Recombinant Mouse Bile acid receptor (Nr1h4)
-
货号:CSB-YP723332MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP723332MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP723332MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP723332MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP723332MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Nr1h4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Nr1h4; Bar; Fxr; Rip14; Bile acid receptor; Farnesoid X-activated receptor; Farnesol receptor HRR-1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 4; Retinoid X receptor-interacting protein 14; RXR-interacting protein 14
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-488
-
氨基酸序列MVMQFQGLEN PIQISLHHSH RLSGFVPEGM SVKPAKGMLT EHAAGPLGQN LDLESYSPYN NVPFPQVQPQ ISSSSYYSNL GFYPQQPEDW YSPGIYELRR MPAETGYQGE TEVSEMPVTK KPRMAAASAG RIKGDELCVV CGDRASGYHY NALTCEGCKG FFRRSITKNA VYKCKNGGNC VMDMYMRRKC QECRLRKCKE MGMLAECMYT GLLTEIQCKS KRLRKNVKQH ADQTANEDDS EGRDLRQVTS TTKFCREKTE LTADQQTLLD YIMDSYNKQR MPQEITNKIL KEEFSAEENF LILTEMATSH VQILVEFTKK LPGFQTLDHE DQIALLKGSA VEAMFLRSAE IFNKKLPAGH ADLLEERIRK SGISDEYITP MFSFYKSVGE LKMTQEEYAL LTAIVILSPD RQYIKDREAV EKLQEPLLDV LQKLCKMYQP ENPQHFACLL GRLTELRTFN HHHAEMLMSW RVNDHKFTPL LCEIWDVQ
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Ligand-activated transcription factor. Receptor for bile acids (BAs) such as chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), lithocholic acid, deoxycholic acid (DCA) and allocholic acid (ACA). Plays a essential role in BA homeostasis through the regulation of genes involved in BA synthesis, conjugation and enterohepatic circulation. Also regulates lipid and glucose homeostasis and is involved in innate immune response. The FXR-RXR heterodimer binds predominantly to farnesoid X receptor response elements (FXREs) containing two inverted repeats of the consensus sequence 5'-AGGTCA-3' in which the monomers are spaced by 1 nucleotide (IR-1) but also to tandem repeat DR1 sites with lower affinity, and can be activated by either FXR or RXR-specific ligands. It is proposed that monomeric nuclear receptors such as NR5A2/LRH-1 bound to coregulatory nuclear responsive element (NRE) halfsites located in close proximity to FXREs modulate transcriptional activity. In the liver activates transcription of the corepressor NR0B2 thereby indirectly inhibiting CYP7A1 and CYP8B1 (involved in BA synthesis) implicating at least in part histone demethylase KDM1A resulting in epigenomic repression, and SLC10A1/NTCP (involved in hepatic uptake of conjugated BAs). Activates transcription of the repressor MAFG (involved in regulation of BA synthesis). Activates transcription of SLC27A5/BACS and BAAT (involved in BA conjugation), ABCB11/BSEP (involved in bile salt export) by directly recruiting histone methyltransferase CARM1, and ABCC2/MRP2 (involved in secretion of conjugated BAs) and ABCB4 (involved in secretion of phosphatidylcholine in the small intestine). In ileal enterocytes activates FABP6/IBABP (involved in cytosolic transport), SLC51A/OSTA and SLC51B/OSTB (involved in secretion of conjugated BAs to the portal blood), and repressor NR0B2/SHP thereby indirectly inhibiting SLC10A2/ASBT (involved in BA uptake). In the intestine activates FGF15 expression and secretion leading to hepatic CYP7A1 repression; the function also involves the coordinated induction of hepatic KLB/beta-klotho expression. Transcriptional activation of FABP6/IBAP and SCD1 but not of ABCB11 is isoform-specific. Regulates transcription of liver UGT2B4 and SULT2A1 involved in BA detoxification; binding to the UGT2B4 promoter seems to imply a monomeric transactivation independent of RXRA. Modulates lipid homeostasis by activating liver NR0B2/SHP-mediated repression of SREBF1 isoform SREBP-1C (involved in de novo lipogenesis), expression of PLTP (involved in HDL formation), SCARB1 (involved in HDL hepatic uptake), APOE, APOC1, APOC4, VLDLR and SDC1 (involved in the hepatic uptake of LDL