytosis of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in response to synaptic activity: this endocytic pathway maintains levels of surface AMPARs in response to chronic changes in neuronal activity through synaptic scaling, thereby contributing to neuronal homeostasis. Acts as a postsynaptic mediator of activity-dependent synapse elimination in the developing cerebellum by mediating elimination of surplus climbing fiber synapses. Accumulates at weaker synapses, probably to prevent their undesired enhancement. This suggests that ARC-containing virion-like capsids may be required to eliminate synaptic material. Required to transduce experience into long-lasting changes in visual cortex plasticity and for long-term memory. Involved in postsynaptic trafficking and processing of amyloid-beta A4 (APP) via interaction with PSEN1. In addition to its role in synapses, also involved in the regulation of the immune system: specifically expressed in skin-migratory dendritic cells and regulates fast dendritic cell migration, thereby regulating T-cell activation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Specific acetylation of lysine residues on Arc promote Arc protein stability. PMID: 29162813
- Stress from escapable electroshock (ES) was associated with up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in amygdala as well as medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Stres from inescapable shock suppressed c-fos in mPFC (0 h) but induced more Arc in amygdala (2 h) in comparison with ES. PMID: 29135807
- Our data support the hypothesis that the kinetics of Arc induction to refine cortical representations of sensory categories is sensitive to the familiarity of the sensory experience. PMID: 29142056
- PSD95 was essential for Arc assembly into 1.5-MDa complexes and activity-dependent recruitment to excitatory synapses. PMID: 29045836
- Data show that although activity-dependent expression of activity regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein (Arc) mRNA does not change with age, expression of Arc protein is maximal during the critical period and declines in adulthood. PMID: 28790183
- It appears that palmitoylation regulates at least a subset of Arc functions in synaptic plasticity. PMID: 29264923
- These results indicate that dopamine is required to drive activity-dependent amplification of Arc mRNA in the developing postnatal frontal cortex. PMID: 27365296
- Study demonstrates in mice that explored novel spatial environments, the involvement of Egr3 in regulating the late protein-dependent phase of Arc expression in the dentate gyrus. PMID: 28589041
- Arc/Arg3.1 effects on memory formation are not only manifested at the level of molecular pathways regulating synaptic plasticity, but also at the systems level. PMID: 27038743
- CTCF knockdown attenuates fear-conditioning-induced hippocampal gene expression of key learning genes and loss of long-range interactions at the BDNF and Arc loci. PMID: 27880914
- Genetic disruption of Arc in mice causes alterations in dopamine and neurobehavioral phenotypes related to schizophrenia. PMID: 27524619
- Data indicate that ARC overexpression diminishes amyloid-induced JNK pathway activation and apoptosis in the beta-cell, a strategy that may reduce beta-cell loss in type 2 diabetes PMID: 28729244
- Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein accumulates in the nucleus in response to cocaine and acts as a brake on chromatin remodeling and long-term behavioral alterations. PMID: 27567310
- This is a promising novel therapeutic approach because it appears to be effective in a model producing severe injury by interfering with an array of proximal signals and effectors of the ischemic cascade, upstream of JNK, caspases, and BIM and BAX activation. PMID: 27488634
- missense mutations in TRIAD3 abolished the interaction of TRIAD3A with Arc, disrupting Arc ubiquitination, and consequently Arc degradation. PMID: 27995769
- The dynamics of the c-Fos and Arc expression has a biphasic pattern: the first peak was observed in 15-30 min after learning and the second less pronounced peak in 1-3 h. PMID: 27160884
- we report that late Arc expression is essential for the persistence of newly-acquired and reactivated memories. Persistent fear memories could be a factor in post-traumatic stress disorder. PMID: 26880136
- Arc-expressing neurons have enhanced intrinsic excitability and are preferentially recruited into newly encoded memory traces. PMID: 25802982
- These findings suggest that 11beta-HSD1 may contribute to the decline in Npas4 and Arc mRNA levels associated with memory impairment during ageing PMID: 26563879
- Transcriptional activity of early genes involved in memory process, such as activity regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein (Arc) gene, is increased in the hippocampus of hypercholesterolemic LDL receptor knockout mice. PMID: 25797218
- Soleus of ARC-deficient mice exhibited lower total, as well as fiber type-specific cross sectional area in type I and IIA skeletal muscle fibers. PMID: 25596718
- Arc enhances dynamin polymerization and GTPase activation. PMID: 25783003
- This study demonstrated a task-specific Arc-dependent cellular consolidation process in M2 cortex during motor learning. PMID: 26051420
