Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5 (Aqp5), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5(Aqp5),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP896235MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5(Aqp5),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP896235MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5(Aqp5),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP896235MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5(Aqp5),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP896235MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Aquaporin-5(Aqp5),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP896235MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Aqp5
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Aqp5; Aquaporin-5; AQP-5
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Forms a water-specific channel. Plays an important role in fluid secretion in salivary glands. Required for TRPV4 activation by hypotonicity. Together with TRPV4, controls regulatory volume decrease in salivary epithelial cells. Seems to play a redundant role in water transport in the eye, lung and in sweat glands.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results indicate that autophagy plays a crucial role in aquaporin 5 (AQP5) degradation in diabetic submandibular gland (SMG). PMID: 29951954
- A daily rhythm was detected in the expression profiles of Aqp5 in submandibular glands in vivo. PMID: 28484984
- AQP5 immunoreactivity was found in the isthmic muscle and lamina propria beneath the epithelia. In cycling females, oviduct aqp5 mRNA levels were the highest at oestrus and the lowest at dioestrus. AQP5 immunoreactivity in non-ciliated cells was notable in the infundibulum, where AQP5 was relatively high at oestrus but low at dioestrus & pro-oestrus, indicating synchrony between aqp5 gene activation and the ovarian cycle. PMID: 26272113
- RUNX1 is essential for the development of the granular convoluted tubules in the submandibular glands; RUNX1 could also be involved in the membrane trafficking of the AQP5 protein of the acinar cells in the SMG in order to allow for the proper secretion of saliva PMID: 28877240
- The AQP5 genotype may influence survival following lipopolysaccharides by altering neutrophil cell migration. PMID: 27871297