and IDL remnants), and inhibiting expression of MTTP (involved in VLDL assembly). Increases expression of APOC2 (promoting lipoprotein lipase activity implicated in triglyceride clearance). Transrepresses APOA1 probably involving a monomeric competition with NR2A1 for binding to a DR1 element. Also reduces triglyceride clearance by inhibiting expression of ANGPTL3 and APOC3 (both involved in inhibition of lipoprotein lipase). Involved in glucose homeostasis by modulating hepatic gluconeogenesis through activation of NR0B2/SHP-mediated repression of respective genes. Modulates glycogen synthesis (inducing phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3). Modulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and is involved in insulin resistance. Involved in intestinal innate immunity. Plays a role in protecting the distal small intestine against bacterial overgrowth and preservation of the epithelial barrier. Down-regulates inflammatory cytokine expression in several types of immune cells including macrophages and mononuclear cells. Mediates transrepression of TLR4-induced cytokine expression; the function seems to require its sumoylation and prevents N-CoR nuclear receptor corepressor clearance from target genes such as IL1B and NOS2. Involved in the TLR9-mediated protective mechanism in intestinal inflammation. Plays a anti-inflammatory role in liver inflammation; proposed to inhibit proinflammatory (but not antiapoptotic) NF-kappa-B signaling.; Activates transcription of IBAP and SDC1.; Activates transcription of IBAP and SDC1.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- FXR pathway activation increases XBP1 splicing and enhances p-IRE1alpha expression in liver PMID: 29377207
- Study provides a novel finding that suppression of miR-194 attenuates dietary-induced NAFLD via upregulation of FXR/Nr1h4. PMID: 28951211
- FXR-dependent concomitant relationships between gut microbiota, bile acids, and metabolic diseases in both genders. PMID: 28496104
- The role of the CAR signaling pathways within testis was validated using specific CAR agonist (TCPOBOP) and inverse agonist (androstanol) that respectively inhibited or reproduced the phenotype observed in Fxralpha-/- males fed Bile acids (BAs)-diet. These data open interesting perspectives to better define how BA homeostasis contributes to physiological or pathophysiological conditions via the modulation of CAR activity. PMID: 28181583
- Study identified an FXR/beta-catenin interaction whose modulation through beta-catenin suppression promotes FXR activation and decreases hepatic bile acids, which may provide unique therapeutic opportunities in cholestatic liver diseases PMID: 28714273
- Farnesoid X receptor gene deficiency impairs urine concentration in renal medulla. PMID: 29739889
- Data, including data from studies using knockout mice, suggest that control of whole-body energy expenditure by Gcgr agonism requires intact Fxr signaling and Fgf21 secretion in liver. (Gcgr = glucagon receptor glucagon; Fxr = farnesoid X receptor; Fgf21 = fibroblast growth factor-21) PMID: 29925501
- FXR exerts its function in L cells through interacting with CREB, a crucial transcriptional regulator of cAMP-CREB signaling pathway, to inhibit its transcriptional activity. Targeting FXR to rescue GLP-1 secretion may be a promising strategy for type II diabetes. PMID: 29940597
- The underlying mechanism of curcumin against cholestasis was restoring bile acid homeostasis and antagonizing inflammatory responses in a FXR-dependent manner and in turn contributed to overall cholestasis attenuation. PMID: 27624003
- FXR alpha helps establish and maintain an undifferentiated germ cell pool and in turn influences male fertility. FXR alpha controls the expression of the pluripotency marker Lin28 in the germ cells. PMID: 28669602
- Loss of FXR or its down-regulation is associated with higher bile acids concentrations and with a pro-tumorigenic phenotype. (Review) PMID: 28400119