- Arc is necessary, but not sufficient, for MEF2-dependent synapse elimination. PMID: 24857654
- The enhanced seizure-like activity, but not the increased ultrasonic vocalizations or motor deficits, is rescued in juvenile Angelman syndrome mice by genetically reducing the expression level of the cytoskeleton-associated protein, Arc. PMID: 25848016
- The present study provides the first atomic structure for Arc and reveals that Arc N- and C-lobes evolved from the capsid domain of Ty3/Gypsy retrotransposon. PMID: 25864631
- Arc expression regulates the perpetuation of fear memoires. PMID: 25589774
- Arc is required for long-term extinction of conditioned fear. PMID: 24758170
- Molecular analysis revealed a remarkable decline in Arc expression in both hippocampus and cerebral cortex of amnesic mice, which was recovered after i-Extract treatment. Arc may be involved in i-Extract mediated recovery from amnesia. PMID: 24012642
- trace-conditioned mice, compared to backward-conditioned (stimulation-control), delay-conditioned and naive mice, exhibited elevated amygdalar Arc expression in the basolateral (BLA) but not the central (CeA) or the lateral amygdala (LA). PMID: 23891993
- Our findings therefore reveal an Arc-dependent molecular pathway by which gene-experience interaction regulates the emergence of persistent firing patterns in specific neuronal populations PMID: 24806683
- Deficits in Arg3.1 and neuronal morphology lead to a deficit in spatial memory consolidation. PMID: 24431439
- dendritic translation of Arc underlies the priming of mGluR-long-term synaptic depression PMID: 24094104
- Novelty exposure induced an increase in Arc and c-Fos mRNA in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), parietal cortex, and hippocampal formation in both APP/PS1DeltaE9 transgenic and wild-type mice PMID: 23598246
- This study demonistrated that Arc mediates the homeostatic response to increased activity by translocating to the nucleus, increasing promyelocytic leukemia protein expression and decreasing GluA1 transcription, ultimately downscaling synaptic strength. PMID: 23749147
- Neuronal subpopulations activated during fear memory retrieval preferentially transcribe Arc during subsequent rest in the lateral amygdala. PMID: 22928932
- the disruption in Arc patterns reveals plaque-associated interference with neural network integration. PMID: 22922786
- the importance of intracellular mGluR5 in the cascade of events associated with sustained synaptic transmission PMID: 22179607
- Kinetics and/or detectability of cortical subcellular is consistent with Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA expression being altered by the initial exposure to the sound, suggesting exposure-induced modifications in the cytoplasmic Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA pool. PMID: 21334422
- Study reports that the immediate early gene Arc is required for activity-dependent generation of Abeta. Arc is a postsynaptic protein that recruits endophilin2/3 and dynamin to early/recycling endosomes that traffic PMID: 22036569
- dopamine D1 receptor agonists cause Erk-dependent increases in Zif268 and Arc/Arg3.1 expression in mouse dentate gyrus PMID: 21559295
- The subset of cells that were initially activated during conditioning in the lateral amygdala preferentially transcribed Arc during subsequent rest. This was most frequently observed in conditioned mice that formed robust associative fear memory. PMID: 21371562
- Results demonstrate that Arc is induced from wheel running but not movement in cages without wheels. PMID: 21497182
- Cognitive improvement of schizophrenic histopathology may be related to a restoration of synaptophysin and/or Arc levels in the frontal cortex. PMID: 20817066
- Arc transcription is dramatically suppressed in acute slices and negatively regulated by the activation of GABAA receptors, and positively regulated by the activation of muscarinic receptors. PMID: 20806412
- Arc/Arg3.1 is a context-dependent Notch regulator of neuronal signaling. PMID: 21315255
- by linking spine morphology with AMPAR endocytosis, Arc balances synaptic downscaling with increased structural plasticity PMID: 20921410
- SRF binding to SRE 6.9 in the Arc promoter is required for the late phase of cerebellar long-term depression PMID: 20694003
- these data suggest that Arc/Arg3.1 dependent long term synaptic changes in spinal pain transmission are a feature of anti-nociceptive, i.e. enkephalinergic, rather than pro-nociceptive neurons. PMID: 20653942
- Increased Arc response to novelty could be suggested as a molecular mechanism underlying failure to adapt to environmental changes, common to chronic stress and altered glutamate function. PMID: 20550627
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Extracellular vesicle membrane; Lipid-anchor. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Cell junction, synapse. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic density. Early endosome membrane. Cell projection, dendrite. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cell projection, dendritic spine. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome.