- Adjusting AQP5 protein levels could be considered a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of acute pulmonary edema induced by H2S and other hazardous gases PMID: 28088675
- GTP-dependent AQP5 expression could act as osmosensor PMID: 24662389
- AQP5 promoter methylation is not a universal mechanism for AQP5 regulation. PMID: 25767807
- The activation of P2X7 receptor was connected with an increase of aquaporin-5, whereas the inhibition of the receptor with oxidized ATP resulted in down regulation of aquaporin-5. PMID: 24941004
- Lung AQP1 and AQP5 expression were significantly decreased in mice with acute lung injury together with increased inflammatory reaction and apoptosis of alveolar epithelial and vascular endothelial cells PMID: 24879973
- The co-regulation of pendrin and AQP5 membrane expression under chronic K(+)-deficiency indicates that these two molecules could cooperate as an osmosensor to rapidly detect and respond to alterations in luminal fluid osmolality. PMID: 24429825
- propose a new function of AQP5 as an inflammatory signal potentiator, which may be mediated by increased activation of ERK and NF-kappaB PMID: 24747567
- AQP5 plays an important role in high altitude pulmonary edema formation induced by high altitude simulation. PMID: 24274330
- Administration of cevimeline maintains the proper localization of AQP-5 in the acinar cells of the salivary glands of mice with Sjogren's syndrome. PMID: 23925155
- this is the first report providing evidence that AQP5 facilitates maintenance of lens transparency and homeostasis by regulating osmotic swelling caused by glucose transporters and cotransporters under hyperglycemic stressful conditions. PMID: 24148248
- The regulated AQP5 translocation may contribute to sweat secretion by increasing the water permeability of apical plasma membranes of sweat glands. PMID: 23473857
- Hypoxia decreases aquaporin 5 (AQP5) expression through both hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and proteasome-mediated pathways. PMID: 23469202
- upregulated Aqp5 may contribute to polyuria, possibly by impairing Aqp2 membrane localization, in Dot1l(AC) mice and in patients with diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 23326416
- AQP5 is a significant component of lens fiber cell membranes, representing the second most abundant water channel in these cells. PMID: 23313152