- These results suggest that lack of FXR impaired FoxO3a-mediated autophagy and in turn exacerbated alcohol-induced liver injury PMID: 25460735
- Bile acids and salts (BA) treatment-farnesoid X-activated receptor (FRXalpha) signaling is a critical actor during sexual maturation. PMID: 26848619
- deletion in liver did not protect against diet-induced steatosis PMID: 28586124
- In livers of mice, FXR regulates amino acid catabolism and detoxification of ammonium via ureagenesis and glutamine synthesis. PMID: 28130067
- Data suggest that FXR and TGR5 expression is down-regulated in aging kidney; caloric restriction prevents these age-related changes. Additionally, in long-lived Ames dwarf mice, renal FXR and TGR5 expression is up-regulated. Treatment of aged mice with dual FXR/TGR5 agonist reverses age-related changes in kidney structure/function. (FXR = farnesoid X activated receptor; TGR5 = G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1) PMID: 28596381
- this study provides evidence for roles of FXR as an important regulator of placental inflammation PMID: 27821667
- These findings suggest that bile acids and FXR play pivotal roles in sepsis via controlling the NLRP3 inflammasome. PMID: 28380377
- Our results indicate that the gut microbiota promotes diet-induced obesity and associated phenotypes through FXR, and that FXR may contribute to increased adiposity by altering the microbiota composition. PMID: 26740296
- findings uncovered a novel mechanism in which INT-767 activation of FXR induces Tgr5 gene expression and increases Ca(2+) levels and cAMP activity to stimulate GLP-1 secretion and improve hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. PMID: 28478385
- In mice, we found transintestinal cholesterol excretion to be regulated by intestinal FXR via induction of its target gene Fgf15. PMID: 28065787
- FXR ligands to inhibit platelet activation. PMID: 27758768
- FXR could be a target molecule for reducing portal hypertension during hepatic fibrosis. PMID: 27896916
- Review of the role of an intestinal microbiota-farnesoid X receptor axis in modulating metabolic disease. PMID: 27639801
- Study shows that experimental chronic jet lag induces persistent deregulation of liver gene expression and metabolism, culminating in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. The bile acid receptor FXR and xenobiotic receptor CAR play an important role in this process. PMID: 27889186
- Vertical sleeve gastrectomy induces a weight loss in obese mice by increasing IFN-gamma secretion in mesenteric lymph nodes, which then increases the FXR expression in the liver and small intestine. PMID: 27376807
- hPCLS respond to OCA treatment by upregulating well-known FXR target genes, demonstrating its suitability to study FXR-mediated gene regulation. PMID: 26812075
- FXR may promote the proliferation of tumor cells and the hepatocytes in the process of liver regeneration by activating the PDK4-mediated metabolic reprogramming to generate glycolytic intermediates essential for rapid biomass generation, establishing a mechanistic link between cell proliferation and metabolic switch. PMID: 26728993
- the structural features that discriminate the selective binding of FXR by avermectin analogues may provide a unique safe approach to design drugs targeting FXR signaling. PMID: 26620317
- FXR can exert its hepatoprotective functions by controlling inflammation and mitochondrial functions, possibly involving an FXR-PPAR delta cross-talk PMID: 26482353
- Activated farnesoid X receptor attenuates apoptosis and liver injury in autoimmune hepatitis. PMID: 26238153
- FXR activation maintains endogenous glutathione homeostasis and protects the kidney in uninephrectomized mice from obesity-induced injury PMID: 26655953
- FXR down regulates MCP-1 expression in macrophages. PMID: 26474702
- FXR activation in L cells decreases proglucagon expression by interfering with the glucose-responsive factor Carbohydrate-Responsive Element Binding Protein (ChREBP) and GLP-1 secretion by inhibiting glycolysis. PMID: 26134028