-
蛋白家族:ARC/ARG3.1 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in brain and testis. In primary visual cortex, detected in all cortical layers with the exception of layer 5: present at highest level in layers 2/3 and 4, the predominant sites of ocular dominance plasticity (at protein level). Also expressed i
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11838
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000023268
UniGene: Mm.491310
Most popular with customers
-
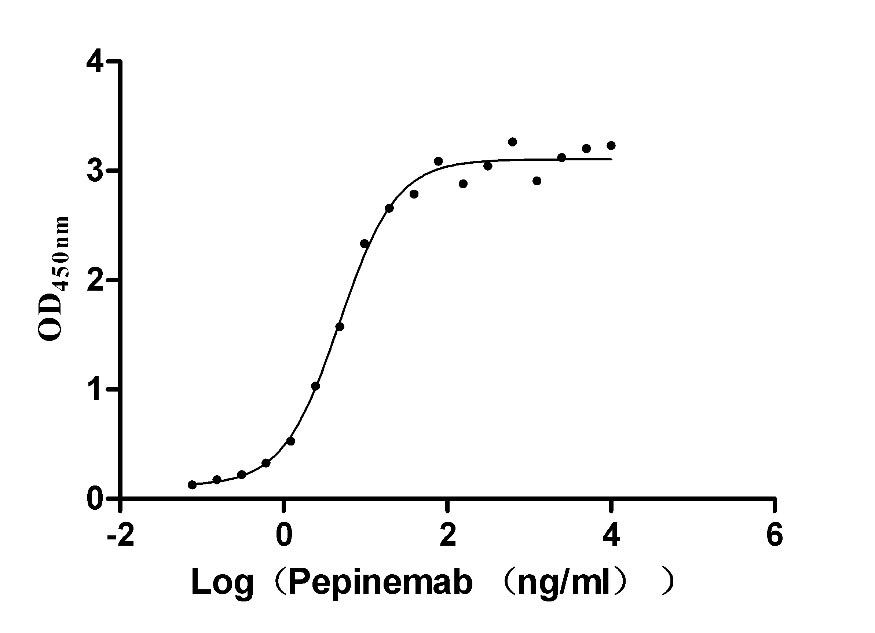
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
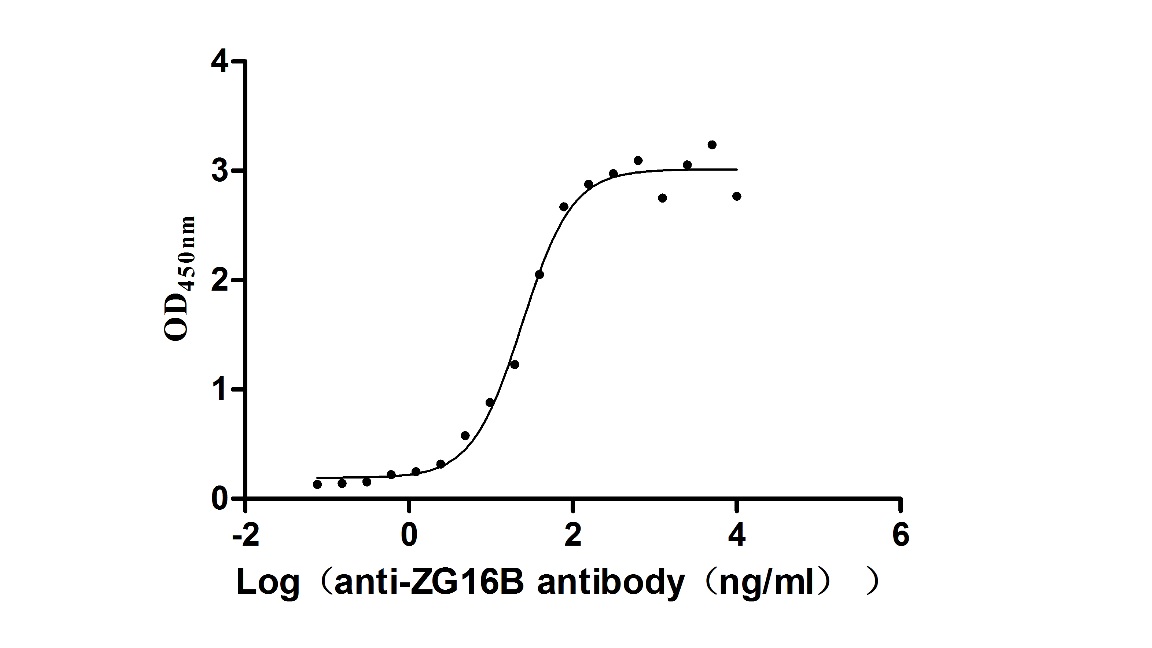
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
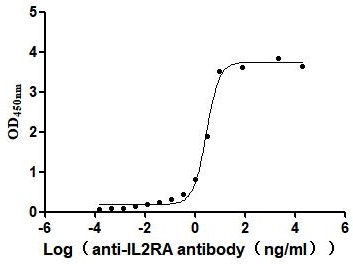
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-1(CDH1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)