- AQP5-mediated high plasma membrane water permeability enhances the apoptosis rate of differentiating bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PMID: 22420587
- Phosphokinase A induces AQP5 internalization in the corneal epithelial cells. PMID: 22550388
- Aquaporin-5 was present at the apical face of the olfactory epithelium, completing a water transport pathway to the surface of the epithelium. PMID: 21745799
- These data provide more evidence that AQP5 plays important roles in the metastasis potential of lung cancer PMID: 21193966
- results indicate that AQP1 and AQP5 are closely related to pulmonary edema but not to eosinophil infiltration or mucus secretion during asthma. PMID: 22226856
- AQP5 plays a role during embryonic salivary gland development. PMID: 21818558
- AQP5 is phosphorylated at its Thr259 by PKA through cAMP, but not Ca(2+), signaling pathways. This phosphorylation does not contribute to AQP5 trafficking in the salivary gland cells. PMID: 21633078
- The results implicate involvement of aquaporin 5 in the development of airway inflammation and mucous hyperproduction during chronic asthma. PMID: 20550619
- results also showed that AQP5 expression increases MUC5AC and MUC5B mucin production PMID: 21455588
- AQP5 expression first occurs in a scattered pattern in the late canalicular stage and becomes more prominent and organized in the terminal tubuli/pro-acinar cells towards birth PMID: 21203896
- These results suggest that LPS-induced potential down-regulation of expression of AQP5 mRNA in the parotid gland is mediated via a complex(es) of these two classes of transcription factors, NF-kappaB and p-c-Jun/c-Fos. PMID: 20522648
- Decreased expression of AQP-1 and AQP-5 in aged mice is sufficient to cause a significant decrease in alveolar water transport. PMID: 19215235
- We conclude that the presence of AQP5 in plasma membranes of sweat glands is essential for secretion, providing potential insight into mechanisms underlying mammalian thermoregulation, tactile sensitivity, and the pathophysiology of hyperhidrosis PMID: 11773623
- These data indicate that skeletal muscle cells express AQP5 protein and its expression is regulated by differentiation and hypertonic stress. PMID: 11989981