- FXR may regulate SOD3 expression to suppress reactive oxygen species production, resulting in decreasing JNK activity. PMID: 25496033
- ransgenic mice that conditionally and tissue specifically express the activated form of FXR in the liver and intestine showed partial neonatal lethality, growth retardation, and spontaneous liver toxicity. PMID: 25719402
- No evidence for a major role of FXR in acute human or murine pancreatitis. The observed altered Fxr activity during the course of disease may be a secondary phenomenon. PMID: 25470824
- Protective effects of farnesoid X receptor on hepatic lipid accumulation are mediated by hepatic FXR and are independent of intestinal FGF15 signaling. PMID: 25156247
- The hepatic FXR alpha2 and FXR alpha4 differentially modulate bile salt and lipoprotein metabolism in mice. PMID: 25506828
- FXR deficiency strongly affects expression of genes related to immunity and bile acid metabolism, as well as the composition of the microbiome PMID: 25184625
- these data demonstrate that copper-mediated nuclear receptor dysfunction disrupts liver function in WD and potentially in other disorders associated with increased hepatic copper levels. PMID: 26241054
- LSD1 is a novel histone-modifying enzyme in the orchestrated regulation mediated by the farnesoid X receptor and small heterodimer partner that reduces hepatic bile acid levels and protects the liver against bile acid toxicity. PMID: 25545350
- FXR agonist, GW4064, upregulates adipokine expression in preadipocytes and HepG2 cells. PMID: 25400456
- FXR activation facilitates homing and function of MDSCs, which function as a critical negative feedback loop in immune-mediated liver injury. PMID: 24721598
- FXR activation attenuates LPS-induced hepatic inflammation in murine NAFLD by reducing expression of proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages. PMID: 25339829
- The data show that the FXR is the most important BA receptor in beta-cells and that FXR signaling in beta-cells is impaired by overnutrition, which alters activatability of the FXR. PMID: 25599407
- Results show that HRG is a novel transcriptional target gene of FXR in human hepatoma cells, human upcyteVR primary hepatocytes and 3D human liver microtissues in vitro and in mouse liver in vivo. PMID: 25363753
- Demonstrate that the activation of FXR uncouples the expression of nuclear SREBP-2 and miR-33, and the regulation of their respective target genes. PMID: 25593129
- FXR, a key regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism was down-regulated in old mice. ER stress was activated and repressed FXR expression through inhibition of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (HNF1alpha) transcriptional activity. PMID: 24333182
- AB23A produces protective effect against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and cholestasis, due to FXR-mediated regulation of transporters and enzymes. PMID: 25655198
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Activation protects mice against cholestasis, development of chronical intestinal inflammation and fibrosis. May suppress intestinal tumorigenesis.
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in liver and kidney. Expressed in pancreatic beta cells and macrophages. Expressed in the villus epithelium in adult ileum, with highest expression in the intervillus regions. Expression in colon is reduced by inflammation.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20186
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000100933
UniGene: Mm.3095
Most popular with customers
-
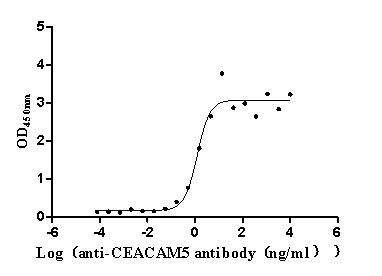
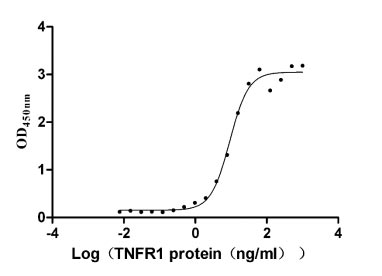
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
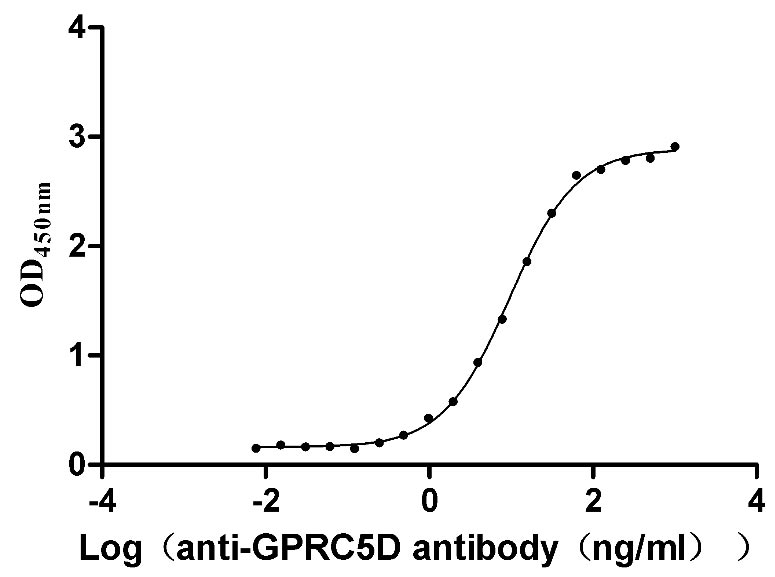
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
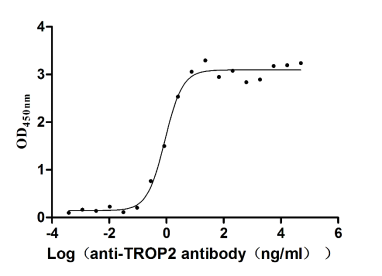
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)