- these results indicate the expression of AQP5 in sweat gland secretory epithelium, but provide direct evidence against its physiological involvement in sweat fluid secretion in mice PMID: 12042359
- Dynamically expressed in developing mouse inner ear. Adult Aqp5 knockout mice show normal hearing and normal inner ear structural development. Redundant or alternative mechanisms likely regulate water homeostasis in developing and mature inner ear. PMID: 12943377
- cAMP and beta-adrenergic agonists produce distinct short and long term effects on AQP5 distribution and abundance that may contribute to regulation of lung water homeostasis. PMID: 15536076
- Aquaporin-1, -3, and -5 dependent water-transporting properties of cornea and conjunctiva. PMID: 15557451
- atRA increases AQP5 expression through transactivation of Sp1, leading to an increase in plasma membrane water permeability. PMID: 17097063
- There is a gender-influenced molecular mechanism involving AQP5 that allows transcellular and paracellular routes of water transport to act in conjunction. PMID: 17360692
- AQP5 may be involved in topiramate-induced hypohidrosis. PMID: 17521680
- Submandibular glands from 24-week-old NOD mice displayed inflammatory infiltrates, increased AQP5 protein expression, and impaired AQP5 distribution. PMID: 17665453
- This is the first evidence demonstrating an association between AQP5 and a signaling pathway, namely the Ras signal transduction pathway, which may be the basis of the oncogenic properties seen in AQP-overexpressing cells. PMID: 18155156
- AQP5 expression was needed for shear-induced barrier enhancement PMID: 18305162
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:MIP/aquaporin (TC 1.A.8) family
-
组织特异性:Detected at the luminal membrane of secretory epithelial cells in hindpaw sweat glands. Detected in acinar cells in salivary glands, in duct cells in lacrimal glands and in lung (at protein level). Detected in lung, parotid, submandibular, sublingual, and
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11830
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000085530
UniGene: Mm.45580
Most popular with customers
-
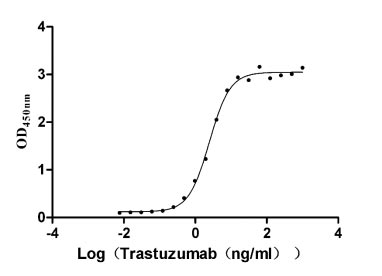
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
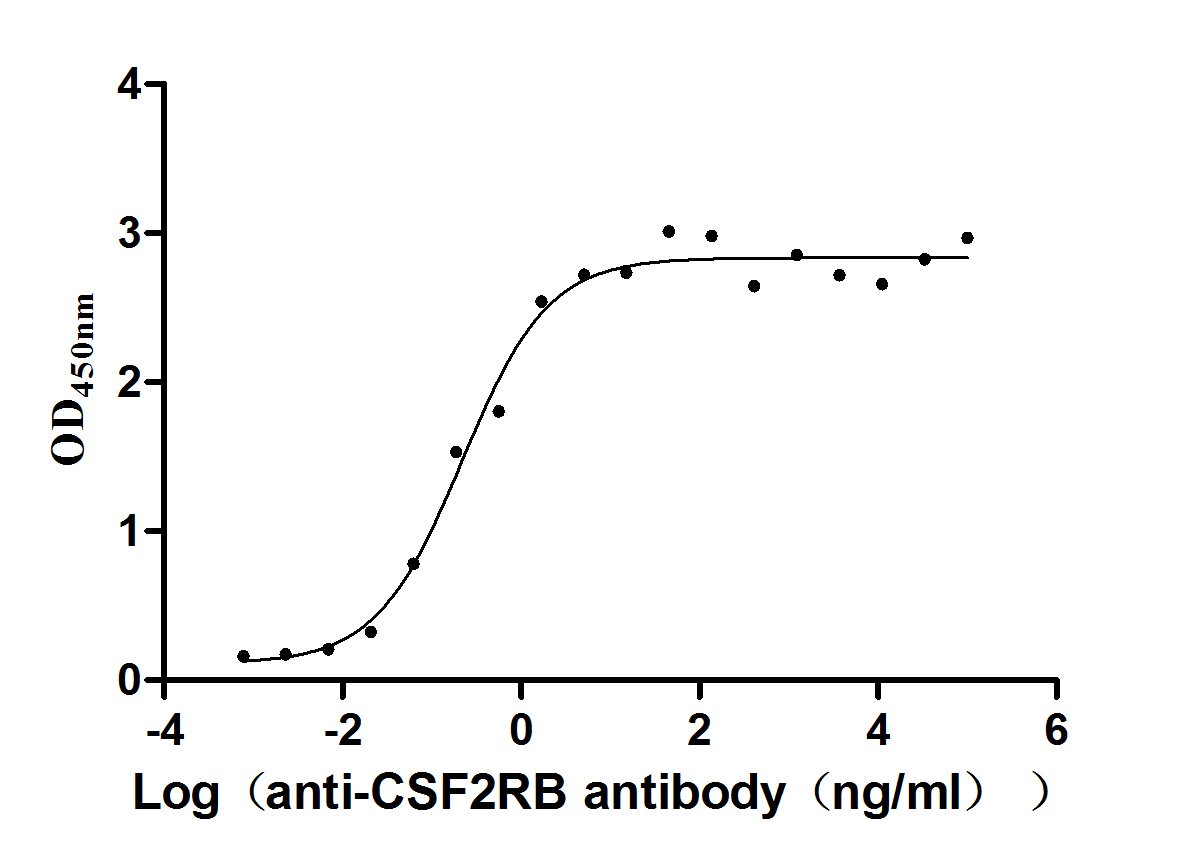
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
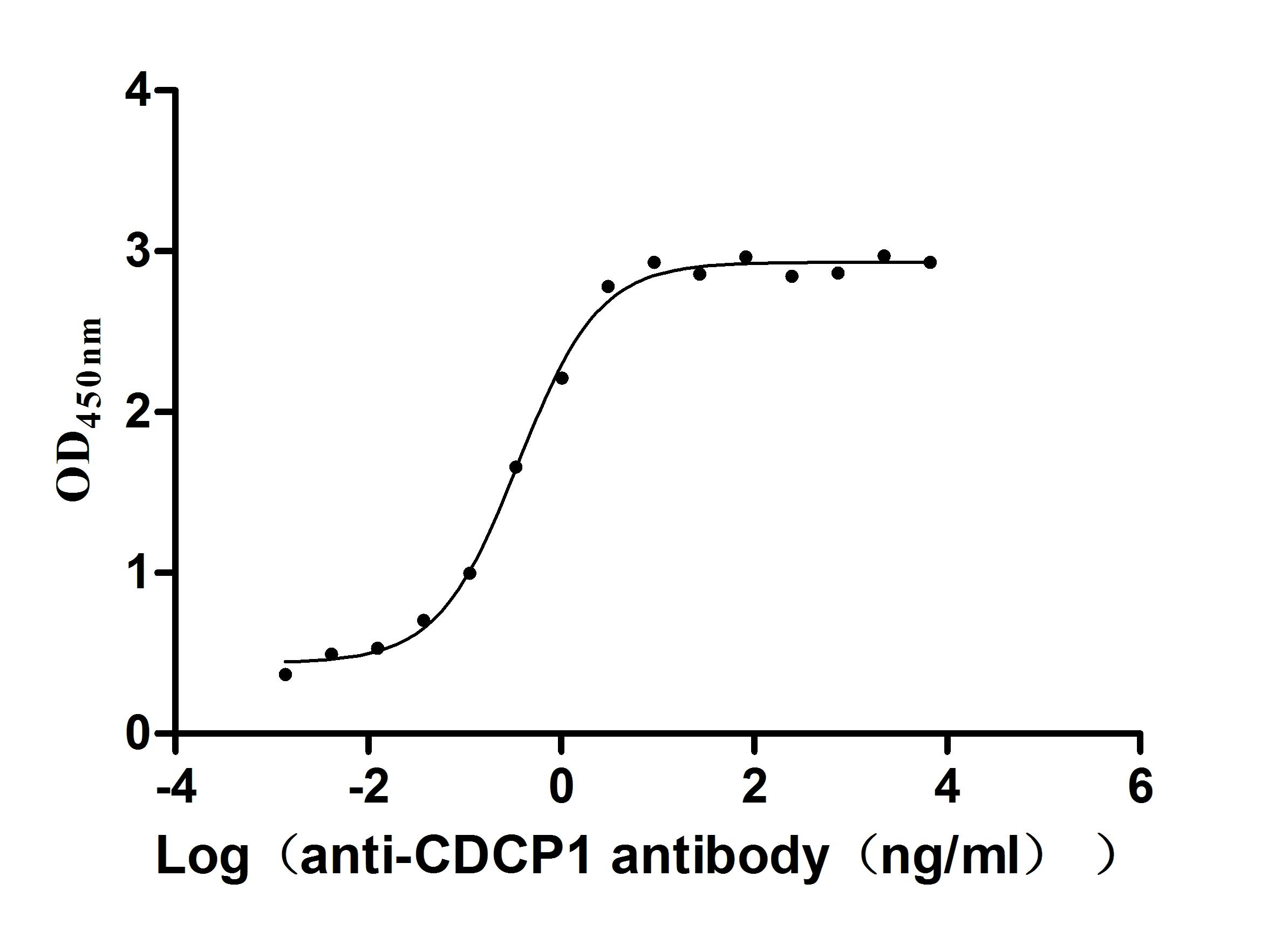
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)